- Mechatronics
-
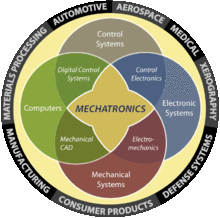
Mechatronics is the combination of Mechanical engineering, Electronic engineering, Computer engineering, Software engineering, Control engineering, and Systems Design engineering in order to design, and manufacture useful products[1][2]. Mechatronics is a multidisciplinary field of engineering, that is to say it rejects splitting engineering into separate disciplines. Originally, mechatronics just included the combination between mechanics and electronics, hence the word is only a portmanteau of mechanics and electronics. However, as technical systems have become more and more complex the word has been "updated" during recent years to include more technical areas.
French standard NF E 01-010 gives the following definition: “approach aiming at the synergistic integration of mechanics, electronics, control theory, and computer science within product design and manufacturing, in order to improve and/or optimize its functionality".
Contents
Description
A mechatronics engineer unites the principles of mechanics, electronics, and computing to generate a simpler, more economical and reliable system. Mechatronics is centered on mechanics, electronics, computing, control engineering, molecular engineering (from nanochemistry and biology), and optical engineering, which, combined, make possible the generation of simpler, more economical, reliable and versatile systems. The portmanteau "mechatronic" was coined by Tetsuro Mori, the senior engineer of the Japanese company Yaskawa in 1969. An industrial robot is a prime example of a mechatronics system; it includes aspects of electronics, mechanical , and computing to do its day-to-day jobs.
Engineering cybernetics deals with the question of control engineering of mechatronic systems. It is used to control or regulate such a system (see control theory). Through collaboration, the mechatronic modules perform the production goals and inherit flexible and agile manufacturing properties in the production scheme. Modern production equipment consists of mechatronic modules that are integrated according to a control architecture. The most known architectures involve hierarchy, polyarchy, heterarchy, and hybrid. The methods for achieving a technical effect are described by control algorithms, which might or might not utilize formal methods in their design. Hybrid systems important to mechatronics include production systems, synergy drives, planetary exploration rovers, automotive subsystems such as anti-lock braking systems and spin-assist, and every-day equipment such as autofocus cameras, video, hard disks, and CD players.
Course structure
Mechatronic students take courses from across the various fields listed below:
- Mechanical engineering and materials science subjects
- Electronic engineering subjects
- Computer engineering subjects
- Computer science subjects
- Systems and control engineering subjects
- Optomechanics (optical engineering) subjects
- Robotics subjects
Application
- Machine vision
- Automation and robotics
- Servo-mechanics
- Sensing and control systems
- Automotive engineering, automotive equipment in the design of subsystems such as anti-lock braking systems
- Computer-machine controls, such as computer driven machines like IE CNC milling machines
- Expert systems
- Industrial goods
- Consumer products
- Mechatronics systems
- Medical mechatronics,medical imaging systems
- Structural dynamic systems
- Transportation and vehicular systems
- Mechatronics as the new language of the automobile
- Diagnostic, reliability, and control system techniques
- Computer aided and integrated manufacturing systems
- Computer-aided design
- Engineering and manufacturing systems
- Packaging
- Microcontrollers / PLC's
- Mobile apps
Physical implementations
For most mechatronic systems, the main issue is no more how to implement a control system, but how to implement actuators and what is the energy source. Within the mechatronic field, mainly two movement: the piezo-electric actuators and motors, or the electromagnetic actuators and motors. Maybe the most famous mechatronics systems are the well known camera autofocus system or camera anti-shake systems.
Concerning the energy sources, most of the applications use batteries. But a new trend is arriving and is the energy harvesting, allowing transforming into electricity mechanical energy from shock, vibration, or thermal energy from thermal variation, and so on.
Variant of the field
An emerging variant of this field is biomechatronics, whose purpose is to integrate mechanical parts with a human being, usually in the form of removable gadgets such as an exoskeleton. Such an entity is often identified in science fiction as a cyborg. This is the "real-life" version of cyberware.
Another emerging variant is Electronical or electronics design centric ECAD/MCAD co-design. Electronical is where the integration and co-design between the design team and design tools of an electronics centric system and the design team and design tools of that systems physical/mechanical enclosure takes place.
