- Grape
-
This article is about the fruits of the genus Vitis. For the European grapevine, see Vitis vinifera. For other uses, see Grape (disambiguation).
Grapes, purple or green Nutritional value per 100 g (3.5 oz) Energy 288 kJ (69 kcal) Carbohydrates 18.1 g - Sugars 15.48 g - Dietary fiber 0.9 g Fat 0.0 g Protein 0.72 g Thiamine (vit. B1) 0.069 mg (6%) Riboflavin (vit. B2) 0.07 mg (6%) Niacin (vit. B3) 0.188 mg (1%) Pantothenic acid (B5) 0.05 mg (1%) Vitamin B6 0.086 mg (7%) Folate (vit. B9) 2 μg (1%) Vitamin B12 0 μg (0%) Vitamin C 10.8 mg (13%) Vitamin K 22 μg (21%) Calcium 10 mg (1%) Iron 0.36 mg (3%) Magnesium 7 mg (2%) Manganese 0.071 mg (3%) Phosphorus 20 mg (3%) Potassium 191 mg (4%) Sodium 3.02 mg (0%) Zinc 0.07 mg (1%) Percentages are relative to US recommendations for adults.
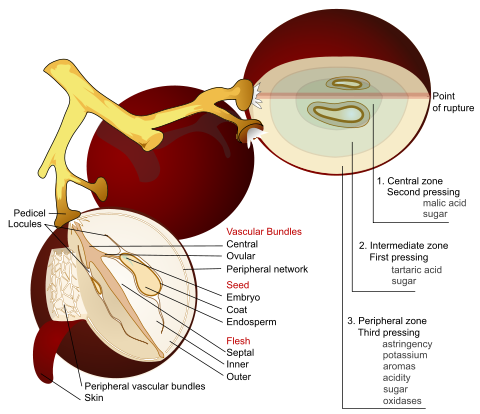
Source: USDA Nutrient DatabaseA grape is a non-climacteric fruit, specifically a berry, that grows on the perennial and deciduous woody vines of the genus Vitis. Grapes can be eaten raw or they can be used for making jam, juice, jelly, vinegar, wine, grape seed extracts, raisins, molasses and grape seed oil. Grapes are also used in some kinds of confectionery. Grapes are typically an ellipsoid shape resembling a prolate spheroid.
Contents
History
The cultivation of the domesticated grape began 6,000-8,000 years ago in the Near East.[1] Yeast, one of the earliest domesticated microorganisms, occurs naturally on the skins of grapes, leading to the innovation of alcoholic drinks such as wine. First traces of red wine is seen in ancient Armenia where apparently, to date, the oldest winery was found, dating to around 4,000 BC. By the 9th century AD the city of Shiraz was known to produce some of the finest wines in the Middle east. Thus it has been proposed that Syrah red wine is named after Shiraz a city in Persia where the grape was used to make Shirazi wine. Ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics record the cultivation of purple grapes, and history attests to the ancient Greeks, Phoenicians and Romans growing purple grapes for both eating and wine production. Later, the growing of grapes spread to Europe, North Africa, and eventually North America.
Native purple grapes belonging to the Vitis genus proliferated in the wild across North America, and were a part of the diet of many North American Native Americans, but were considered by European colonists to be unsuitable for wine. The first Old World Vitis vinifera purple grapes were cultivated in California.[citation needed]
Description
Grapes are a type of fruit that grow in clusters of 15 to 300, and can be crimson, black, dark blue, yellow, green, orange, and pink. "White" grapes are actually green in color, and are evolutionarily derived from the purple grape. Mutations in two regulatory genes of white grapes turn off production of anthocyanins which are responsible for the color of purple grapes.[2] Anthocyanins and other pigment chemicals of the larger family of polyphenols in purple grapes are responsible for the varying shades of purple in red wines.[3][4]
Grapevines
Main article: VitisMost grapes come from cultivars of Vitis vinifera, the European grapevine native to the Mediterranean and Central Asia. Minor amounts of fruit and wine come from American and Asian species such as:
- Vitis labrusca, the North American table and grape juice grapevines (including the concord cultivar), sometimes used for wine, are native to the Eastern United States and Canada.
- Vitis riparia, a wild vine of North America, is sometimes used for winemaking and for jam. It is native to the entire Eastern U.S. and north to Quebec.
