- 2000s (decade)
-
From left, clockwise: The World Trade Center towers, in the wake of the September 11 attacks; the Euro enters into European currency in 2002; a statue of Saddam Hussein being toppled during the Iraq War; U.S. troops heading toward an army helicopter during the War in Afghanistan, part of the US government's War on Terror campaign; social media through the Internet spreads across the world; a Chinese soldier gazes at the 2008 Summer Olympics commencing; an economic crisis, the largest since the Great Depression, hits the world in 2008; a tsunami from the Indian Ocean following an earthquake kills over 250,000 on Boxing Day, 2004.

Millennium: 3rd millennium Centuries: 20th century – 21st century – 22nd century Decades: 1970s 1980s 1990s – 2000s – 2010s 2020s 2030s Years: 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 Categories: Births – Deaths – Architecture
Establishments – DisestablishmentsThe 2000s was a decade that started on January 1, 2000 and ended on December 31, 2009. It was the decade in which the 21st century and 3rd millennium began.
Globalization, which had intensified in the post-Cold War 1990s, continued to influence the world in the 2000s. The growth of the Internet was one of the prime contributors to globalization during the decade, making it possible for people to interact with other people, express ideas, introduce others to different cultures and backgrounds, use goods and services, sell and buy online, research and learn about anything, along with experiencing the whole world without having to leave home.[1][2][3][4][5]
The institutions, linkages and technologies that emerged or were redefined earlier would subsequently in this decade benefit many countries, in particular China and India. However, in other parts of the world such progress failed to address ongoing struggles with modernity, most notably characterized by the rise of al-Qaeda and other Islamist groups.[6]
The September 11 attacks in 2001 ultimately led to the United States, United Kingdom and other nations invading and occupying Afghanistan, as well as implementing various anti-terrorist measures at home and abroad in what was known as the War on Terror. The European Union saw further integration and expansion throughout much of Europe.
The economic growth of the 2000s, while responsible for lifting millions out of poverty, also had considerable environmental consequences, raised demand for diminishing energy resources,[7][8] and was still shown to be vulnerable as demonstrated during the Global Financial Crisis of the late 2000s.[9]
Contents
Names for the decade
In the English-speaking world, a name for the decade was never universally accepted in the same manner as for decades such as the '90s, the '80s, etc.[10][11][12]
Orthographically, the decade can be written as the "2000s" or the "'00s". Some people read "2000s" as "two-thousands", and thus simply refer to the decade as the "two-thousands". Some read it as the "00s" (pronounced "Ohs", "Oh Ohs", "Double Ohs" or "Ooze"), while others referred to it as the "Twenty-ohs". The single years within the decade are usually referred to as starting with an "Oh", such as "Oh-Seven" to refer to the year 2007. On January 1, 2000, the BBC listed "the noughties" (derived from "nought"[13] a word used for zero in many English-speaking countries), as a potential moniker for the new decade.[14] Others have advocated the term "the aughts", which was widely used at the beginning of the previous century for its first decade.[15][16]
The "noughties" is a play on words on "naughty" – bad behaviour, and "nought" an English word meaning nothing, or zero. The excesses of the decade are so succinctly expressed by the word, that it has become the only term for the decade in common use in the UK.[17][18][19][20][21]
The American Dialect Society holds a lighthearted annual poll for word of the year and related subcategories; for 2009, the winner of "least likely to succeed" was "Any name of the decade 2000–2009, such as: Naughties, Aughties, Oughties, Pot stickers, etc."[22]
Politics and wars
The "War on Terrorism" and War in Afghanistan began after the September 11 attacks in 2001.[23][24] The International Criminal Court was formed a year later. A United States-led coalition invaded Iraq, and the Iraq war led to the end of Saddam Hussein's rule as Iraqi President and the Ba'ath Party regime in Iraq. Al-Qaeda and affiliated Islamist militant groups performed terrorist acts throughout the decade. These acts included the Madrid Train Bombings in 2004, 7/7 London Bombings in 2005, and the Mumbai attacks related to al-Qaeda in 2008. The EU expanded, incorporating some former Eastern block nations. North Korea and Iran were seen as strong nuclear threats, following two North Korea nuclear tests, and Iran's failure to comply with its transparency obligations under the Nuclear Non Proliferation Treaty and UN resolutions.
The War on Terrorism generated extreme controversy around the world, with questions regarding the justification for U.S. actions leading to a loss of support for the American government, both in and outside the United States.[25] Additional armed conflict occurred in the Middle East, including between Israel and Hezbollah, then with Israel and the Hamas. The greatest loss of life due to natural disaster came from the 2004 tsunami killing around a quarter-million people and displacing well over a million others. Cooperative international rescue missions by many countries from around the world including the United States helped in efforts by the most affected nations to rebuild and recover from the devastation. An enormous loss of life and property value came in 2005, when Hurricane Katrina flooded nearly the entire city of New Orleans. The resulting political fallout was severely damaging to the George W. Bush administration because of its perceived failure to act promptly and effectively. In 2008, Barack Obama was elected President of the United States, and became the first African-American U.S. president when he succeeded Bush in 2009.[26]
Terrorist attacks
Main article: List of terrorist incidents#1970s–2000sThe most prominent terrorist attacks committed against civilian population during the decade include:
- September 11, 2001 attacks in Washington, D.C., New York City and Shanksville, Pennsylvania (2,992 killed)
- 2002 Bali bombings in Bali, Indonesia (202 killed)
- 2003 Istanbul bombings in Istanbul, Turkey (57 killed)
- 11 March 2004 Madrid train bombings (192 killed)
- Beslan school hostage crisis (334 killed)
- 2005 London bombings (56 killed)
- 2008 Mumbai attacks (175 killed)
Wars
Main articles: List of wars 1990–2002 and List of wars 2003–currentThe most prominent armed conflicts of the decade include:
International wars
 The Iraq War
The Iraq War
- War on Terrorism (2001–present) – refers to several ideological, military, and diplomatic campaigns aimed at putting an end to international terrorism by preventing groups defined by the US and its allies as terrorist (largely Islamist groups such as al-Qaeda, Hezbollah and Hamas) from posing a threat to the US and its allies, and by putting an end to state sponsorship of terrorism. The campaigns were launched by the United States, with support from NATO and other allies, following the September 11, 2001 attacks which were carried out by al-Qaeda. Today the term has become mostly associated with Bush administration-led wars in Afghanistan and Iraq.
- War in Afghanistan (2001–present) – In 2001, the United States, the United Kingdom, Canada and Australia invaded Afghanistan seeking to oust the Taliban and find al-Qaeda mastermind Osama bin Laden. In 2011, Navy Seals killed Bin Laden and buried his body at sea.
- Iraq War (2003–2011) – In 2003, the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia and Poland invaded and occupied Iraq, following what was ultimately shown to be a false claim that Iraq had weapons of mass destruction at its disposal.[27] The war, which ended the rule of Saddam Hussein's Ba'ath Party, also led to violence against the coalition forces and between many Sunni and Shia Iraqi groups, and to al-Qaeda operations in Iraq.
- Arab–Israeli conflict (Early 20th century–present)
- 2006 Lebanon War (summer 2006) – took place in southern Lebanon and northern Israel. The principal parties were Hezbollah paramilitary forces and the Israeli military. The war which began as military operation in response to the abduction of two Israeli reserve soldiers by the Hezbollah, gradually strengthened and became a wider confrontation.
- Israeli–Palestinian conflict (Early 20th century–present)
- Second Intifada (2000–2005) – After the signing of the Oslo Accords failed to bring about a Palestinian state, in September 2000 the Second Intifada (uprising) broke out, a period of intensified Palestinian-Israeli violence, which has been taking place until the present day. As a result of the significant increase of suicide bombing attacks within Israeli population centers during the first years of the Al-Aqsa Intifada,[28] in June 2002 Israel began the construction of the West Bank Fence along the Green Line border arguing that the barrier is necessary to protect Israeli civilians from Palestinian terrorism. The significantly reduced number of incidents of suicide bombings from 2002 to 2005 has been partly attributed to the barrier.[29] The barrier's construction, which has been highly controversial, became a major issue of contention between the two sides. The Second Intifada has caused thousands of victims on both sides, both among combatants and among civilians – The death toll, including both military and civilian, is estimated to be 5,500 Palestinians and over 1,000 Israelis, as well as 64 foreign citizens.[30] Many Palestinians consider the Second Intifada to be a legitimate war of national liberation against foreign occupation, whereas many Israelis consider it to be a terrorist campaign.[31]
- 2008–2009 Israel–Gaza conflict – the frequent Hamas Qassam rocket and mortar fire launched from within civilian population centers in Gaza towards the Israeli southern civilian communities led to an Israeli military operation in Gaza which had the stated aim of reducing the Hamas rocket attacks and stopping the arms smuggling into the Gaza Strip. Throughout the conflict Hamas further intensified its rocket and mortar attacks against Israel, hitting civilian targets and reaching major Israeli cities Beersheba and Ashdod for the first time. The intense urban warfare in densely populated Gaza and the intensified Hamas rocket attacks towards populated Israeli civilian targets lead to a high toll on both sides and among civilians.
- The Second Congo War (1998–2003) – took place largely in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. The widest interstate war in modern African history, it directly involved nine African nations, as well as about twenty armed groups, and earned the epithet of "Africa's World War" and the "Great War of Africa." An estimated 3.8 million people died, mostly from starvation and disease brought about by the deadliest conflict since World War II. Millions more were displaced from their homes or sought asylum in neighboring countries.
- 2008 South Ossetia war – Russia invaded Georgia in response to Georgia's unprovoked aggression towards civilians and eventually paramilitary personnel of South Ossetia. Both Russia and Georgia were condemned internationally for their actions.
- The Second Chechen War (1999–2000) – the war was launched by the Russian Federation at August 26, 1999 in response to the Invasion of Dagestan and the Russian apartment bombings which were blamed on the Chechens. During the war Russian forces largely recaptured the separatist region of Chechnya.[32] The campaign largely reversed the outcome of the First Chechen War, in which the region gained de facto independence as the Chechen Republic of Ichkeria.
- The Eritrean–Ethiopian War came to a close in 2000.
- Kivu conflict (2004–2009) – an armed conflict between the military of the Democratic Republic of the Congo (FARDC) and the Hutu Power group Democratic Forces for the Liberation of Rwanda (FDLR).
- 2009 Nigerian sectarian violence – an armed conflict between Boko Haram, a militant Islamist group and Nigerian security forces.