Education
Countries offering education in mechatronics are Australia[3], Austria, Brazil, Canada[4][5], Chile[6], Perú[7], Colombia, Czechia[2], Denmark,[8] Egypt,[9] Estonia,[10] France,[11] Germany,[12][13] Hungary,[14][15], India[16], Iran[17], Ireland[18], Israel[19] Italy[20], Iceland[21], Japan, Jordan[22], Malaysia[23], México[24][25][26][27][28], Norway[29], Pakistan[30][31], Poland[32], Singapore, Slovenia, Sweden[33], Turkey[34], UK[35], United States, New Zealand, Vietnam.
See also
- Mechanical Engineering Technology
- Cybernetics
- Electromechanics
- List of engineering topics
- National Instruments
- Robotics
- Systems Engineering
- Mechatronics Journals
Further reading
- Bishop, Robert H., Mechatronics: an introduction. CRC Press, 2006.
- De Silva, Clarence W., Mechatronics: an integrated approach. CRC Press, 2005
- Onwubolu, Godfrey C., Mechatronics: principles and applications. Butterworth-Heinemann, 2005.
References
Books
- Bradley, Dawson et al., Mechatronics, Electronics in products and processes, Chapman and Hall Verlag, London, 1991.
- Karnopp, Dean C., Donald L. Margolis, Ronald C. Rosenberg, System Dynamics: Modeling and Simulation of Mechatronic Systems, 4th Edition, Wiley, 2006. ISBN 0-471-70965-4 Bestselling system dynamics book using bond graph approach.
- Cetinkunt, Sabri, Mechatronics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc, 2007 ISBN 978-0-4714798-1
- James J. Nutaro (2010). Building software for simulation: theory and algorithms, with applications in C++. Wiley.
Journals
Websites
- List of publications concerning examples of mechatronic applications and realisation
Standards
- NF E 01-010 2008 – AFNOR (French standard NF E 01-010)
- XP E 01-013 2009 – AFNOR (French standard NF E 01-013)
Citations
- ^ Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering Department. "What is Mechatronics Engineering?". Prospective Student Information. University of Waterloo. http://www.mme.uwaterloo.ca/undergrad/mechatronics/prospective/prospective.html. Retrieved 30 May 2011.
- ^ a b Faculty of Mechatronics, Informatics and Interdisciplinary Studies TUL. "Mechatronics (Bc., Ing., PhD.)". http://mechatronics.tul.cz. Retrieved 15 April 2011.
- ^ ""University of Queensland – Bachelor of Engineering (Mechatronics)", accessed 12 January 2011". Engineering.uq.edu.au. 6 April 2011. http://www.engineering.uq.edu.au/mechatronic. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ Mechanical and Mechatronics Engineering Department. "Welcome to Mechatronics Engineering". University of Waterloo. http://www.mme.uwaterloo.ca/undergrad/mechatronics/home.html. Retrieved 30 May 2011.
- ^ ""McMaster University – Mechatronics Engineering", accessed 2 Jan 2011". Cas.mcmaster.ca. http://www.cas.mcmaster.ca/cas/0template1.php?902/. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Universidad de Talca". Utalca.cl. http://www.utalca.cl/link.cgi//CarrerasPregrado/2125. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ http://www.utp.edu.pe/fac.aspx?idC=000032&idC1=000035
- ^ ""University of Southern Denmark – BEng in Mechatronics" (Bachelor | Master), accessed 16 May 2011". Sdu.dk. 15 June 2011. http://www.sdu.dk/Uddannelse/Diplomingenioer/Mekatronik. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ ""Alexandria Higher Institute Of Engineering And Technology , B.Sc Engineering in Mechartronics"". Ait.edu.eg. http://ait.edu.eg/AllYears_Course.asp. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Mehhatroonikainstituut". Ttu.ee. http://www.ttu.ee/mehhatroonikainstituut/. Retrieved 13 November 2011.