- Vitis rotundifolia, the muscadines, used for jams and wine, are native to the Southeastern United States from Delaware to the Gulf of Mexico.
- Vitis amurensis is the most important Asian species.
Distribution and production
According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), 75,866 square kilometres of the world are dedicated to grapes. Approximately 71% of world grape production is used for wine, 27% as fresh fruit, and 2% as dried fruit. A portion of grape production goes to producing grape juice to be reconstituted for fruits canned "with no added sugar" and "100% natural". The area dedicated to vineyards is increasing by about 2% per year.
The following table of top wine-producers shows the corresponding areas dedicated to grapes for wine making:
Country Area dedicated Spain 11,750 km2 France 8,640 km2 Italy 8,270 km2 Turkey 8,120 km2 United States 4,150 km2 Iran 2,860 km2 Romania 2,480 km2 Portugal 2,160 km2 Argentina 2,080 km2 Chile 1,840 km2 Australia 1,642 km2 Armenia 1,459 km2 Lebanon 1,122 km2 Top Ten Grapes Producers – 8 October 2009 Country Production (Tonnes) Footnote  Italy
Italy8,519,418 F  China
China6,787,081 F  United States
United States6,384,090 F  France
France6,044,900 F  Spain
Spain5,995,300 F  Turkey
Turkey3,612,781 F  Iran
Iran3,000,000 F  Argentina
Argentina2,900,000 F  Chile
Chile2,350,000 F  India
India1,667,700 F World 67,221,000 A No symbol = official figure, P = official figure, F = FAOSTAT 2007, * = Unofficial/Semi-official/mirror data, C = Calculated figure, A = Aggregate (may include official, semi-official or estimates);
There are no reliable statistics that break down grape production by variety. It is, however, believed that the most widely planted variety is Sultana, also known as Thompson Seedless, with at least 3,600 km2. (880,000 acres) dedicated to it. The second most common variety is Airén. Other popular varieties include Cabernet Sauvignon, Sauvignon blanc, Cabernet Franc, Merlot, Grenache, Tempranillo, Riesling and Chardonnay.[5]
Table and wine grapes
Commercially cultivated grapes can usually be classified as either table or wine grapes, based on their intended method of consumption: eaten raw (table grapes) or used to make wine (wine grapes). While almost all of them belong to the same species, Vitis vinifera, table and wine grapes have significant differences, brought about through selective breeding. Table grape cultivars tend to have large, seedless fruit (see below) with relatively thin skin. Wine grapes are smaller, usually seeded, and have relatively thick skins (a desirable characteristic in winemaking, since much of the aroma in wine comes from the skin). Wine grapes also tend to be very sweet: they are harvested at the time when their juice is approximately 24% sugar by weight. By comparison, commercially produced "100% grape juice", made from table grapes is usually around 15% sugar by weight.[6]
Seedless grapes
Although grape seeds contain many nutrients, some consumers choose seedless grapes; seedless cultivars now make up the overwhelming majority of table grape plantings. Because grapevines are vegetatively propagated by cuttings, the lack of seeds does not present a problem for reproduction. It is, however, an issue for breeders, who must either use a seeded variety as the female parent or rescue embryos early in development using tissue culture techniques.
There are several sources of the seedlessness trait, and essentially all commercial cultivators get it from one of three sources: Thompson Seedless, Russian Seedless, and Black Monukka, all being cultivars of Vitis vinifera. There are currently more than a dozen varieties of seedless grapes. Several, such as Einset Seedless, Reliance and Venus, have been specifically cultivated for hardiness and quality in the relatively cold climates of northeastern United States and southern Ontario.[7]
An offset to the improved eating quality of seedlessness is the loss of potential health benefits provided by the enriched phytochemical content of grape seeds (see Health claims, below).[8][9]
Raisins, currants and sultanas
In most of Europe, dried grapes are referred to as "raisins" or the local equivalent. In the UK, three different varieties are recognized, forcing the EU to use the term "Dried vine fruit" in official documents.
A raisin is any dried grape. While raisin is a French loanword, the word in French refers to the fresh fruit; grappe (from which the English grape is derived) refers to the bunch (as in une grappe de raisins).