Civil wars and guerrilla wars
 Darfur refugee camp in Chad
Darfur refugee camp in Chad
- War in Darfur (2003–2009) – an armed conflict in the Darfur region of western Sudan. The conflict began when the Sudan Liberation Movement/Army (SLM/A) and Justice and Equality Movement (JEM) in Darfur took up arms, accusing the government of oppressing black Africans in favor of Arabs. One side was composed mainly of the Sudanese military and the Sudanese militia group Janjaweed, recruited mostly from the Afro-Arab Abbala tribes of the northern Rizeigat region in Sudan. The other side was made up of rebel groups, notably the Sudan Liberation Movement/Army and the Justice and Equality Movement, recruited primarily from the non-Arab Muslim Fur, Zaghawa, and Masalit ethnic groups. Millions of people were displaced from their homes during the conflict.[33] There are various estimates on the number of human casualties – Sudanese authorities claim a death toll of roughly 19,500 civilians[34] while certain non-governmental organizations, such as the Coalition for International Justice, controversially claim that over 400,000 people have been killed during the conflict.[35]
- Mexican Drug War (2006 – present) – an armed conflict fought between rival drug cartels and government forces in Mexico. Although Mexican drug cartels, or drug trafficking organizations, have existed for quite some time, they have become more powerful since the demise of Colombia's Cali and Medellín cartels in the 1990s. Mexican drug cartels now dominate the wholesale illicit drug market in the United States.[36] Arrests of key cartel leaders, particularly in the Tijuana and Gulf cartels, have led to increasing drug violence as cartels fight for control of the trafficking routes into the United States.[37][38][39] Roughly more than 16,851 people in total were killed between December 2006 until November 2009.[40]
- In India, Naxalite-Maoist insurgency (1967– present) has grown alarmingly with attacks such as April 2010 Maoist attack in Dantewada, Jnaneswari Express train derailment, and Rafiganj train disaster. Naxalites are a group of far-left radical communists, supportive of Maoist political sentiment and ideology. It is presently the longest continuously active conflict worldwide. In 2006 Prime Minister Manmohan Singh called the Naxalites "The single biggest internal security challenge ever faced by our country."[41] In 2009, he said the country was "losing the battle against Maoist rebels".[42] According to standard definitions the Naxalite–Maoist insurgency is an ongoing conflict[43] between Maoist groups, known as Naxalites or Naxals, and the Indian government.[41] On April 6, 2010, Maoist rebels killed 75 security forces in a jungle ambush in central India in the worst-ever massacre of security forces by the insurgents. On the same day, Gopal, a top Maoist leader, said the attack was a "direct consequence" of the government's Operation Green Hunt offensive. This raised some voices of use of Indian Air Force against Naxalites, which were however declined citing "We can't use oppressive force against our own people".[44]
- The Colombian Armed Conflict continues causing deaths and terror in Colombia. Beginning in 1964, the FARC and ELN narcoterrorist groups were taking control of rural areas of the country by the beginning of the decade, while terrorist paramilitaries grew in other places as businesspeople and politicians thought the State would lose the war against guerrillas. However, after the failure of the peace process and the activation of Plan Colombia, Álvaro Uribe Vélez was elected President in 2002, starting a massive attack on terrorist groups, with cooperation from civil population, foreign aid and legal armed forces. The AUC paramilitary organization disbanded in 2006, while ELN guerrillas have been weakened. The Popular Liberation Army demobilized while the country's biggest terrorist group, FARC has been weakened and most of their top commanders have been killed or died during the decade. During the second half of the decade, a new criminal band has been formed by former members of AUC who didn't demobilize, calling themselves Aguilas Negras. Although the Colombian State has taken back control over most of the country, narcoterrorism still causes pain in the country. Since 2008, the Internet has become a new field of battle. Facebook has gained nationwide popularity and has become the birthplace of many civil movements against narcoterrorism such as "Colombia Soy Yo" (I am Colombia) or "Fundación Un Millón de Voces" (One Million Voices Foundation), responsible for the international protests against illegal groups during the last years.
- The Sierra Leone Civil War (1991–2002) came to an end when the Revolutionary United Front (RUF) finally laid down their arms. More than two million people were displaced from their homes because of the conflict (well over one-third of the population) many of whom became refugees in neighboring countries. Tens of thousands were killed during the conflict.[45]
- The Sri Lankan Civil War (1983–2009) came to an end after the government defeated the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam. Over 80,000 people were killed during the course of the conflict.[46]
- War in North-West Pakistan (2004–present) – an armed conflict between the Pakistani Armed Forces and Islamic militants made up of local tribesmen, the Taliban, and foreign Mujahideen (Holy Warriors). It began in 2004 when tensions rooted in the Pakistani Army's search for al-Qaeda members in Pakistan's mountainous Waziristan area (in the Federally Administered Tribal Areas) escalated into armed resistance by local tribesmen. The violence has displaced 3.44 million civilians[47] and led to more than 7,000 civilians being killed.[48]
- The Angolan Civil War (1975–2002), once a major proxy conflict of the Cold War, the conflict ended after the anti-Communist organization UNITA disbanded to become a political party. By the time the 27-year conflict was formally brought to an end, an estimated 500,000 people had been killed.[49]
- Sa'dah insurgency (2004 – present) – a civil war in the Sa'dah Governorate of Yemen. It began after the Shī‘a Zaidiyyah sect launched an uprising against the Yemeni government. The Yemeni government has accused Iran of directing and financing the insurgency.[50] Thousands of rebels and civilians have been killed during the conflict.[51][52]
- Somali Civil War (1991–present)
- War in Somalia (2006–2009) – involved largely Ethiopian and Somali Transitional Federal Government (TFG) forces whom fought against the Somali Islamist umbrella group, the Islamic Court Union (ICU), and other affiliated militias for control of the country. The war spawned pirates who hijacked hundreds of ships off the coast of Somalia, holding ships and crew for ransom often for months (see also Piracy in Somalia). 1.9 million people were displaced from their homes during the conflict[53] and the number of civilian casualties during the conflict is estimated at 16,724.[54]
- War in Somalia (2009 – present) – involved largely the forces of the Somali Somali Transitional Federal Government (TFG) assisted by African Union peacekeeping troops, whom fought against various militant Islamist factions for control of the country. The violence has displaced thousands of people residing in Mogadishu, the nation's capital. 1,739 people in total were killed between January 1, 2009 until January 1, 2010.[55]
- Conflict in the Niger Delta (2004 – present) – an ongoing conflict in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. The conflict was caused due to the tensions between the foreign oil corporations and a number of the Niger Delta's minority ethnic groups who felt they were being exploited, particularly the Ogoni and the Ijaw. The competition for oil wealth has led to an endless violence cycle between innumerable ethnic groups, causing the militarization of nearly the entire region which was occupied by militia groups as well as Nigerian military and the forces of the Nigerian Police.
- Algerian Civil War (1991–2002) – the conflict effectively ended with a government victory, following the surrender of the Islamic Salvation Army and the 2002 defeat of the Armed Islamic Group. It is estimated that more than 100,000 people were killed during the course of the conflict.
- Civil war in Chad (1998–present)
- Civil war in Chad (1998–2002) – involved the Movement for Justice and Democracy in Chad (MDJT) rebels that skirmished periodically with government troops in the Tibesti region, resulting in hundreds of civilian, government, and rebel casualties.
- Civil war in Chad (2005–present) – involved Chadian government forces and several Chadian rebel groups. The Government of Chad estimated in January 2006 that 614 Chadian citizens had been killed in cross-border raids.[56] The fighting still continues despite several attempts to reach agreements.
- Nepalese Civil War (1996–2006) – the conflict ended with a peace agreement was reached between the government and the Maoist party in which it was set that the Maoists would take part in the new government in return for surrendering their weapons to the UN. It is estimated that more than 12,700 people were killed during the course of the conflict.[57]
- Second Liberian Civil War (1999–2003) – The conflict began in 1999 when a rebel group Liberians United for Reconciliation and Democracy (LURD), with support from the Government of Guinea, took over northern Liberia through a coup. In early 2003, a different rebel group, the Movement for Democracy in Liberia, emerged in the south. As a result, by June–July 2003, president Charles Taylor's government controlled only a third of the country. The capital Monrovia was besieged by LURD, and that group's shelling of the city resulted in the deaths of many civilians. Thousands of people were displaced from their homes as a result of the conflict.
- Insurgency in the Maghreb (2002–present) – Algeria has been the subject of an Islamic insurgency since 2002 waged by the Sunni Islamic Jihadist militant group Salafist Group for Preaching and Combat (GSPC). GSPC allied itself with the Al-Qaeda Organization in the Islamic Maghreb against the Algerian government. The conflict has since spread to other neighboring countries.
- Ituri conflict (1999–2007) – a conflict fought between the Lendu and Hema ethnic groups in the Ituri region of northeastern Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). While there have been many phases to the conflict, the most recent armed clashes ran from 1999 to 2003, with a low-level conflict continuing until 2007. More than 50,000 people have been killed in the conflict and hundreds of thousands forced from their homes.[58]
- Central African Republic Bush War (2004–2007) – began with the rebellion by the Union of Democratic Forces for Unity (UFDR) rebels, after the current president of the Central African Republic, François Bozizé, seized power in a 2003 coup. The violence has displaced around 10,000 civilians and has led to hundreds of civilians being killed.
- Civil war in Afghanistan (1996–2001) – an armed conflict which continued after the capture of Kabul by the Taliban, in which the formation of the Afghan Northern Alliance attempted to oust the Taliban. It proved largely unsuccessful, as the Taliban continued to make gains and eliminated much of the Alliance's leadership.
Coups
Main article: List of coups d'état and coup attempts#2000 - 2009The most prominent coups d'état of the decade include:
- 2002 Venezuelan coup d'état attempt – a failed military coup d'état on April 11, 2002 which aimed to overthrow the president of Venezuela Hugo Chávez. During the coup Hugo Chávez was arrested and Pedro Carmona became the interim President for 47 hours. The coup led to a pro-Chávez uprising that the Metropolitan Police attempted to suppress. The pro-Chávez Presidential Guard eventually retook the Miraflores presidential palace without firing a shot, leading to the collapse of the Carmona government.
- 2004 Haitian rebellion – a conflict fought for several weeks in Haiti during February 2004 that resulted in the premature end of President Jean-Bertrand Aristide's second term, and the installment of an interim government led by Gerard Latortue.
- 2006 Thai coup d'état – on 19 September 2006, while the elected Thai Prime Minister Thaksin Shinawatra was in New York for a meeting of the UN, Army Commander-in-Chief Lieutenant General Sonthi Boonyaratglin launched a bloodless coup d'état.
- Fatah–Hamas conflict (2006–2009) – an armed conflict fought between the two main Palestinian factions, Fatah and Hamas with each vying to assume political control of the Palestinian territories. In June 2007, Hamas took control of the entire Gaza Strip, and established a separate government while Fatah remained in control of the West Bank. This in practice divided the Palestinian Authority into two. Various forces affiliated with Fatah engaged in combat with Hamas, in numerous gun battles. Most Fatah leaders eventually escaped to Egypt and the West Bank, while some were captured and killed.
- 2009 Honduras coup d'état – The armed forces of the country entered the president's residence and threw president Manuel Zelaya
Nuclear threats
- Since 2005, Iran's nuclear program has become the subject of contention with the Western world due to suspicions that Iran could divert the civilian nuclear technology to a weapons program. This has led the UN Security Council to impose sanctions against Iran on select companies linked to this program, thus furthering its economic isolation on the international scene. The U.S. Director of National Intelligence said in February 2009 that Iran would not realistically be able to a get a nuclear weapon until 2013, if it chose to develop one.[59]
- In 2003, the United States invaded Iraq over concerns leader Saddam Hussein had weapons of mass destruction including chemical and biological weapons. The Iraq Inquiry (still ongoing) may explain more on this situation, but in the meantime, the U.S. ended the regime of Saddam Hussein. However a lot of controversy rages around the fact that no evidence of any nuclear programs has been found in Iraq, leading some to believe that the Bush administration declared war simply to gain influence over Middle-Eastern oil supplies.
- North Korea successfully performed two nuclear tests in 2006 and 2009.
- Operation Orchard – during the operation, Israel bombed what was believed to be a Syrian nuclear reactor on September 6, 2007 which was thought to be built with the aid of North Korea.[60] The White House and Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) later declared that American intelligence indicated the site was a nuclear facility with a military purpose, though Syria denies this.[61]
- The Doomsday Clock, the symbolic representation of the threat of nuclear annihilation, moved four minutes closer to midnight: two minutes in 2002 and two minutes in 2007 to 5 minutes to midnight.
National sovereignty
- East Timor regains independence from Indonesia in 2002. Portugal granted independence to East Timor in 1975, but it was soon after invaded by Indonesia, which only recognized East Timorese independence in 2002.
- Montenegro gains independence from State union with Serbia in 2006
- Kosovo gains independence from Serbia in 2008, though its independence remains unrecognized by many countries even today.
- On August 23, 2005 Israel's unilateral disengagement from 25 Jewish settlements in the Gaza Strip and West Bank ends.
- On August 26, 2008 Russia formally recognises the disputed Georgian regions of Abkhazia and South Ossetia as independent states.[62] The vast majority of United Nations member states maintain that the areas belong to Georgia.
Democracy
During this decade, the peaceful transfer of power through elections first occurred in Mexico, Indonesia, Taiwan, and several other countries. (See below.)
Political events
The prominent political events of the decade include:
Americas
 George W. Bush, the 43rd president of the United States, 2001–2009
George W. Bush, the 43rd president of the United States, 2001–2009
- Vicente Fox was elected President of Mexico in the 2000 presidential election, making him the first president elected from an opposition party in 71 years, defeating the then-dominant Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI).
- George W. Bush was sworn in as the 43rd President of the United States on January 20, 2001 following a sharply contested election.
- On October 26, 2001 U.S. President George W. Bush signs the USA PATRIOT Act into law.