- ^ "Institut des Sciences et Techniques des Yvelines"[dead link]
- ^ Alexander Prusak, Dipl.-Ing.. ""University of Siegen – Mechatronics (Master)", accessed 1 March 2011". .uni-siegen.de. http://www2.uni-siegen.de/mechatronics/. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ ""Aachen University of Applied Sciences – Mechatronics (Master)", accessed 12 Dec 2010". Fh-aachen.de. http://www.fh-aachen.de/8575.html?L=1. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "ÓBUDAI EGYETEM Bánki Donát Gépész és Biztonságtechnikai Mérnöki Kar". Bgk.uni-obuda.hu. http://bgk.uni-obuda.hu/index.php?sid=kepzeseink&pid=mechatronics_eng. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "" Budapest University of Technology and Economics"". Mogi.bme.hu. http://www.mogi.bme.hu/?p=education&c=bsc. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Acharya Institute Of Technology". Vtu.ac.in. 11 August 2009. http://vtu.ac.in/index.php/affiliated-institutes/114.html?article=. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Sharif University of Technology, Master of Science Program in Mechartronics Engineering", accessed 11 May 2011
- ^ ""Dublin City University – B.Eng. in Mechatronic Engineering (Bachelor Honours Degree)", accessed 02 February 2011". Dcu.ie. http://www.dcu.ie/prospective/deginfo.php?classname=ME. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ Israel
- ^ ""PT of Turin – Mechanical Engineering & Mechatronics", accessed 22 Jun 2011". Polito.it. http://www.polito.it. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ ""University of Reykjavik – Bachelor of Engineering (Mechatronics)", accessed 12 January 2011" (in (Icelandic)). Ru.is. http://www.ru.is/tvd/grunnnam/verkfraedi/hataekniverkfraedi-bsc/. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Welcome to Website Faculty of Engineering Technology". Fet.edu.jo. http://www.fet.edu.jo/Academic%20_Departments/Mechatronics%20Engineering%20Department.htm. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Diploma in Mechatronics | KBU International College". Kbu.edu.my. 15 September 2011. http://www.kbu.edu.my/schools-centres/engineering-computing/diploma-in-mechatronics/. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Tecnológico de Monterrey | Carreras Profesionales | Áreas de estudio | Ingeniero en Mecatrónica". Itesm.edu. http://www.itesm.edu/wps/wcm/connect/itesm/tecnologico+de+monterrey/carreras+profesionales/areas+de+estudio/ingenieria+y+ciencias/imt. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "::Bienvenidos a la Facultad de Ingeniería de la UNAM::". Ingenieria.unam.mx. http://www.ingenieria.unam.mx/paginas/Carreras/ingenieriaMecatronica/ingMecatronica_Desc.php. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Catálogo de Oferta Educativa | UAQ". Uaq.mx. http://www.uaq.mx/ofertaeducativa/ingenieria/ing_elec.html. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Catálogo de Oferta Educativa | UAQ". Uaq.mx. http://www.uaq.mx/ofertaeducativa/ingenieria/ing_auto.html. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Cinvestav, Electrical Engineering Department – Master|PhD in Mechatronics"
- ^ ""University of Agder – Master in Mechatronics" (Bachelor | Master | PhD.), accessed 16 May 2011". Uia.no. http://www.uia.no/en/portals/about_the_university/engineering_and_science/-_engineering/-_-_mechatronics/-_-_master_in_mechatronics. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Bachelor of Engineering in Mechatronics Engineering-Air University". Au.edu.pk. http://www.au.edu.pk/be_mechatronics.aspx. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "National University of Sciences & Technology". Nust.edu.pk. http://www.nust.edu.pk. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Faculty of Mechatronics / Faculties / Warsaw University of Technology – Strona główna" (in Template:Po icon). Eng.pw.edu.pl. http://eng.pw.edu.pl/Faculties/Faculty-of-Mechatronics. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ ""Chalmers University of Technology – System, Control and Mechatronics", accessed 12 Dec 2010". Chalmers.se. http://www.chalmers.se/en/education/programmes/masters-info/Pages/Systems,-control-and-mechatronics.aspx. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ "Atılım Üniversitesi | Mekatronik Mühendisliği Bölümü| Anasayfa". Mechatronics.atilim.edu.tr. 15 February 2011. http://mechatronics.atilim.edu.tr/index.php?lang=en. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
- ^ ""University of Dundee – Mechanical Engineering & Mechatronics", accessed 12 Dec 2010". Dundee.ac.uk. http://www.dundee.ac.uk/mecheng/. Retrieved 17 October 2011.
Categories:- Embedded systems
- Electro mechanical engineering
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.