A currant is a dried Zante Black Corinth grape, the name being a corruption of the French raisin de Corinthe (Corinth grape). Currant has also come to refer to the blackcurrant and redcurrant, two berries unrelated to grapes.
A sultana was originally a raisin made from Sultana grapes of Turkish origin (known as Thompson Seedless in the United States), but the word is now applied to raisins made from either white grapes, or red grapes which are bleached to resemble the traditional sultana.
Health claims
Main articles: Wine and health, French Paradox, and ResveratrolFrench Paradox
Comparing diets among Western countries, researchers have discovered that although the French tend to eat higher levels of animal fat, surprisingly the incidence of heart disease remains low in France. This phenomenon has been termed the French Paradox, and is thought to occur from protective benefits of regularly consuming red wine. Apart from potential benefits of alcohol itself, including reduced platelet aggregation and vasodilation,[10] polyphenols (e.g., resveratrol) mainly in the grape skin provide other suspected health benefits, such as:[11]
- Alteration of molecular mechanisms in blood vessels, reducing susceptibility to vascular damage
- Decreased activity of angiotensin, a systemic hormone causing blood vessel constriction that would elevate blood pressure
- Increased production of the vasodilator hormone, nitric oxide (endothelium-derived relaxing factor)
Although adoption of wine consumption is not recommended by some health authorities,[12] a significant volume of research indicates moderate consumption, such as one glass of red wine a day for women and two for men, may confer health benefits.[13][14][15] Emerging evidence is that wine polyphenols like resveratrol[16] provide physiological benefit whereas alcohol itself may have protective effects on the cardiovascular system.[17]
Resveratrol
Grape phytochemicals such as resveratrol (a polyphenol antioxidant), have been positively linked to inhibiting any cancer, heart disease, degenerative nerve disease, viral infections and mechanisms of Alzheimer's disease.[18][19]
Protection of the genome through antioxidant actions may be a general function of resveratrol.[20] In laboratory studies, resveratrol bears a significant transcriptional overlap with the beneficial effects of calorie restriction in heart, skeletal muscle and brain. Both dietary interventions inhibit gene expression associated with heart and skeletal muscle aging, and prevent age-related heart failure.[21]
Resveratrol is the subject of several human clinical trials,[22] among which the most advanced is a one year dietary regimen in a Phase III study of elderly patients with Alzheimer's disease.[23]
Synthesized by many plants, resveratrol apparently serves antifungal and other defensive properties. Dietary resveratrol has been shown to modulate the metabolism of lipids and to inhibit oxidation of low-density lipoproteins and aggregation of platelets.[24]
Resveratrol is found in wide amounts among grape varieties, primarily in their skins and seeds which, in muscadine grapes, have about one hundred times higher concentration than pulp.[25] Fresh grape skin contains about 50 to 100 micrograms of resveratrol per gram.[26]
Anthocyanins and other phenolics
Anthocyanins tend to be the main polyphenolics in purple grapes whereas flavan-3-ols (i.e. catechins) are the more abundant phenolic in white varieties.[27] Total phenolic content, a laboratory index of antioxidant strength, is higher in purple varieties due almost entirely to anthocyanin density in purple grape skin compared to absence of anthocyanins in white grape skin.[27] It is these anthocyanins that are attracting the efforts of scientists to define their properties for human health.[28] Phenolic content of grape skin varies with cultivar, soil composition, climate, geographic origin, and cultivation practices or exposure to diseases, such as fungal infections.
Red wine may offer health benefits more so than white because potentially beneficial compounds are present in grape skin, and only red wine is fermented with skins. The amount of fermentation time a wine spends in contact with grape skins is an important determinant of its resveratrol content.[29] Ordinary non-muscadine red wine contains between 0.2 and 5.8 mg/L,[30] depending on the grape variety, because it is fermented with the skins, allowing the wine to absorb the resveratrol. By contrast, a white wine contains lower phenolic contents because it is fermented after removal of skins.
Wines produced from muscadine grapes may contain more than 40 mg/L, an exceptional phenolic content.[25][31] In muscadine skins, ellagic acid, myricetin, quercetin, kaempferol, and trans-resveratrol are major phenolics.[32] Contrary to previous results, ellagic acid and not resveratrol is the major phenolic in muscadine grapes.