- On February 15, 2003 anti-war protests break out around the world in opposition to the U.S. Invasion of Iraq, in what the Guinness Book of World Records called the largest anti-war rally in human history.[63]
- Barack Obama is sworn in as the 44th President of the United States in 2009, becoming the nation's first African American president.
- Álvaro Uribe is elected President of Colombia in 2002, the first political independent to do so in more than a century and a half. creating the centre-right political movement known as uribism. Uribe was re-elected in 2006.
- In 2006, Michele Bachelet is elected as the first female President of Chile.[64]
- Left-wing governments emerge in South American countries. These governments include those of Hugo Chávez in Venezuela since 1999, Fernando Lugo in Paraguay, Rafael Correa in Ecuador, and Evo Morales in Bolivia. With the creation of the ALBA, Fidel Castro—leader of Cuba since 1959—and Hugo Chávez reaffirmed their opposition to the perceived imperialism of the United States.
- Fidel Castro resigns in 2008 on health reasons. Castro's brother Raúl is elected to succeed him.
- Paul Martin replaces Jean Chrétien as Prime Minister of Canada in 2003 by becoming the new leader of the Liberal Party. Stephen Harper was elected Prime Minister in 2006 following the defeat of Paul Martin's government in a motion of no confidence.
- Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva was elected (2002) and reelected (2006) President of Brazil.
- May 23, 2008 – The Union of South American Nations, a supranational union, is made from joining together the Andean Community and Mercosur.[65]
Asia
 Protesters in Tehran during the 2009 Iranian election protests
Protesters in Tehran during the 2009 Iranian election protests
 Israel's prime minister Ehud Barak and PLO head Yasser Arafat with the president of the United States Bill Clinton at Camp David Summit, 2000
Israel's prime minister Ehud Barak and PLO head Yasser Arafat with the president of the United States Bill Clinton at Camp David Summit, 2000
- 2009 Iranian election protests – The 2009 Iranian presidential election sparked massive protests in Iran and around the world against alleged electoral fraud and in support of defeated candidate Mir-Hossein Mousavi. During the protests the Iranian authorities closed universities in Tehran, blocked web sites, blocked cell phone transmissions and text messaging,[66] and banned rallies.[67] Several demonstrators in Iran were killed or imprisoned during the protests. Dozens of human casualties were reported or confirmed.[68][69][70]
- Israeli withdrawal from the Israeli security zone in southern Lebanon – on May 25, 2000 Israel withdrew IDF forces from the Israeli Security Zone in southern Lebanon after 22 years.
- In July 2000 the Camp David 2000 Summit was held which was aimed at reaching a "final status" agreement between the Palestinians and the Israelis. The summit collapsed after Yasser Arafat would not accept a proposal drafted by American and Israeli negotiators. Barak was prepared to offer the entire Gaza Strip, a Palestinian capital in a part of East Jerusalem, 73% of the West Bank (excluding eastern Jerusalem) raising to 90–94% after 10–25 years, and financial reparations for Palestinian refugees for peace. Arafat turned down the offer without making a counter-offer.[71]
- January 4, 2006 – Powers are transferred from Israeli Prime Minister Ariel Sharon to his deputy, Vice Prime Minister Ehud Olmert, after Sharon suffers a massive hemorrhagic stroke.
- In 2003 the 12 year self-government in Iraqi Kurdistan ends, developed under the protection of the UN "No-fly zone" during the now-ousted Saddam Hussein regime.
- Premier Wen Jiabao and President Hu Jintao, replaced former People's Republic of China Premier Zhu Rongji and former People's Republic of China President Jiang Zemin.
- Manmohan Singh was elected (2004) and reelected (2009) Prime Minister in India. He is the only Prime Minister since Jawaharlal Nehru to return to power after completing a full five-year term. Singh previously carried out economic reforms in India in 1991, during his tenure as the Finance Minister.[72]
- Recep Tayyip Erdogan was elected as Prime Minister of Turkey in 2002. Abdullah Gul was elected as President of Turkey.
- 2007 political crisis in Pakistan, Pervez Musharraf retired after the assassination of Benazir Bhutto
- January 9, 2005 – Mahmoud Abbas is elected to succeed Yasser Arafat as Palestinian Authority President.[73]
- 2008–2009 Thai political crisis
Europe
- European integration makes progress with the definitive circulation of the euro in fifteen countries in 2002 and the widening of European Union to 27 countries in 2007. A European Constitution bill is rejected by French and Dutch voters in 2005, but a similar text, the Treaty of Lisbon, is drafted in 2007 and finally adopted by the 27 members countries.
- Gordon Brown succeeds Tony Blair as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom in 2007.
- José Luis Rodríguez Zapatero replaced José María Aznar as President of the Government of Spain in 2004.
- Dmitry Medvedev succeeded Vladimir Putin as the President of Russia in 2008.
- Angela Merkel becomes the first female Chancellor of Germany in 2005.
- Nicolas Sarkozy is elected President of France in 2007 succeeding Jacques Chirac, who had held the position for 12 years.
- Silvio Berlusconi becomes President of the Council of Ministers of Italy in 2001 and again in 2008, after two years of a government held by Romano Prodi.
- Parties broadly characterised by political scientists as being right-wing populist soar throughout the 2000s, in the wake of increasing anti-Islam and anti-immigration sentiment in most Western European countries.[74] By 2010, such parties (albeit often significant differences between them) were present in the national parliaments of Belgium, the Netherlands, Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Switzerland, Austria, Italy and Greece.[74] In Austria, Italy and Switzerland, the Freedom Party of Austria, Lega Nord and Swiss People's Party, respectively, were at times also part of the national governments, and in Denmark, the Danish People's Party tolerated a right-liberal minority government from 2001 throughout the decade.[74] While not being present in the national parliaments of France and the United Kingdom, Jean-Marie Le Pen of the National Front came second in the first round of the 2002 French presidential elections, and in the 2009 European Parliament election, the UK Independence Party came second, beating even the Labour Party, while the British National Party managed to win two seats for the first time.
Assassinations
The prominent assassinations of the decade included:
- Israeli Minister of Tourism Rehavam Ze'evi was assassinated by three Palestinian assailants, members of the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine, on October 17, 2001.
- Dutch politician Pim Fortuyn was assassinated by environmentalist activist Volkert van der Graaf, on May 6, 2002.
- Serbian Prime Minister Zoran Đinđić was assassinated on March 12, 2003.
- Swedish foreign minister Anna Lindh was assassinated on September 10, 2003, after being stabbed in the chest, stomach, and arms by Serbian national Mijailo Mijailović while shopping in a Stockholm department store.
- Ahmed Yassin, the founder and spiritual leader of the militant Islamist group Hamas, was killed in a targeted killing in the Gaza Strip in an operation conducted by the Israeli Air Force on March 22, 2004.
- Dutch film maker Theo van Gogh, a critic of Islamic culture, was assassinated in Amsterdam by Mohammed Bouyeri on November 2, 2004.
- Former Prime Minister of Lebanon Rafik Hariri was assassinated on February 14, 2005, when explosives equivalent to around 1,000 kg of TNT were detonated as his motorcade drove past the St. George Hotel in Beirut. The assassination attempt killed also at least 16 other people and injured 120 others.
- Former Pakistani prime minister Benazir Bhutto was assassinated at an election rally in Rawalpindi on December 27, 2007, by a bomb blast. The assassination attempt killed also at least 20 other people.
- The President of Guinea-Bissau, João Bernardo Vieira, was assassinated on March 2, 2009, during an armed attack on his residence in Bissau.
- Anti-abortion extremist[75] Scott Roeder assassinates George Tiller, a pro-choice advocate and late-term abortion provider, on May 31, 2009 at Tiller's church in Wichita, Kansas.
Disasters
Natural disasters
See also: Category:2000 natural disasters, Countries affected by the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, Humanitarian response to the 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake, and Economic effects of Hurricane Katrina 2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. The tsunami caused by the December 26, 2004 earthquake strikes Ao Nang, Thailand.
2004 Indian Ocean earthquake. The tsunami caused by the December 26, 2004 earthquake strikes Ao Nang, Thailand.
The 2000s experienced some of the worst and most destructive natural disasters in history.
Earthquakes (including tsunamis)
- On January 13, 2001, a 7.6 earthquake strikes El Salvador, killing 944 people.
- On January 26, 2001, an earthquake hits Gujarat, India, killing more than 12,000.
- On February 13, 2001, a 6.6 magnitude earthquake hits El Salvador, killing at least 400.
- On May 21, 2003, an earthquake in the Boumerdès region of northern Algeria kills 2,200.
- On December 26, 2003, the massive 2003 Bam earthquake devastates southeastern Iran; over 40,000 people are reported killed in the city of Bam.
- On December 26, 2004, one of the worst natural disasters in recorded history hits Southeast Asia, when the strongest earthquake in 40 years hits the entire Indian Ocean region. The massive 9.3 magnitude earthquake, epicentered just off the west coast of the Indonesian island of Sumatra, generates enormous tsunami waves that crash into the coastal areas of a number of nations including Thailand, India, Sri Lanka, the Maldives, Malaysia, Myanmar, Bangladesh, and Indonesia. The official death toll from the Boxing Day Tsunami in the affected countries stands at approximately 230,000 people dead or still missing.
- On October 8, 2005, the 2005 Kashmir earthquake kills about 80,000 people.
- On May 12, 2008, over 69,000 are killed in central south-west China by the Wenchuan quake, an earthquake measuring 7.9 Moment magnitude scale. The epicenter was 90 kilometers (56 mi) west-northwest of the provincial capital Chengdu, Sichuan province.
Tropical cyclones, other weather, and bushfires
- On May 3, 2008, Over 146,000 in Burma/Myanmar are killed by Cyclone Nargis.
- Several typhoons and hurricanes resulted in extreme destruction in this decade, with Hurricane Katrina nearly destroying New Orleans, followed by Hurricane Rita, which wreaked destruction along the U.S. Gulf Coast. In 2008 the massive Hurricane Ike became the third most destructive hurricane to ever make landfall in the United States.
- 2003 produced one of the worst heatwaves in recorded human history, as Europe was hit by a 40 °C (104 °F) heatwave killing thousands.
- The Black Saturday bushfires – the deadliest bushfires in Australian history took place across the Australian state of Victoria on and around Saturday February 7, 2009 during extreme bushfire-weather conditions, resulting in 173 people killed and, more than 500 injured and around 7,500 homeless. The fires came after Melbourne recorded the highest-ever temperature (46.4 °C, 115 °F) of any capital city in Australia. The majority of the fires were ignited by either fallen or clashing power lines or deliberately lit.
Epidemics
- The 2009 H1N1 (swine flu) flu pandemic is also considered a natural disaster. On October 25, 2009 U.S. President Barack Obama officially declared H1N1 a national emergency[76] Despite President Obama's concern, a Fairleigh Dickinson University PublicMind poll found in October 2009 that an overwhelming majority of New Jerseyans (74%) were not very worried or not at all worried about contracting the H1N1 flu virus.[77]
A study conducted in coordination with the University of Michigan Health Service is scheduled for publication in the December 2009 American Journal of Roentgenology warning that H1N1 flu can cause pulmonary embolism, surmised as a leading cause of death in this current pandemic. The study authors suggest physician evaluation via contrast enhanced CT scans for the presence of pulmonary emboli when caring for patients diagnosed with respiratory complications from a "severe" case of the H1N1 flu.[78]
March 21, 2010 worldwide update by the U.N.'s World Health Organization (WHO) states that "213 countries and overseas territories/communities have reported laboratory confirmed cases of pandemic influenza H1N1 2009, including at least 16,931 deaths." [79]
As of May 30, 2010 worldwide update by World Health Organization(WHO) more than 214 countries and overseas territories or communities have reported laboratory confirmed cases of pandemic influenza H1N1 2009, including over 18,138 deaths.[80]
Non-natural disasters
Vehicular wrecks
- On July 25, 2000, Air France Flight 4590, a Concorde aircraft, crashes into a hotel in Gonesse just after takeoff from Paris, killing all 109 aboard and 4 in the hotel.
- On August 12, 2000, the Russian submarine K-141 Kursk sinks in the Barents Sea, killing all 118 men on board.
- On July 27, 2002, a Sukhoi Su-27 fighter crashes at an air show in Ukraine, killing 85 and injuring more than 100, making it the worst air show disaster in history.
