- Nikolaus Otto
-
Nikolaus August Otto 
Nikolaus OttoBorn 10 June 1832
Holzhausen an der HaideDied 26 January 1891 (aged 58)
CologneNationality German Occupation Inventor Known for internal-combustion engine Nikolaus August Otto (14 June 1832, Holzhausen an der Haide, Nassau - 26 January 1891, Cologne) was the German inventor of the first internal-combustion engine to efficiently burn fuel directly in a piston chamber. Although other internal combustion engines had been invented (e.g. by Étienne Lenoir) these were not based on four separate strokes. Though the concept of four strokes had been theorised in 1861 by Alphonse Beau de Rochas, Otto was the first to make it practical.
Contents
Early years
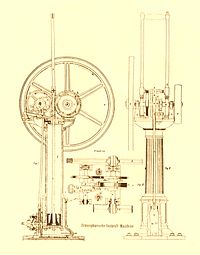
Otto was the son of a farmer: his father also ran the local post office. He served an apprenticeship in commerce and following his apprenticeship worked as a business man in Frankfurt am Main and in Cologne. After relocating to Cologne he quit his office job in order to construct small gas engines, starting out by seeking to improve on the existing design of Étienne Lenoir.[1] Otto met another engineer Eugen Langen in 1864. The technically trained Langen recognized the potential of Otto's development, and one month after the meeting, founded the first engine factory in the world, NA Otto & Cie. At the 1867 Paris World Exhibition their improved engine was awarded the Grand Prize [2].
The Otto & Langen engine was a free piston atmospheric engine (the explosion of gas was used to create a vacuum and the power came from atmospheric pressure returning the piston). It consumed less than half the gas of the Lenoir and Hugon engines and so was a commercial success. The principle of operation was described by the Italian inventors Eugenio Barsanti and Felice Matteucci in their British Patent no 1625 of 1857, though they never produced a marketable example.
Otto later turned his attention to the 4-stroke cycle (as described in a pamphlet by Alphonse Beau de Rochas in 1862 [3]). It is this engine (the Otto Silent Engine), and not the Otto & Langen engine, to which the Otto cycle refers. This was the first commercially successful engine to use in-cylinder compression (as patented by William Barnett in 1838).Otto married Anna Gossi and the couple produced seven recorded children. His son Gustav Otto grew up to become an aircraft builder.
The Otto cycle
The Otto engine was designed as a stationary engine and in the action of the engine, the stroke is an upward or downward movement of a piston in a cylinder. Used later in an adapted form as an automobile engine, four strokes are involved: (1) downward intake stroke—coal-gas and air enter the piston chamber, (2) upward compression stroke—the piston compresses the mixture, (3) downward power stroke—ignites the fuel mixture by electric spark, and (4) upward exhaust stroke—releases exhaust gas from the piston chamber. Otto only sold his engine as a stationary motor.
Earlier patents
This is a video montage of the Otto engines running at the Western Minnesota Steam Threshers Reunion (WMSTR), in Rollag, Minnesota. (2min 16sec, 320x240, 340kbit/s video)
According to recent historical studies, the Italian inventors Eugenio Barsanti and Felice Matteucci patented a first working efficient version of an internal combustion engine in 1854 in London (pt. Num. 1072). It is claimed that the Otto engine is in many parts at least inspired from this precedent invention [1], but, as yet there is no documentation of knowledge about the Italian engine by Otto. The concept of the four-stroke engine was also patented (October 26, 1860) by the Austrian Christian Reithmann for one year and by the French Alphonse Beau de Rochas (January 16, 1862).
- This article incorporates information from the equivalent article on the German Wikipedia.
See also
- History of the internal combustion engine
- German inventors and discoverers
References
- ^ "Happy Centenary Otto...". Motor 149 (3827): 41. 14 February 1976.
- ^ http://www.dhub.org/object/207174
- ^ Dugald Clerk, "Gas and Oil Engines", Longman Green & Co, 1897, pp 17-18.
External links
Categories:- 1832 births
- 1891 deaths
- German inventors
- National Inventors Hall of Fame inductees
- People associated with the internal combustion engine
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.