The flavonols syringetin, syringetin 3-O-galactoside, laricitrin and laricitrin 3-O-galactoside are also found in purple grape but absent in white grape.[33]
Seed constituents
Main articles: Grape seed extract and Grape seed oilSince the 1980s, biochemical and medical studies have demonstrated significant antioxidant properties of grape seed oligomeric proanthocyanidins.[34] Together with tannins, polyphenols and polyunsaturated fatty acids, these seed constituents display inhibitory activities against several experimental disease models, including cancer, heart failure and other disorders of oxidative stress.[35][36]
Grape seed oil from crushed seeds is used in cosmeceuticals and skincare products for many perceived health benefits. Grape seed oil is notable for its high contents of tocopherols (vitamin E), phytosterols, and polyunsaturated fatty acids such as linoleic acid, oleic acid and alpha-linolenic acid.[37][38][39]
Concord grape juice
Commercial juice products from Concord grapes have been applied in medical research studies, showing potential benefits against the onset stage of cancer,[40] platelet aggregation and other risk factors of atherosclerosis,[41] loss of physical performance and mental acuity during aging[42] and hypertension in humans.[43]
Religious significance
See also: Wine#Religious_usesIn the Bible, grapes are first mentioned when Noah grows them on his farm (Genesis 9:20-21). Instructions concerning wine are given in the book of Proverbs and in the book of Isaiah, such as in Proverbs 20:1 and Isaiah 5:20-25. Deuteronomy 18:3-5,14:22-27,16:13-15 tell of the use of wine during Jewish feasts. Grapes were also significant to both the Greeks and Romans, and their God of agriculture, Dionysus, was linked to grapes and wine, being frequently portrayed with grape leaves on his head.[44] Grapes are especially significant for Christians, who since the Early Church have used wine in their celebration of the Eucharist.[45] Views on the significance of the wine vary between denominations. In Christian art, grapes often represent the blood of Christ, such as the grape leaves in Caravaggio’s John the Baptist.
Gallery
-
Vineyard in the Troodos Mountains
See also
Sources
- Footnotes
- ^ Patrice This, Thierry Lacombe, Mark R. Thomash. "Historical Origins and Genetic Diversity of Wine Grapes". Trends in Genetics 22 (8). http://oak.cats.ohiou.edu/~ballardh/pbio480/thisetal2006-winegrapegeneticdiversity.pdf.
- ^ Walker AR, Lee E, Bogs J, McDavid DA, Thomas MR, Robinson SP, AR (Mar 2007). "White grapes arose through the mutation of two similar and adjacent regulatory genes". Plant J 49 (5): 772–85. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02997.x. ISSN 0960-7412. PMID 17316172.
- ^ Waterhouse AL, AL (May 2002). "Wine phenolics". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 957: 21–36. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02903.x. ISSN 0077-8923. PMID 12074959. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0077-8923&date=2002&volume=957&spage=21.
- ^ Brouillard R, Chassaing S, Fougerousse A, R (December 2003). "Why are grape/fresh wine anthocyanins so simple and why is it that red wine color lasts so long?". Phytochemistry 64 (7): 1179–86. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(03)00518-1. ISSN 0031-9422. PMID 14599515. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0031942203005181.
- ^ "The most widely planted grape in the world". http://www.freshplaza.com/news_detail.asp?id=29614.
- ^ "Wine Grapes and Grape-y Wines". http://www.wineloverspage.com/dibbern/grapetaste07.phtml. Retrieved 03/07/2010.
- ^ Reisch BI, Peterson DV, Martens M-H. "Seedless Grapes", in "Table Grape Varieties for Cool Climates", Information Bulletin 234, Cornell University, New York State Agricultural Experiment Station, retrieved December 30, 2008
- ^ Shi J, Yu J, Pohorly JE, Kakuda Y, J (Winter 2003). "Polyphenolics in grape seeds-biochemistry and functionality". J Med Food 6 (4): 291–9. doi:10.1089/109662003772519831. ISSN 1096-620X. PMID 14977436.
- ^ Parry J, Su L, Moore J, et al., J (May 2006). "Chemical compositions, antioxidant capacities, and antiproliferative activities of selected fruit seed flours". J. Agric. Food Chem. 54 (11): 3773–8. doi:10.1021/jf060325k. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 16719495.