- On February 1, 2003, at the conclusion of the STS-107 mission, the Space Shuttle Columbia disintegrates during reentry over Texas, killing all seven astronauts onboard.
Economics
Main article: 2000s in economicsThe most significant evolution of the early 2000s in the economic landscape was the long-time predicted breakthrough of economic giant China, that had a double-digit growth during nearly the whole decade. To a lesser extent, India also benefited from an economic boom [81] which saw the two most populous countries becoming an increasingly dominant economic force.[82] The rapid catching-up of emerging economies with developed countries sparked some protectionist tensions during the period and was partly responsible for an increase in energy and food prices at the end of the decade. The economic developments in the latter third of the decade were dominated by a worldwide economic downturn, which started with the crisis in housing and credit in the United States in late 2007, and led to the bankruptcy of major banks and other financial institutions.[83] The outbreak of this global financial crisis sparked a global recession, beginning in the United States and affecting most of the industrialized world.
Economic growth in the world
See also: List of countries by GDP (nominal), List of countries by past GDP (nominal), and List of countries by GDP (PPP)Between 1999 to 2009, according to the World Bank statistics for GDP:[84][85]
- The world economy by nominal GDP almost doubled in size from U.S. $30.21 trillion in 1999 to U.S. $58.23 trillion in 2009. This figure is not adjusted for inflation. By PPP, world GDP rose 78%, according to the IMF. But inflation adjusted nominal GDP rose only 42%, according to IMF constant price growth rates.[86] The following figures are not inflation adjusted nominal GDP and should be interpreted with extreme caution:
- The United States (U.S. $14.26 trillion) retained its position of possessing the world's largest economy. However, the size of its contribution to the total global economy dropped from 28.8% to 24.5% by nominal price or a fall from 23.8% to 20.4% adjusted for purchasing power.
- Japan (U.S. $5.07 trillion) retained its position of possessing the second largest economy in the world, but its contribution to the world economy also shrank significantly from 14.5% to 8.7% by nominal price or a fall from 7.8% to 6.0% adjusted for purchasing power.
- China (U.S. $4.98 trillion) went from being the sixth largest to the third largest economy, and in 2009 contributed to 8.6% of the world's economy, up from 3.3% in 1999 by nominal price or a rise from 6.9% to 12.6% adjusted for purchasing power.
- Germany (U.S. $3.35 trillion), France (U.S. $2.65 trillion), United Kingdom (U.S. $2.17 trillion) and Italy (U.S. $2.11 trillion) followed as the 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th largest economies, respectively in 2009.
- Brazil (U.S. $1.57 trillion) retained its position as the 8th largest economy, followed by Spain (U.S. $1.46 trillion), which remained at 10th.
- Other major economies included Canada (U.S. $1.34 trillion; 10th, down from 9th), India (U.S. $1.31 trillion; remaining at 11th from 12th), Russia (U.S. $1.23 trillion; from 16th to 12th) Mexico (U.S. $875 billion; 14th, down from 11th), Australia (U.S. $925 billion; from 14th to 13th) and South Korea (U.S. $832 billion; 15th, down from 13th).
- In terms of purchasing power parity in 2009, the ten largest economies were the United States (U.S. $14.26 trillion), China (U.S. $9.10 trillion), Japan (U.S. $4.14 trillion), India (U.S. $3.75 trillion), Germany (U.S. $2.98 trillion), Russia (U.S. $2.69 trillion), United Kingdom (U.S. $2.26 trillion), France (U.S. $2.17 trillion), Brazil (U.S. $2.02 trillion), and Italy (U.S. $1.92 trillion).[87][88]
Globalization and its discontents
See also: Globalization#Effects of globalization, Offshore outsourcing#Source of conflict, and Business process outsourcing in India Offshore outsourcing of jobs, such as this call centre in India, significantly increased during the decade as many multinational corporations moved their manufacturing and services from western countries to developing countries.
Offshore outsourcing of jobs, such as this call centre in India, significantly increased during the decade as many multinational corporations moved their manufacturing and services from western countries to developing countries.
The removal of trade and investment barriers, the growth of domestic markets, artificially low currencies, the proliferation of education, the rapid development of high tech and information systems industries and the growth of the world economy lead to a significant growth of offshore outsourcing during the decade as many multinational corporations significantly increased subcontracting of manufacturing (and increasingly, services) across national boundaries in developing countries and particularly in China and India, due to many benefits and mainly because the two countries which are the two most populous countries in the world provide huge pools from which to find talent and as because both countries are low cost sourcing countries. As a result of this growth, many of these developing countries accumulated capital and started investing abroad. Other countries, including the United Arab Emirates, Australia, Brazil and Russia, benefited from increased demand for their mineral and energy resources that global growth generated. The hollowing out of manufacturing was felt in Japan and parts of the United States and Europe which had not been able to develop successful innovative industries. Opponents point out that the practice of offshore outsourcing by countries with higher wages leads to the reduction of their own domestic employment and domestic investment. As a result, many customer service jobs as well as jobs in the information technology sectors (data processing, computer programming, and technical support) in countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom have been or are potentially affected.
While global trade rose in the decade (partially driven by China's entry into the WTO in 2001), there was little progress in the multilateral trading system. International trade continued to expand during the decade as emerging economies and developing countries, in particular China and South-Asian countries, benefited low wages costs and most often undervalued currencies. However, global negotiations to reduce tariffs did not make any progress, as member countries of the World Trade Organization did not succeed in finding agreements to stretch the extent of free trade.[89] The Doha Round of negotiations, launched in 2001 by the WTO to promote development, failed to be completed because of growing tensions between regional areas. Nor did the Cancún Conference in 2003 find a consensus on services trade[90] and agricultural subsidies.[91]
The comparative rise of China, India and other developing countries also contributed to their growing clout in international fora. In 2009, it was determined that the G20, originally a forum of finance ministers and central bank governors, would replace the G8 as the main economic council of wealthy nations.
The age of turbulence
 People queuing outside a Northern Rock bank branch in Birmingham, United Kingdom on September 15, 2007, to withdraw their savings because of the Subprime mortgage crisis.
People queuing outside a Northern Rock bank branch in Birmingham, United Kingdom on September 15, 2007, to withdraw their savings because of the Subprime mortgage crisis.
The decade was marked by two financial and economic crises. In 2000, the Dot-com bubble burst, causing turmoil in financial markets and a decline in economic activity in the developed economies, in particular in the United States.[92] However, the impact of the crisis on the activity was limited thanks to the intervention of the central banks, notably the U.S. Federal Reserve System. Indeed, Alan Greenspan, leader of the Federal Reserve until 2006, cut the interest rates several times to avoid a severe recession,[93] allowing an economic revival in the U.S.[94]
As the Federal Reserve maintained low interest rates to favor economic growth, a housing bubble began to appear in the United States. In 2007, the rise in interest rates and the collapse of the housing market caused a wave of loan payment failures in the U.S. The subsequent mortgage crisis caused a global financial crisis, because the subprime mortgages had been securitized and sold to international banks and investment funds. Despite the extensive intervention of central banks, including partial and total nationalization of major European banks,[95][96] the crisis of sovereign debt became particularly acute first in Iceland, though as events of the early 2010s would show, it was not an isolated European example. Economic activity was severely affected around the world in 2008 and 2009,[97] with disastrous consequences for carmakers.[98]
Reactions of governments in all developed and developing countries against the economic slowdown were largely inspired by keynesian economics. The end of the decade was characterized by a Keynesian resurgence,[99] while the influence and media popularity of left-wing economists[100] Joseph Stiglitz and Paul Krugman (Nobel Prize recipients in 2001 and 2008, respectively) did not stop growing during the decade.[101] Several international summits were organized to find solutions against the economic crisis and to impose greater control on the financial markets. The G-20 became in 2008 and 2009 a major organization, as leaders of the member countries held two major summits in Washington in November 2008 and in London in April 2009 to regulate the banking and financial sectors,[102] and also succeeding in coordinating their economic action and in avoiding protectionist reactions.
Energy crisis
Main article: 2000s energy crisis Gas prices in late May 2008.
Gas prices in late May 2008.
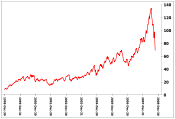
From the mid-1980s to September 2003, the inflation-adjusted price of a barrel of crude oil on NYMEX was generally under $25/barrel. During 2003, the price rose above $30, reached $60 by August 11, 2005, and peaked at $147.30 in July 2008.[103] Commentators attributed these price increases to many factors, including reports from the United States Department of Energy and others showing a decline in petroleum reserves, worries over peak oil, Middle East tension, and oil price speculation.[104]
For a time, geopolitical events and natural disasters indirectly related to the global oil market had strong short-term effects on oil prices. These events and disasters included North Korean missile tests, the 2006 conflict between Israel and Lebanon, worries over Iranian nuclear plants in 2006 and Hurricane Katrina. By 2008, such pressures appeared to have an insignificant impact on oil prices given the onset of the global recession. The recession caused demand for energy to shrink in late 2008 and early 2009 and the price plunged as well. However, it surged back in May 2009, bringing it back to November 2008 levels.[105]
Many fast-growing economies throughout the world, especially in Asia, also were a major factor in the rapidly increasing demand for fossil fuels, which—along with fewer new petroleum finds, greater extraction costs, and political turmoil—forced two other trends: a soar in the price of petroleum products and a push by governments and businesses to promote the development of environmentally friendly technology (known informally as "green" technology). However, a side-effect of the push by some industrial nations to "go green" and utilize biofuels was a decrease in the supply of food and a subsequent increase in the price of the same. It partially caused the 2007 food price crisis, which seriously affected the world's poorer nations with an even more severe shortage of food.[106]
The rise of the Euro
See also: Euro and Economic and Monetary Union of the European UnionA common currency for most EU member states, the euro, was established electronically in 1999, officially tying all the currencies of each participating nation to each other. The new currency was put into circulation in 2002 and the old currencies were phased out. Only three countries of the then 15 member states decided not to join the euro (The United Kingdom, Denmark and Sweden). In 2004 the EU undertook a major eastward enlargement, admitting 10 new member states (eight of which were former communist states). Two more, Bulgaria and Romania, joined in 2007, establishing a union of 27 nations.
The euro has since become the second largest reserve currency and the second most traded currency in the world after the U.S. dollar.[107] As of October 2009[update], with more than €790 billion in circulation, the euro was the currency with the highest combined value of banknotes and coins in circulation in the world, having surpassed the U.S. dollar.[note 1]
Science and technology
Main article: 2000s in science and technologyScience
Space exploration
- The Mars Exploration Rover (MER) Mission successfully reached the surface of Mars in 2004, and sent detailed data and images of the landscape there back to Earth. Opportunity discovers evidence that an area of Mars was once covered in water. Both rovers were each expected to last only 90 days, however both completely exceeded expectations and continued to explore through the end of the decade and beyond.
- Space tourism/Private spaceflight begins with American Dennis Tito, paying Russia $20 million USD for a week long stay to the International Space Station.
- The Voyager I spacecraft entered the heliosheath, marking its departure from our solar system.[108]
- After having analyzed the data from the LCROSS lunar impact, in 2009 NASA announced that the discovery of a "significant" quantity of water in the Moon's Cabeus crater.[109][110]
- Astrophysicists studying the universe confirm its age at 13.7 billion years,[111] discover that it will most likely expand forever without limit, and conclude that only 4% of the universe's contents are ordinary matter (the other 96% being still-mysterious dark matter, dark energy, and dark flow).
- Beginning on November 2, 2000, the International Space Station has remained continuously inhabited. The Space Shuttles helped make it the largest space station ever, despite one of the Shuttles disintegrating upon re-entry in 2003. By the end of 2009 the station was supporting 5 long-duration crew members.
Biology
- The Human Genome Project was completed in 2003, with 99% of the human genome sequenced to 99.99% accuracy.
- National Geographic Society and IBM established The Genographic Project in 2005, which aims to trace the ancestry of every living human down to a single male ancestor.
- The world's first self-contained artificial heart was implanted in Robert Tools in 2001.
- In 2005 surgeons in France carried out the first successful partial human face transplant.
- In 2006, Australian scientist Ian Frazer developed a vaccine for the Human Papillomavirus, a common cause of cervical cancer.
Other
- In 2003 an old dwarf human species, Homo floresiensis was discovered (report published initially October 2004).
- As a result of the discovery of Eris, a Kuiper Belt object larger than Pluto, in August 2006 Pluto is demoted to a "dwarf planet" after being considered a planet for 76 years, redefining the solar system to have eight planets and three dwarf planets.
- CERN's Large Hadron Collider, the world's largest and highest-energy particle accelerator ever made, was completed in 2008.[112]
Technology
Computing and Internet
In the 2000s the Internet became a mainstay, strengthening its grip on Western society while becoming increasingly available in the developing world.
Main article: Timeline of computing 2000–2009 Google becomes the Internet's most visited website.
Google becomes the Internet's most visited website.
- A huge jump in broadband internet usage globally – for example, from 6% of U.S. internet users in June, 2000[113] to what one mid-decade study predicted would be 62% by 2010.[114] By February 2007, over 80% of US Internet users were connected via broadband and broadband internet has been almost a required standard for quality internet browsing.[115]
- Wireless internet became prominent by the end of the decade, as well as internet access in devices besides computers, such as mobile phones and gaming consoles.
- Email became a standard form of interpersonal written communication, with popular addresses available to the public on Hotmail, Gmail and Yahoo! Mail.
- Normalisation became increasingly important as massive standardized corpora and lexicons of spoken and written language became widely available to laypeople, just as documents from the paperless office were archived and retrieved with increasing efficiency using XML-based markup.
- Folksonomy was promoted as an alternative to pyramidal taxonomy.
 Various iPod digital audio players
Various iPod digital audio players
- Peer-to-peer technology gained massive popularity with file sharing systems enabling users to share any audio, video and data files or anything in digital format, as well as with applications which share real-time data, such as telephony traffic.
- VPNs (virtual private networks) became likewise accessible to the general public, and data encryption remained a major issue for the stability of web commerce.
- Boom in music downloading and the use of data compression to quickly transfer music over the Internet, with a corresponding rise of portable digital audio players. As a result, the entertainment industry struggled through the decade to find digital delivery systems for music, movies, and other media that reduce piracy and preserve profit.
- The USB flash drive replaces the Floppy disk as the preferred form of low-capacity mobile data storage.
- During the decade Windows XP and Microsoft Office 2003 become the ubiquitous industry standard in personal computer software until the end of the decade when Apple began to slowly gain market share.
- With the advent of the Web 2.0 dynamic technology became widely accessible, and by the mid-1990s PHP and MySQL became (with Apache) the backbone of many sites, making programming knowledge unnecessary to publish to the web. Blogs, portals, and wikis become common electronic dissemination methods for professionals, amateurs, and businesses to conduct knowledge management typified by success of the online encyclopedia Wikipedia which launched on January 15, 2001, grew rapidly and became the largest and most popular general reference work on the Internet [116][117] as well as the best known wiki in the world and the largest encyclopedia in the world.
 In the late 2000's Facebook became the most popular social networking site in the world. It currently has over 800 million active users.
In the late 2000's Facebook became the most popular social networking site in the world. It currently has over 800 million active users.
- Open Source software such as the Linux operating system and the Mozilla Firefox web browser gain ground.
- Internet commerce became standard for reservations; stock trading; promotion of music, arts, pornography, literature, and film; shopping; and other activities.
- During this decade certain websites and search engines became prominent worldwide as transmitters of goods, services and information. Some of the most popular and successful online sites or search engines of the 2000s included: Google, Yahoo!, Wikipedia, Amazon, eBay, MySpace, Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube.
- More and more businesses began providing paperless services, clients accessing bills and bank statements directly through a web interface.
Video
 Flat panel displays begin to displace cathode-ray tubes
Flat panel displays begin to displace cathode-ray tubes
- Digital cameras become widely popular due to rapid decreases in size and cost while photo resolution steadily increases. As a result, the digital cameras largely supplanted the analog cameras and the integration into mobile phones increase greatly. Since 2007 digital cameras started being manufactured with the face recognition feature built in.
- Graphic cards become powerful enough to render ultra-high-resolution (e.g. 2560x1600) scenes in real time with substantial detail and texture.
- Flat panel displays started becoming widely popular in the second half of the decade displacing cathode ray tubes.[118][119]
- Handheld projectors enter the market and are then integrated into cellphones.[citation needed]
- DVR devices such as TiVo became popular, making it possible to record television broadcasts to a hard drive-based digital storage medium and allowing many additional features including the option to fast-forward through commercials or to use an automatic Commercial skipping feature. This feature created controversy, with major television networks and movie studios claiming it violates copyright and should be banned. With the commercial skipping feature, many television channels place advertisements on the bottom on the TV screen.
- VOD technology became widely available among cable users worldwide, enabling the users to select and watch video content from a large variety of avialable content stored on a central server, as well as gaining the possibility to freeze the image, as well as fast-forward and rewind the VOD content.
- DVDs, and subsequently Blu-ray Discs, replace VCR technology as the common standard in homes and at video stores.
- Free Internet video portals like YouTube, Hulu, and Internet TV software solutions like Joost became new popular alternatives to TV broadcasts.
- TV becomes available on the networks run by some mobile phone providers, such as Verizon Wireless's Vcast.[citation needed]
- High-definition television becomes very popular towards the second half of the decade with the increase of HD television channels and the conversion from analog to digital signals.[120]
Communications
- The popularity of mobile phones and text messaging surged in the 2000s in the Western world. The advent of text messaging made possible new forms of interaction that were not possible before, leading to positive implications such as having the ability to receive information on the move. Nevertheless, it also led to negative social implications such as "cyberbullying" and "sexting," and the rise of traffic collisions caused by drivers who were distracted as they were texting while driving.
- E-mail continued to be popular throughout the decade, and began to replace "snail mail" as the primary way of sending letters and other messages to people in faraway locations. Also, social networking sites arose as a new way for people to stay in touch no matter where they are, as long as they have an internet connection.
- Smartphones, which combine mobile phones with the features of personal digital assistants and portable media players, first emerged in the 1990s but did not become very popular until late in the 2000s. Smartphones are rich in features and often have high resolution touchscreens and web browsers.
- Due to the major success of broadband Internet connections, Voice over IP begins to gain popularity as a replacement for traditional telephone lines.
Robotics
- The U.S. Army used increasingly effective unmanned aerial vehicles in war zones, such as Afghanistan.
- Emerging use of robotics, especially telerobotics in medicine, particularly for surgery.
- Home automation and home robotics advance in North America; iRobot's "Roomba" is the most successful domestic robot and has sold 1.5 million units.
Automobiles
- Automotive navigation systems become widely popular making it possible to direct vehicles to any destination in real-time as well as detect traffic and suggest alternate routes with the use of GPS navigation devices.
- Greater interest in future energy development due to global warming and the potential exhaustion of crude oil. Photovoltaics increase in popularity as a result.
- The Hybrid vehicles market, which became somewhat popular towards the middle of the decade, underwent major advances notably typified by such cars as the Toyota Prius, Ford Escape, and the Honda Insight though by December 2010 they accounted for less than 0.5% of the world cars.
- Many more computers and other technologies were implemented in vehicles throughout the decade such as: Xenon HID headlights, GPS, DVD players, self-diagnosing systems, memory systems for car settings, back-up sensors and cameras, in-car media systems, MP3 player compatibility, USB drive compatibility, keyless start and entry, satellite radio, voice-activation, cellphone connectivity, HUD (Head-Up-Display) and infrared cameras. In addition, more safety features were implemented in vehicles throughout the decade such as: advanced pre-collision safety systems, Backup cameras, Blind spot monitor, Adaptive cruise control, Adaptive headlamps, Automatic parking, Lane departure warning systems and the Advanced Automatic Collision Notification system Onstar (on all GM models).
- Car styling in the 2000s differed throughout the decade. Many automakers strayed from the round and ovoid designs of the 1990s in favor of more boxy, angular designs – the Dodge Charger and Chrysler 300 being notable examples. Many vehicles, especially crossovers, were abstract and futuristic, a trend started by the successful Nissan Murano and Infiniti FX crossovers.
Other
- GPS (Global Positioning System) becomes very popular especially in the tracking of items or people, and the use in cars (see Automotive navigation systems). Games that utilize the system, such as geocaching, emerge and become popular.
Population and social issues
The decade saw further expansion of same-sex rights, with many European, Oceanic, and American countries recognizing civil unions and partnerships and a number of countries extending marriage to same-sex couples. The Netherlands was the first country in the world to legalize same-sex marriage in 2001. By 2010 Same-sex marriage was legal and performed in 11 countries worldwide, although only in some jurisdictions in Mexico and the United States.
AIDS continued to expand during the decade, mainly in Sub-Saharan Africa. New diseases of animal origin appeared for a short time, the mad cow disease in 2003 and the bird flu in 2007, but they appeared not to be dangerous for man. On the contrary, the swine flu was declared a pandemic by the World Health Organization in 2009.
Population continued to grow in most countries, in particular in developing countries, though overall the rate slowed. According to United Nations estimates, world population reached six billion in late 1999,[121] and continued to climb to 6.8 billion in late 2009.[122] In 2007 the population of the United States reached 300 million inhabitants, and Japan's population peaked at 127 million before going into decline.[123]
Environment and climate change
Climate change and global warming became household words in the 2000s. Predictions tools made significant progress during the decade, UN-sponsored organisations such as the IPCC gained influence, and studies such as the Stern report influenced public support for paying the political and economic costs of countering climate change.
The global temperature kept growing during the decade. In December 2009, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) announced that the 2000s may have been the warmest decade since records began in 1850, with four of the five warmest years since 1850 having occurred in this decade.[124][125] The WMO's findings were later echoed by the NASA and the NOAA.[126]
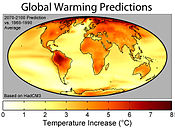 Scientific studies on climate helped establish a consensus.
Scientific studies on climate helped establish a consensus.
Major natural disasters became more frequent and helped change public opinion. One of the deadliest heat waves in human history happened during the 2000s, mostly in Europe, with the 2003 European heat wave killing 37,451 people over the summer months.[127] In February 2009, a series of highly destructive bushfires started in Victoria, Australia, lasting into the next month. While the fires are believed to have been caused by arson, they were widely reported as having been fueled by an excessive heatwave that was due in part to climate change. It has also been alleged that climate change was a cause of increased storms intensity, notably in the case of Hurricane Katrina.
International actions
Climate change became a major issue for governments, populations and scientists. Debates on global warming and its causes made significant progress, as climate change denials were refuted by most scientific studies. Decisive reports such as the Stern Review and the 2007 IPCC Report almost established a climate change consensus. NGOs' actions and the commitment of political personalities (such as former U.S. Vice President Al Gore) also urged to international reactions against climate change. Documentary films An Inconvenient Truth and Home may have had a decisive impact.
Under the auspices of The UN Convention on Climate Change the Kyoto Protocol (aimed at combating global warming) entered into force on 16 February 2005. As of November 2009, 187 states have signed and ratified the protocol.[128] In addition The UN Convention on Climate Change helped coordinate the efforts of the international community to fight potentially disastrous effects of human activity on the planet and launched negotiations to set an ambitious program of carbon emission reduction that began in 2007 with the Bali Road Map. However, the representatives of the then 192 member countries of the United Nations gathered in December 2009 for the Copenhagen Conference failed to reach a binding agreement to reduce carbon emissions because of divisions between regional areas.
However, as environmental technologies were to make up a potential market, some countries made large investments in renewable energies, energy conservation and sustainable transport. Many governments launched national plans to promote sustainable energy. In 2003, the European Union members created an emission trading scheme, and in 2007 they assembled a climate and energy package to reduce further their carbon emission and improve their energy-efficiency. In 2009, the United States Obama administration set up the Green New Deal, an ambitious plan to create millions of jobs in sectors related to greenery.
Additional notable world-wide events
 US Airways Flight 1549, 15 January 2009
US Airways Flight 1549, 15 January 2009
- June 28, 2000 – Elian Gonzalez returns to Cuba with his father, Juan Miguel Gonzalez, ending a protracted custody battle.
- March 3, 2005 – Steve Fossett breaks a world record by completing the first non-stop, non-refueled, solo flight around the world in the Virgin Atlantic GlobalFlyer.[129]
- August 2, 2005 – Air France Flight 358 crashes on landing at Toronto Pearson International Airport and engulfs in flames. All 309 people on board survive.