- ^ Providência R, R (November 2006). "Cardiovascular protection from alcoholic drinks: scientific basis of the French Paradox" (Free full text). Rev Port Cardiol 25 (11): 1043–58. ISSN 0870-2551. PMID 17274460. http://toxnet.nlm.nih.gov/cgi-bin/sis/search/r?dbs+hsdb:@term+@rn+64-17-5.
- ^ Opie LH, Lecour S, LH (July 2007). "The red wine hypothesis: from concepts to protective signalling molecules" (Free full text). Eur. Heart J. 28 (14): 1683–93. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm149. ISSN 0195-668X. PMID 17561496. http://eurheartj.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17561496.
- ^ American Heart Association, Alcohol, wine and cardiovascular disease
- ^ Alcohol. Harvard School of Public Health
- ^ Mukamal KJ, Kennedy M, Cushman M, et al., KJ (January 2008). "Alcohol consumption and lower extremity arterial disease among older adults: the cardiovascular health study" (Free full text). Am. J. Epidemiol. 167 (1): 34–41. doi:10.1093/aje/kwm274. ISSN 0002-9262. PMID 17971339. http://aje.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=17971339.
- ^ de Lange DW, van de Wiel A, DW (May 2004). "Drink to prevent: review on the cardioprotective mechanisms of alcohol and red wine polyphenols". Semin Vasc Med 4 (2): 173–86. doi:10.1055/s-2004-835376. ISSN 1528-9648. PMID 15478039.
- ^ Das S, Das DK, S (June 2007). "Resveratrol: a therapeutic promise for cardiovascular diseases". Recent Patents Cardiovasc Drug Discov 2 (2): 133–8. doi:10.2174/157489007780832560. ISSN 1574-8901. PMID 18221111.
- ^ Sato M, Maulik N, Das DK, M (May 2002). "Cardioprotection with alcohol: role of both alcohol and polyphenolic antioxidants". Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 957: 122–35. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb02911.x. ISSN 0077-8923. PMID 12074967. http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/openurl?genre=article&sid=nlm:pubmed&issn=0077-8923&date=2002&volume=957&spage=122.
- ^ Shankar S, Singh G, Srivastava RK, S (Sep 2007). "Chemoprevention by resveratrol: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential". Front. Biosci. 12 (12): 4839–54. doi:10.2741/2432. ISSN 1093-9946. PMID 17569614. http://www.bioscience.org/2007/v12/af/2432/fulltext.htm.
- ^ Mancuso C, Bates TE, Butterfield DA, et al., C (December 2007). "Natural antioxidants in Alzheimer's disease". Expert Opin Investig Drugs 16 (12): 1921–31. doi:10.1517/13543784.16.12.1921. ISSN 1354-3784. PMID 18042001.
- ^ Gatz SA, Wiesmüller L, SA (February 2008). "Take a break—resveratrol in action on DNA" (Free full text). Carcinogenesis 29 (2): 321–32. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgm276. ISSN 0143-3334. PMID 18174251. http://carcin.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=18174251.
- ^ Barger JL, Kayo T, Vann JM, et al., JL (Jun 2008). Tomé, Daniel. ed. "A Low Dose of Dietary Resveratrol Partially Mimics Caloric Restriction and Retards Aging Parameters in Mice" (Free full text). PLoS ONE 3 (6): e2264. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0002264. PMC 2386967. PMID 18523577. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0002264.
- ^ "Listing of resveratrol clinical trials". US National Institutes of Health. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=resveratrol.
- ^ "Randomized Trial of a Nutritional Supplement in Alzheimer's Disease". US Department of Veterans Affairs, Mount Sinai School of Medicine. May 2008. http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT00678431?term=resveratrol&rank=5.
- ^ Chan WK, Delucchi AB, WK (November 2000). "Resveratrol, a red wine constituent, is a mechanism-based inactivator of cytochrome P450 3A4". Life Sci. 67 (25): 3103–12. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(00)00888-2. ISSN 0024-3205. PMID 11125847. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0024320500008882.
- ^ a b LeBlanc, MR (2005). "Cultivar, Juice Extraction, Ultra Violet Irradiation and Storage Influence the Stilbene Content of Muscadine Grapes (Vitis Rotundifolia Michx". PhD Dissertation. Louisiana State University. http://etd.lsu.edu/docs/available/etd-01202006-082858/.