- September 30, 2005 – Controversial drawings of Muhammad are printed in the Danish newspaper Jyllands-Posten.
- April 16, 2007 – The Virginia Tech Massacre killed 32 people and maimed many others before the gunman, Seung-Hui Cho, committed suicide. It became the deadliest shooting on a school campus as well as the deadliest shooting carried out by a single gunman in United States history.
- August 22, 2008 – Somali Pirates hijack German, Iranian, and Japanese cargo ships off the coast of Somalia, in seven such attacks since June 20.[130]
- January 15, 2009 – US Airways Flight 1549, an Airbus A320-214 N106US ditches in the Hudson River, New York City after both engines are disabled by a birdstrike. All passengers and crew are rescued.[131]
Popular culture
Film
See also: 2000s in filmUsage of computer-generated imagery became more widespread in films during the 2000s. Documentary and mockumentary films, such as March of the Penguins and Super Size Me, were popular in the 2000s. Online films become popular, and conversion to digital cinema started, but was not finished. This conversion is still continuing into the 2010s.
 The highest-grossing film of the decade was Avatar (2009)
The highest-grossing film of the decade was Avatar (2009)
- Oscar winners: Gladiator (2000), A Beautiful Mind (2001), Chicago (2002), The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King (2003), Million Dollar Baby (2004), Crash (2005), The Departed (2006), No Country for Old Men (2007), Slumdog Millionaire (2008), The Hurt Locker (2009)
- The 20 highest-grossing films of the decade are (in order from highest to lowest grossing): Avatar, The Lord of the Rings: The Return of the King, Pirates of the Caribbean: Dead Man's Chest, The Dark Knight, Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone, Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End, Harry Potter and the Order of the Phoenix, Harry Potter and the Half-Blood Prince, The Lord of the Rings: The Two Towers, Shrek 2, Harry Potter and the Goblet of Fire, Spider-Man 3, Ice Age: Dawn of the Dinosaurs, Harry Potter and the Chamber of Secrets, The Lord of the Rings: The Fellowship of the Ring, Finding Nemo, Star Wars Episode III: Revenge of the Sith, Transformers: Revenge of the Fallen, Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban and Shrek the Third.[132]
- The top 15 highest-grossing film series of the decade are (in order from highest to lowest grossing): Harry Potter-film series, Lord of the Rings film trilogy, Pirates of the Caribbean-film series, Spider-Man-film series, Shrek-film series, Ice Age-film series, Transformers-film series, X-Men-film series, Batman-film series' Batman Begins and The Dark Knight, Star Wars Attack of the Clones and Revenge of the Sith, The Da Vinci Code and Angels & Demons, The Matrix-film series' The Matrix Reloaded and Matrix Revolutions, The Chronicles of Narnia-film series, Mission: Impossible-film series' and The Mummy-film series.[132]
Music
See also: 2000s in music and 2000s in the music industry The best-selling artist of the decade was Eminem
The best-selling artist of the decade was Eminem
By the 2000s Rap and Hip Hop had reached its commercial peak, and the genre continued to dominate the music scene of the decade [133][134] The best-selling artist of the decade was the American rapper Eminem, who sold 32 million albums, followed by The Beatles (who split in 1970 but have stayed extremely popular since). The best-selling female artist of the decade was Britney Spears.[135][136]
- Billboard magazine named Eminem as the artist with the best performance on the Billboard charts and named Beyoncé as the female artist of the decade.[137][138] In the UK, the biggest selling artist of the decade is Robbie Williams and the biggest selling band of the decade is Westlife.
- The American performer and recording artist Michael Jackson died on June 25, 2009, creating the largest public mourning since the death of Diana, Princess of Wales in 1997.[139][140][141]
- Oasis was named "most successful act of the last decade" in the Guinness book of world records, between 1995 and 2005. Innovator, inventor, performer and guitar virtuoso Les Paul also died on August 12, 2009 at the age of 94.
Trends
The late 2000s displayed a new trend in music, Auto-tune. This pitch-correction software became the norm on practically all mainstream music since 2007. The 2000s also brought in more dance and electronic music toward the end of the decade and even less rock music in the mainstream.[142][143]Hip hop music also sees a sharp decline in the mainstream during the later 2000s, because of Pop's rising popularity.[144] According to The Guardian, music styles during the 2000s changed very little from how they were at last half of the 1990s.[145] The 2000s had a profound impact on the condition of music distribution. Recent advents in digital technology have fundamentally altered industry and marketing practices as well as players in unusual rapidity.[146][147][148] According to Nielson Soundscan, by 2009 CDs accounted for 79 percent of album sales, with 20 percent coming from digital, representing both a 10 percent drop and gain for both formats in 2 years.[149]
Television
See also: 2000s in televisionAmerican television in the 2000s saw the sharp increase in popularity of reality television, with numerous competition shows such as American Idol, Dancing with the Stars, Survivor and The Apprentice attracting large audiences, as well as documentary or narrative style shows such as Big Brother, The Hills, The Real Housewives, Cheaters, among many others. The decade has since seen a steady decline in the number of sitcoms and an increase in reality shows, crime and medical dramas, such as CSI: Crime Scene Investigation and Grey's Anatomy, paranormal/crime shows like Medium (2005–2011) and Ghost Whisperer (2005–2010), and action/drama shows, including 24 and Lost. Comedy-dramas have became more serious, dealing with such hot button issues, such as drugs, teenage pregnancy, and gay rights. Popular comedy-drama programs include Desperate Housewives, Ugly Betty, and Glee. Adult-oriented animated programming also continued a sharp upturn in popularity with shows like South Park (1997-today) and Family Guy (1999–2002, 2005-today) along with the longtime running cartoon The Simpsons (1989-today).
Although there were less in this decade than there were in the 1990s, the 2000s still saw many popular and notable sitcoms, including Will and Grace, Malcolm in the Middle, The King of Queens, Arrested Development, How I Met Your Mother, The Office, Two and a Half Men, The Big Bang Theory, It's Always Sunny in Philadelphia, and 30 Rock, among many others. A trend seen in several sitcoms of the late 2000s was the absence of a laugh track.
Popular anime include Naruto, One Piece, Dinosaur King, Inazuma Eleven, Cardcaptors, Yu-Gi-Oh!, Saint Seiya Hades, Bakugan and new seasons of Pokémon.
The decade also saw the rise of premium cable dramas such as The Sopranos, Deadwood, The Wire, Battlestar Galactica (2004 TV series), and Mad Men, all of which received critical accolades and attention from academe. The nuanced scripts, character depth, and allusiveness of these shows helped set new standards for quality on television. The critic Daniel Mendelsohn wrote a critique of Mad Men in which he also claimed this last decade was a golden age for episodic television, citing Battlestar Galactica, The Wire, and the network series Friday Night Lights as especially deserving of critical and popular attention.
Radio
The 2000s saw a decrease in the popularity of radio as more listeners starting using MP3 players in their cars to customize driving music. Satellite radio receivers started selling at a much higher rate, which allowed listeners to pay a subscription fee for thousands of ad-free stations. Clear Channel Communications was the largest provider of radio entertainment in the United States with over 900 stations nation-wide. Many radio stations began streaming their content over the Internet, allowing a market expansion far beyond the reaches of a radio transmitter.
During the 2000s, FM radio faced its toughest competition ever for in-car entertainment. iPod, satellite radio, and HD radio were all new options for commuters. CD players had a steady decline in popularity throughout the 2000s but stayed prevalent in most vehicles, while cassette tapes became virtually extinct.
Video games
See also: 2000s in video gamingThe world of video games reached the 7th Generation in the form of consoles like the Wii, the PlayStation 3 and Xbox 360 by the mid 2000s. The number-one-selling game console as of the decade, the PlayStation 2, was released in 2000 and remained popular up to the end of the decade, even after the PlayStation 3 was released. MMORPGs, originating in the mid-to-late 1990s, become a popular PC trend and virtual online worlds become a reality as games such as RuneScape (2001), Final Fantasy XI (2002), Eve Online (2003), Star Wars Galaxies: An Empire Divided (2003), World of Warcraft (2004), and Everquest II (2004), The Lord of the Rings Online: Shadows of Angmar (2007) and Warhammer Online: Age of Reckoning (2008) are released. These worlds come complete with their own economies and social organization as directed by the players as a whole. The persistent online worlds allow the games to remain popular for many years. World of Warcraft, premiered in 2004, remains one of the most popular games in PC gaming and is still being developed into the 2010s.
The Grand Theft Auto series sparked a fad of Mature-rated video games based on including gang warfare, drug use, and perceived "senseless violence" into gameplay. Though violent video games date back to the early 1990s, they became much more common after 2000.
The 7th generation sparked a rise in first person shooting games led by Halo: Combat Evolved, which changed the formula of the first person shooter. Halo 2 started online console gaming and was on top of the Xbox live charts until its successor, Halo 3, took over. Some other popular first-person shooters during the 2000s include the Medal of Honor series, with Medal of Honor: Frontline's release in 2002 bringing the first game in the series to 7th generation consoles.
In the late 2000s, motion controlled video games grew in popularity, from the PlayStation 2's EyeToy to Nintendo's successful Wii console. During the decade 3D video games become the staple of the video-game industry, with 2D games nearly fading from the market. Partially 3D and fully 2D games were still common in the industry early in the decade, but these have now become rare as developers look almost exclusively for fully 3D games to satisfy the increasing demand for them in the market. An exception to this trend is the indie gaming community, which often produces games featuring 'old-school' or retro gaming elements, such as Super Meat Boy and Shadow Complex. These games, which are not developed by the industry giants, are often available in the form of downloadable content from services such as Microsoft's Xbox Live or Apple's App Store and usually cost much less than more major releases.
Dance Dance Revolution was released in Japan and later the United States, where it became immensely popular among teenagers. Another music game, Guitar Hero, was released in North America in 2005 and had a huge cultural impact on both the music and video games industries. It became a worldwide billion-dollar franchise within three years, spawning several sequels and leading to the creation of a competing franchise, Rock Band.
Japanese media giant Nintendo released 9 out of the 10 top selling games of the 2000s, further establishing the company's dominance over the market.[150]
Sports
Main article: 2000s in sports The opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics, held in Beijing, China.
The opening ceremony of the 2008 Summer Olympics, held in Beijing, China.
The Sydney Games, held in 2000, followed the hundredth anniversary of the Olympic Games in Atlanta in 1996. The Athens Games, in 2004, were also a strong symbol, for modern Olympic Games were inspired by the competitions organized in Ancient Greece. Finally, the Beijing Games saw the emergence of China as a major sports power, with the highest number of titles for the first time. The 2002 Salt Lake City and the 2006 Turin Winter Olympic Games were also major events, though less popular. One of the highlights of the 2008 Summer Olympics held in Beijing was the achievement of Michael Phelps the American swimmer, frequently cited as the greatest swimmer and one of the greatest Olympians of all time.[151][152][153] He has won 14 career Olympic gold medals, the most by any Olympian. As of August 2, 2009, Phelps has broken thirty-seven world records in swimming. Phelps holds the record for the most gold medals won in a single Olympics, his eight at the 2008 Beijing Games surpassed American swimmer Mark Spitz's seven-gold performance at Munich in 1972.
Usain Bolt of Jamaica dominated the male sprinting events at the Beijing Olympics, in which he broke three world records, allowing him to be the first man to ever accomplish this at a single Olympic game. He holds the world record for the 100 metres, the 200 metres and, along with his teammates, the 4x100 metres relay.
Football important events included two World Cups, one organized in South Korea, Japan, which saw Brazil win a record fifth title, and the other in Germany, and the regional competitions Copa América and Euro Cup.
Rugby increased in size and audience, as the Rugby World Cup became the third most watched sporting event in the world with the 2007 Rugby World Cup organized in France.
The Boston Red Sox won the World Series of Major League Baseball in 2004, their first since 1918.
Michael Schumacher, the most titled F1 driver, won five F1 World Championships during the decade and finally retired in 2006, yet eventually confirming his come-back to F1 for 2010. Lance Armstrong won all the Tour de France between 1999 and 2005, also an all-time record. Swiss tennis player Roger Federer won 16 Grand Slam titles to become the most titled player.
Architecture
See also: Category:2000s architecture- Taipei 101 became the tallest building in the world ever built after it officially opened on December 31, 2004, a record it held until the opening of the Burj Khalifa (Formerly known as Burj Dubai) in January 2010, standing at 828 m (2,717 ft).
Literature
See also: 2000s in literature- The decade saw the rise of digital media as opposed to the use of print, and the steady decline of printed books in countries where e-readers had become available.
- The deaths of John Updike and other authors marked the end of various major writing careers influential during the late 20th century.
- Popular book series such as Harry Potter, Twilight and Dan Brown's "Robert Langdon" (consisting of The Da Vinci Code, Angels and Demons, and The Lost Symbol) saw increased interest in various genres such as fantasy, romance, vampire fiction, and detective fiction, as well as young-adult fiction in general.
- Manga (also known as Japanese comics) became popular among the international audience, mostly in English-speaking countries. Such popular manga works include Lucky Star, FullMetal Alchemist, and Naruto.
Fashion
Main article: 2000s in fashion Slim-fitting jeans remained popular through the decade, especially on women
Slim-fitting jeans remained popular through the decade, especially on women
Fashion trends varied from 1930s to 1960s and 1990s styles. Fashion trends of the 2000s include Crocs and Ugg boots for feet. Hair styles included the wings haircut for boys, which slowly but surely increased to a very high level by 2009 and semi-long and straight hair for girls continued, amongst many other hairstyles from the 1990s. Many films followed the fashion trends of the time, and for head gear, the Chullo became a very popular winter wear in the late 2000s. In the first part of the 2000s Nike was the dominant sneaker brand for adults and Sketchers were popular for children. Starting in 2004, trends for sneakers started to shift toward brands like Converse and Vans high tops.
By 2004, the grunge style of the 1990s had faded away into a more hip hop dominated fashion scene. Shirts that exposed the belly button and low rise baggy cargo pants which debuted in the late 1990s, became mainstream. Tube tops were extremely popular in the mid-2000s. Spaghetti straps were popular until about 2007.
The late 2000s saw a huge revival of 1980s fashion trends such as off the shoulder tops and neon colors came back in style. Skinny jeans became a staple clothing for young women and men by 2009, with mass brands Gap and Levi launching their own lines.[154] High top Converse and basketball shoes such as Nike and Reebok became very popular. Studded belts and tucked in shirts became popular once again. A dramatic shift in fashion from tightly fitted clothing on top and baggy clothing on the bottom shifted to loose clothing on top and extremely tight clothing on the bottom. These trends remain in fashion for the 2010s.
Print media
- The decade saw the steady decline of books, magazines and newspapers as the main conveyors of information and advertisements in favor of the Internet and other digital forms of information.[155][156][157]
- News blogs grew in readership and popularity; cable news and other online media outlets became competitive in attracting advertising revenues and capable journalists and writers are joining online organizations. Books became available online, and electronic devices such as Amazon Kindle threatened the popularity of printed books.[158][159]
- According to the National Endowment for the Arts (NEA), the decade showed a continuous increase in reading, although circulation of newspapers has declined in conjunction with the Economic Recession.[160]
See also
- 2000s in books
- 2000s in economics
- 2000s in fashion
- 2000s in film
- 2000s in music
- 2000s in music industry
- 2000s in television
- 2000s in sports
- 2000s in science and technology
- 2000s in video gaming
Timeline
The following articles contain brief timelines which list the most prominent events of the decade:
2000 • 2001 • 2002 • 2003 • 2004 • 2005 • 2006 • 2007 • 2008 • 2009
References
- ^ As of October 30, 2009[update]:
Total EUR currency (coins and banknotes) in circulation 771.5 (banknotes) + 21.032 (coins) =792.53 billion EUR * 1.48 (exchange rate) = 1,080 billion USD
Total USD currency (coins and banknotes) in circulation 859 billion USD- "Table 2: Euro banknotes, values (EUR billions, unless otherwise indicated, not seasonally adjusted)" (PDF). ECB. https://stats.ecb.europa.eu/stats/download/bkn_notes_val/bkn_notes_val/bkn_notes_val.pdf. Retrieved December 13, 2009. "2009, October: Total banknotes: 771.5 [billion EUR)"
- "Table 4: Euro coins, values (EUR millions, unless otherwise indicated, not seasonally adjusted)" (PDF). ECB. https://stats.ecb.europa.eu/stats/download/bkn_coins_val/bkn_coins_val/bkn_coins_val.pdf. Retrieved December 13, 2009. "2009, October: Total coins: 21,032 [million EUR)"
- "Money Stock Measures". Federal Reserve Statistical Release. Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h6/current/h6.htm. Retrieved December 13, 2009. "Table 5: Not Seasonally Adjusted Components of M1 (Billions of dollars), not seasonally adjusted, October 2009: Currency: 859.3 (billion USD)"
- "Euro foreign exchange reference rates". ECB. http://www.ecb.europa.eu/stats/eurofxref/eurofxref-hist-90d.xml. Retrieved December 13, 2009. "Exchange rate October 30, 2009: 1 EUR = 1.48 USD"
- ^ Ludden D (1998). The newness of globalization: A schematic view of the historical zones of territoriality University of Pennsylvania. Unfinished draft. Retrieved December 30, 2009.
- ^ Gordon PH; Meunier S (2001). The French challenge: Adapting to globalization. Washington, D.C.: Brookings.
- ^ Heizo T; Ryokichi C (1998). "Japan". Domestic Adjustments to Globalization (CE Morrison & H Soesastro, Eds.). Tokyo: Japan Center for International Exchange, pp. 76–102. Retrieved December 30, 2009.
- ^ Fry EH (2003). Local governments adapting to globalization. National League of Cities. Retrieved 30 Dec. 2009.
- ^ Haarstad H; Fløysand A (2007). "Globalization and the power of rescaled narratives: A case of opposition to mining in Tambogrande, Peru". Political Geography 26(3), pp. 289–308. Abstract. Retrieved December 30, 2009.[dead link]
- ^ Curtis A; Lambert S (Producers). 2005. The power of nightmares: The rise of the politics of fear (film). BBC Two.
- ^ Swartz, Spencer (July 18, 2010). "China Tops U.S. in Energy Use". The Wall Street Journal. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703720504575376712353150310.html.
- ^ "Is ‘Peak Oil' Behind Us?". The New York Times. November 14, 2010. http://green.blogs.nytimes.com/2010/11/14/is-peak-oil-behind-us/.
- ^ Roubini-10 Risks to Global Growth
- ^ Yahoo News
- ^ Theweek.com
- ^ Rohrer, Finlo (December 31, 2009). "Decade dilemma". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/uk_news/magazine/8436194.stm. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
- ^ Allwords.com
- ^ "The noughties: So where are we now?". BBC News. January 1, 2000. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/special_report/1999/02/99/e-cyclopedia/585224.stm. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
- ^ Slate.com
- ^ Irwin, Neil (January 2, 2010). "Aughts were a lost decade for U.S. economy, workers". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/01/01/AR2010010101196.html.
- ^ Hill, Dave (March 29, 2011). "Olympic hockey and Leyton Orient: the astroturf connection". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/uk/davehillblog/2011/mar/29/leyton-orient-olympic-hockey-astroturf-connection.
- ^ McCormick, Neil (September 18, 2009). "100 songs that defined the Noughties". The Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/culture/music/rockandpopfeatures/6198897/100-songs-that-defined-the-Noughties.html.
- ^ "The Noughties year by year". The Times (London). October 20, 2009. http://women.timesonline.co.uk/tol/life_and_style/women/the_way_we_live/article6881549.ece.
- ^ Tremlett, Giles (March 28, 2011). "At-a-glance guide to Spain". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2011/mar/28/spain-at-glance-guide.
- ^ Bowers, Simon (March 23, 2011). "Budget 2011: Chancellor moves to close online VAT loophole". The Guardian (London). http://www.guardian.co.uk/uk/2011/mar/23/budget-2011-chancellor-to-close-online-vat-loophole.
- ^ Barrett, Grant; Ben Zimmer, David K. Barnhart (January 8, 2010). ""Tweet" 2009 Word of the Year, "Google" Word of the Decade, as voted by American Dialect Society" (Press release). American Dialect Society. http://www.americandialect.org/2009-Word-of-the-Year-PRESS-RELEASE.pdf. Retrieved January 18, 2010.
- ^ "Security Council Condemns, 'In Strongest Terms', Terrorist Attacks on the United States". United Nations. September 12, 2001. http://www.un.org/News/Press/docs/2001/SC7143.doc.htm. Retrieved September 11, 2006. "The Security Council today, following what it called yesterday's "horrifying terrorist attacks" in New York, Washington, D.C., and Pennsylvania, unequivocally condemned those acts, and expressed its deepest sympathy and condolences to the victims and their families and to the people and Government of the United States."
- ^ "Bin Laden claims responsibility for 9/11". CBC News. October 29, 2004. http://www.cbc.ca/world/story/2004/10/29/binladen_message041029.html. Retrieved January 11, 2009. "al-Qaeda leader Osama bin Laden appeared in a new message aired on an Arabic TV station Friday night, for the first time claiming direct responsibility for the 2001 attacks against the United States."
- ^ "U.S. Losing War on Terror". NPR. August 21, 2007. http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=13818670. Retrieved Jun 01, 2010.
- ^ President Obama
- ^ "Hussein's Iraq and al Qaeda not linked, Pentagon says". CNN. March 13, 2008. http://www.cnn.com/2008/US/03/13/alqaeda.saddam/. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
- ^ "Questions and Answers". Israel's Security Fence. The State of Israel. February 22, 2004. http://www.securityfence.mod.gov.il/Pages/ENG/questions.htm. Retrieved April 17, 2007. "The Security Fence is being built with the sole purpose of saving the lives of the Israeli citizens who continue to be targeted by the terrorist campaign that began in 2000. The fact that over 800 men, women and children have been killed in horrific suicide bombings and other terror attacks clearly justifies the attempt to place a physical barrier in the path of terrorists. It should be noted that terrorism has been defined throughout the international community as a crime against humanity. As such, the State of Israel not only has the right but also the obligation to do everything in its power to lessen the impact and scope of terrorism on the citizens of Israel."
- ^ Nissenbaum, Dion (January 10, 2007). "Death toll of Israeli civilians killed by Palestinians hit a low in 2006". Washington Bureau. McClatchy Newspapers. http://www.mcclatchydc.com/staff/dion_nissenbaum/story/15469.html. Retrieved April 16, 2007. "Fewer Israeli civilians died in Palestinian attacks in 2006 than in any year since the Palestinian uprising began in 2000. Palestinian militants killed 23 Israelis and foreign visitors in 2006, down from a high of 289 in 2002 during the height of the uprising. Most significant, successful suicide bombings in Israel nearly came to a halt. Last year, only two Palestinian suicide bombers managed to sneak into Israel for attacks that killed 11 people and wounded 30 others. Israel has gone nearly nine months without a suicide bombing inside its borders, the longest period without such an attack since 2000[...] An Israeli military spokeswoman said one major factor in that success had been Israel's controversial separation barrier, a still-growing 250-mile (400 km) network of concrete walls, high-tech fencing and other obstacles that cuts through parts of the West Bank. ‘The security fence was put up to stop terror, and that's what it's doing,’ said Capt. Noa Meir, a spokeswoman for the Israel Defense Forces. [...] Opponents of the wall grudgingly acknowledge that it's been effective in stopping bombers, though they complain that its route should have followed the border between Israel and the Palestinian territories known as the Green Line. [...] IDF spokeswoman Meir said Israeli military operations that disrupted militants planning attacks from the West Bank also deserved credit for the drop in Israeli fatalities."
- ^ B'Tselem – Statistics – Fatalities, B'Tselem.
- ^ "Israel, the Conflict and Peace: Answers to FAQ." Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs. November 3, 2003. April 20, 2009.
- ^ GlobalSecurity.org, Second Chechnya War – 1999–???
- ^ de Montesquiou, Alfred (October 16, 2006). "African Union Force Ineffective, Complain Refugees in Darfur". Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2006/10/15/AR2006101500655.html.
- ^ Weekly.ahram.org.eg
- ^ Lacey, Marc (May 11, 2005). "Tallying Darfur Terror: Guesswork with a Cause". International Herald Tribune. http://www.iht.com/articles/2005/05/10/news/journal.php. Retrieved April 7, 2008.