- ^ Li X, Wu B, Wang L, Li S, X (November 2006). "Extractable amounts of trans-resveratrol in seed and berry skin in Vitis evaluated at the germplasm level". J. Agric. Food Chem. 54 (23): 8804–11. doi:10.1021/jf061722y. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 17090126.
- ^ a b Cantos E, Espín JC, Tomás-Barberán FA, E (September 2002). "Varietal differences among the polyphenol profiles of seven table grape cultivars studied by LC-DAD-MS-MS". J. Agric. Food Chem. 50 (20): 5691–6. doi:10.1021/jf0204102. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 12236700.
- ^ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry Presents Research from the 2007 International Berry Health Benefits Symposium, Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry ACS Publications, February 2008
- ^ pbrc.edu
- ^ Gu X, Creasy L, Kester A, Zeece M, X (August 1999). "Capillary electrophoretic determination of resveratrol in wines". J. Agric. Food Chem. 47 (8): 3223–7. doi:10.1021/jf981211e. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 10552635.
- ^ Ector BJ, Magee JB, Hegwood CP, Coign MJ. "Resveratrol Concentration in Muscadine Berries, Juice, Pomace, Purees, Seeds, and Wines". http://www.ajevonline.org/cgi/content/abstract/47/1/57.
- ^ Pastrana-Bonilla E, Akoh CC, Sellappan S, Krewer G, E (August 2003). "Phenolic content and antioxidant capacity of muscadine grapes". J. Agric. Food Chem. 51 (18): 5497–503. doi:10.1021/jf030113c. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 12926904.
- ^ Metabolite Profiling of Grape: Flavonols and Anthocyanins. Fulvio Mattivi, Raffaele Guzzon, Urska Vrhovsek, Marco Stefanini and Riccardo Velasco, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2006, 54 (20), pp 7692–7702
- ^ Bagchi D, Bagchi M, Stohs SJ, et al., D (August 2000). "Free radicals and grape seed proanthocyanidin extract: importance in human health and disease prevention". Toxicology 148 (2–3): 187–97. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(00)00210-9. ISSN 0300-483X. PMID 10962138. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0300483X00002109.
- ^ Agarwal C, Singh RP, Agarwal R, C (November 2002). "Grape seed extract induces apoptotic death of human prostate carcinoma DU145 cells via caspases activation accompanied by dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential and cytochrome c release". Carcinogenesis 23 (11): 1869–76. doi:10.1093/carcin/23.11.1869. ISSN 0143-3334. PMID 12419835. http://carcin.oxfordjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=12419835.
- ^ Bagchi D, Sen CK, Ray SD, et al., D (Feb 2003). "Molecular mechanisms of cardioprotection by a novel grape seed proanthocyanidin extract". Mutat. Res. 523-524: 87–97. doi:10.1016/S0027-5107(02)00324-X. ISSN 0027-5107. PMID 12628506. http://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S002751070200324X.
- ^ Beveridge TH, Girard B, Kopp T, Drover JC, TH (March 2005). "Yield and composition of grape seed oils extracted by supercritical carbon dioxide and petroleum ether: varietal effects". J. Agric. Food Chem. 53 (5): 1799–804. doi:10.1021/jf040295q. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 15740076.
- ^ Crews C, Hough P, Godward J, et al., C (August 2006). "Quantitation of the main constituents of some authentic grape-seed oils of different origin". J. Agric. Food Chem. 54 (17): 6261–5. doi:10.1021/jf060338y. ISSN 0021-8561. PMID 16910717.
- ^ Tangolar SG, Ozoğul Y, Tangolar S, Torun A, SG (September 2007). "Evaluation of fatty acid profiles and mineral content of grape seed oil of some grape genotypes". Int J Food Sci Nutr 60 (1): 1–8. doi:10.1080/09637480701581551. ISSN 0963-7486. PMID 17886077.
- ^ Jung KJ, Wallig MA, Singletary KW, KJ (February 2006). "Purple grape juice inhibits 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA)-induced rat mammary tumorigenesis and in vivo DMBA-DNA adduct formation". Cancer Lett. 233 (2): 279–88. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2005.03.020. ISSN 0304-3835. PMID 15878797.
- ^ Shanmuganayagam D, Warner TF, Krueger CG, Reed JD, Folts JD, D (January 2007). "Concord grape juice attenuates platelet aggregation, serum cholesterol and development of atheroma in hypercholesterolemic rabbits". Atherosclerosis 190 (1): 135–42. doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2006.03.017. ISSN 0021-9150. PMID 16780846.
- ^ Shukitt-Hale B, Carey A, Simon L, Mark DA, Joseph JA, B (March 2006). "Effects of Concord grape juice on cognitive and motor deficits in aging". Nutrition 22 (3): 295–302. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2005.07.016. ISSN 0899-9007. PMID 16412610.
- ^ Park YK, Kim JS, Kang MH, YK (2004). "Concord grape juice supplementation reduces blood pressure in Korean hypertensive men: double-blind, placebo controlled intervention trial". Biofactors 22 (1–4): 145–7. doi:10.1002/biof.5520220128. ISSN 0951-6433. PMID 15630270. http://iospress.metapress.com/openurl.asp?genre=article&issn=0951-6433&volume=22&issue=1&spage=145.
- ^ Garden Guides
- ^ Justin Martyr, First Apology, "Chapter LXV. Administration of the sacraments" and "Chapter LXVII. Weekly worship of the Christians".
Further reading
- Books
- Creasy, G.L. / Creasy, L.L. (2009). Grapes (Crop Production Science in Horticulture). CABI. ISBN 9781845934019
- Review articles
- Xia, E.-Q. et al. “Biological Activities of Polyphenols from Grapes”, International Journal of Molecular Sciences (2010),11(2):622-646.
- Dohadwala, M.M. / Vita, J.A. “Grapes and Cardiovascular Disease”, Journal of Nutrition (2009),139(9):1788S-1793S.
External links
- Taxonomic listings for Vitis genus, US Department of Agriculture, Germplasm Resources Information Network
- safecrop.org, Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Grapevine Downy and Powdery Mildew]
- Nutrition information for grapes
- Botanical and Nutritional Information
- Information on virus diseases of wine grapes
Viticulture Biology and horticulture Environmental variation Terroir · Topography (slope, aspect, elevation) · Soil · Climate · Macroclimate · Microclimate · Temperature · DrainageVineyard planting Vineyard management Harvest Harvest · Vintage · Weather · Sugar content (Brix) · Noble rot · Physiological ripeness · Traditions and lorePests and diseases Diseases · Phylloxera · Vine moth · Red spider mite · Nematodes · Birds · Powdery mildew · Downy mildew · Grey rot · Black rot · Pierce's diseaseApproaches and issues Precision viticulture · Adaptive management · Organic agriculture · Biodynamics · Sustainability · Environmental stewardship · Climate changeSee also Sources of condensed tannins Areca catechu seed (arecatannins) | Broad bean (Vicia faba) | Grape (Vitis vinifera) | Quebracho wood | Mimosa bark (Acacia mollissima) | Myrtan or black marlock (Eucalyptus redunca)Sources of hydrolysable tannins Chestnut wood | Dhawa (Anogeissus latifolia) | Myrobalan fruit (Terminalia chebula) | Oak wood, bark or acorn cup (Valonea Quercus macrolepis) | Sumac (Tanner's sumach leaves - Rhus coriaria or Chinese gall on Rhus chinensis) | Tara pod (Caesalpinia spinosa)Other sources Alder (Alnus sp) | Avaram (Senna auriculata) | Babul (Acacia nilotica) | Birch (Betula sp) | Larch (Larix sp) | Hemlock (Tsuga sp) | mangrove | Pine (Pinus sp) | Spruce (Picea sp) | Urunday (Myracrodruon urundeuva) | Willow (Salix caprea)Badan (Bergenia crassifolia) | Gambier (Uncaria gambir) | Redoul (Coriaria myrtifolia)Cutch (Acacia catechu)Divi-divi pod (Caesalpinia coriaria) | Sant pod (Acacia nilotica) | Teri pod (Caesalpinia digyna)Gall oak (Quercus lusitanica)Whole plantProsopis sp. bark and wood (eg Prosopis humilis or Algarrobilla) | Tanoak (Lithocarpus densiflorus) | Tizra heartwood and root (Rhus pentaphylla)Misc Categories:- Grape varieties
- Vitaceae
- Viticulture
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.