- ^ Cook, Colleen W., ed. (October 16), "Mexico's Drug Cartels" (PDF), CRS Report for Congress, Congressional Research Service, p. 7, http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/row/RL34215.pdf, retrieved August 9, 2009
- ^ "Progress in Mexico drug war is drenched in blood". Associated Press. March 10, 2009. http://www.google.com/hostednews/ap/article/ALeqM5ilIZ5du3hOOeN7yatYIRIhFY-MJAD96RBGO00. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ "High U.S. cocaine cost shows drug war working: Mexico". Reuters. September 14, 2007. http://www.reuters.com/article/domesticNews/idUSN1422771920070914. Retrieved April 1, 2009.
- ^ Sullivan, Mark P., ed. (December 18), "CRS Report for Congress" (PDF), Mexico – U.S. Relations: Issues for Congress, Congressional Research Service, pp. 2, 13, 14, http://www.fas.org/sgp/crs/row/RL32724.pdf, retrieved April 1, 2009
- ^ The attorney general's office says that 9 of 10 victims are members of organized-crime groups."Briefing: How Mexico is waging war on drug cartels.". The Christian Science Monitor. August 16, 2009. http://www.csmonitor.com/2009/0819/p10s01-woam.html. Retrieved August 20, 2009.
- ^ a b "Armed Conflicts Report – India-Andhra Pradesh". Ploughshares.ca. Archived from the original on June 3, 2009. http://web.archive.org/web/20090603175725/http://www.ploughshares.ca/libraries/ACRText/ACR-IndiaAP.html. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ^ "India is 'losing Maoist battle'". BBC News. 2009-09-15. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/south_asia/8256692.stm. Retrieved 2010-05-20.
- ^ "India's Naxalites: A spectre haunting India". The Economist. 2006-04-12. http://www.economist.com/world/asia/displaystory.cfm?story_id=7799247. Retrieved 2009-07-13.
- ^ Chhatisgarh attack 'consequence' of Green Hunt: Maoist leader - Hindustan Times
- ^ Twentieth Century Atlas – Death Tolls
- ^ Sri Lanka military, rebels trade death toll claims Reuters India – March 1, 2008.
- ^ CNN.com
- ^ SATP.org
- ^ Madsen, Wayne (May 17, 2002). "Report Alleges US Role in Angola Arms-for-Oil Scandal". CorpWatch. http://www.corpwatch.org/article.php?id=2576. Retrieved February 10, 2008.
- ^ Yemen Accuses Iran of Meddling in its Internal Affairs[dead link]
- ^ Ploughshares.com[dead link]
- ^ "Yemeni military battles Shi'ite rebels". The Age (Melbourne). March 20, 2007. http://www.theage.com.au/news/World/Yemeni-military-battles-Shiite-rebels/2007/03/20/1174153010354.html.
- ^ ReliefWeb ť Document ť Nearly 9,500 Somalis die in insurgency-group
- ^ Sharif back in Mogadishu as death toll hits 16,210 | International | Reuters
- ^ allafrica More Than 1,700 Killed in Clashes in 2009, January 1, 2010
- ^ "Chad wants Sudan to disarm rebels". Al Jazeera. January 12, 2006. http://english.aljazeera.net/English/archive/archive?ArchiveId=17880.
- ^ Ed Douglas. "Inside Nepal's Revolution..... (just to check..!!!)". National Geographic Magazine, p. 54, November 2005. Douglas lists the following figures: "Nepalis killed by Maoists from 1996 to 2005: 4,500. Nepalis killed by government in same period: 8,200."
- ^ BBC.co.uk
- ^ Charbonneau, Louis (October 26, 2009). "RPT-EXCLUSIVE-Iran would need 18 months for atom bomb-diplomats". Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/idUSN25158068.
- ^ Wright, Robin. "N. Koreans Taped At Syrian Reactor". The Washington Post. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2008/04/23/AR2008042302906_pf.html. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
- ^ NKorea-Syria nuclear work had military aims: White House, Associated French Press, April 24, 2008. Retrieved on April 24, 2008.
- ^ "Statement by President of Russia Dmitry Medvedev". Russia's President web site. August 26, 2008. http://kremlin.ru/eng/speeches/2008/08/26/1543_type82912_205752.shtml. Retrieved August 26, 2008.
- ^ El Mundo contra la guerra (In Spanish)
- ^ Chile gets first woman president
- ^ Towardsunity.org
- ^ Robert F. Worth and Nazila Fathi (June 13, 2009). "Protests Flare in Tehran as Opposition Disputes Vote". New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2009/06/14/world/middleeast/14iran.html. Retrieved June 19, 2009.
- ^ Anna Johnson and Brian Murphy (June 15, 2009). "Iranian protester killed after opposition rally". Associated Press. http://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20090615/ap_on_re_mi_ea/ml_iran_election. Retrieved June 18, 2009.[dead link]
- ^ "Iran official says 36 killed in post-vote unrest". AFP. September 10, 2009. http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5j8GPoWmrf2qerPWQNHb8Z9eGjT3Q.
- ^ Google.com
- ^ Lake, Eli. Iran protesters alter tactics to avoid death. Washington Times. (June 25, 2009
- ^ Camp David Proposals for Final Palestine-Israel Peace Settlement
- ^ Biswas, Soutik (14 October 2005). "India's architect of reforms". BBC News. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/south_asia/3725357.stm. Retrieved 11 December 2008.
- ^ "Profile: Mahmoud Abbas". BBC. January 10, 2005. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/world/middle_east/1933453.stm. Retrieved October 14, 2009.
- ^ a b c "Continent of Fear: The Rise of Europe's Right-Wing Populists". Der Spiegel. 28 September 2010. http://www.spiegel.de/international/europe/0,1518,719842,00.html. Retrieved 18 December 2010., Part 2, Part 3
- ^ Gibbs N (2009). "Tiller's murder: The logic of extremism on abortion". TIME. Retrieved February 9, 2010.
- ^ "Obama declares swine flu a national emergency". The Daily Herald. 2009. http://heraldextra.com/news/national/article_a4de47bf-1dd4-52ea-9f2d-db535ba581b4.html. Retrieved 2009-10-26.
- ^ http://publicmind.fdu.edu/h1n1/release.pdf
- ^ Mollura DJ, Asnis DS, Crupi RS, et al. (December 2009). "Imaging findings in a fatal case of pandemic swine-origin influenza A (H1N1)". AJR Am J Roentgenol 193 (6): 1500–3. doi:10.2214/AJR.09.3365. PMC 2788497. PMID 19933640. http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=19933640.
- ^ "WHO | Situation updates – Pandemic (H1N1) 2009". Who.int. http://www.who.int/csr/disease/swineflu/updates/en. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ "WHO | Pandemic (H1N1) 2009 – update 103". Who.int. http://www.who.int/csr/don/2010_06_04/en/index.html. Retrieved 2010-10-16.
- ^ "India Reaps Benefits of Economic Boom". CNN. November 2, 2006. http://edition.cnn.com/2006/WORLD/asiapcf/11/01/india.economy/index.html.
- ^ "A New World Economy". Bloomberg Business Week. August 22, 2005. http://www.businessweek.com/magazine/content/05_34/b3948401.htm. Retrieved June 1, 2011.
- ^ BusinessWeek. "Iceland goes bankrupt". Archived from the original on July 22, 2009. http://www.businessweek.com/the_thread/economicsunbound/archives/2008/10/iceland_goes_ba.html. Retrieved July 19, 2009.
- ^ "The World Bank: World Development Indicators database, 1 July 2009. Gross domestic product (2008).". World Bank. January 7, 2009. http://siteresources.worldbank.org/DATASTATISTICS/Resources/GDP.pdf. Retrieved October 7, 2009.
- ^ "The World Bank: World Development Indicators database, 8 February 2000. Gross domestic product (2008).". World Bank. January 7, 2009. http://malchish.org/lib/economics/vvp.pdf. Retrieved December 27, 2009.
- ^ "IMF WEO Database: Report for Selected Country Groups and Subjects, April 2010.". International Monetary Fund. April, 2010. http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2010/01/weodata/weorept.aspx?pr.x=58&pr.y=7&sy=1999&ey=2009&scsm=1&ssd=1&sort=country&ds=.&br=1&c=001,110,163,119,203,123,998,200,904,901,505,511,406,603,205&s=NGDP_RPCH,PPPGDP&grp=1&a=1. Retrieved October 2, 2010.
- ^ Gross domestic product 2009, PPP
- ^ IMF.org
- ^ EFE Fracasan las negociaciones de la Ronda de Doha para liberalizar el comercio July 28, 2008, [[ABC (Spain)|]]
- ^ El Mundo, "El fracaso de la Cumbre de la OMC muestra la fortaleza negociadora de los países pobres" September 16, 2003
- ^ Food and Agricultural Organization "La Ronda de Doha necesita un cambio de orientación" August 8, 2006 «El fracaso de la Ronda de Doha de negociaciones para liberalizar el comercio internacional se debe sobre todo a la lucha para obtener ventajas en los mercados agrícolas por parte de las grandes potencias, empresas y lobbies» (Spanish)
- ^ BBC Mundo, Se contrae la economía mundial November 21, 2001
- ^ BBC Mundo, ¿Recesión global?, September 8, 2001
- ^ Agence France Presse Greenspan dijo que las tasas se mantienen bajas, La Nación, February 16, 2005
- ^ "European banking collapse including nationalisation of three banks", Credit Writedown, Ed Harrison, 29 September 2008, retrieved 11 January 2011, Creditwritedowns.com
- ^ "Anglo Irish Bank Shares Suspended after Nationalization", NY Times, 16 January 2009, retrieved 11 January 2011, NYtimes.com
- ^ ABC Noticias, The economic crisis
- ^ Reuters Se extiende crisis de la industria automotriz, November 15, 2008, El Universo
- ^ ABC Noticias La fascinación del keynesianismo, esperemos que sin resaca February 22, 2009
- ^ El País, Stiglitz y Krugman reclaman una globalización 'gobernada' para reducir las desigualdades September 25, 2004
- ^ El Mundo Paul Krugman, un polémico economista que marca tendencia
- ^ La Vanguardia El G-20 acuerda erigirse en el árbitro de la economía internacional September 25, 2009[dead link]
- ^ TFC-charts.com
- ^ Spiegel.de
- ^ Yahoo Finance Archived 14 May 2009 at WebCite
- ^ Global Policy Global Policy Forum, Are We Approaching a Global Food Crisis?<
- ^ "Triennial Central Bank Survey 2007 – BIS – December 2007". BIS. December 19, 2007. http://www.bis.org/publ/rpfxf07t.pdf. Retrieved July 25, 2009.
- ^ "SPACE.com – It's Official: Water Found on the Moon". Archived from the original on October 8, 2009. http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/090923-moon-water-discovery.html. Retrieved October 5, 2009.
- ^ 21, 2009 "NASA's LCROSS Impacts Confirm Water in Lunar Crater" (Press release). NASA. November 13, 2009. Archived from the original on November 21, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/query?url=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.nasa.gov%2Fhome%2Fhqnews%2F2009%2Fnov%2FHQ_09-265_LCROSS_Confirms_Water.html&date=November 21, 2009. Retrieved November 21, 2009. "Preliminary data from NASA's Lunar Crater Observation and Sensing Satellite, or LCROSS, indicates the mission successfully uncovered water in a permanently shadowed lunar crater."
- ^ "NASA finds 'significant' water on moon". CNN. November 13, 2009. http://www.cnn.com/2009/TECH/space/11/13/water.moon.nasa/index.html. Retrieved November 21, 2009.
- ^ WMAP mission (March 16, 2006). "The Age of the Universe with New Accuracy". NASA. http://map.gsfc.nasa.gov/m_mm/mr_age.html.
- ^ "NASA finds 'significant' water on moon". CNN. November 14, 2009. http://www.cnn.com/2009/TECH/space/11/13/water.moon.nasa/index.html. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
- ^ Bethea, Neil, Jacob Williams and Yiwen Yu (June 2003). "Broadband services in the United States" (PDF). Ohio State University. p. 9. http://64.233.169.104/search?q=cache:evSCwGCD1m0J:www.nrri.ohio-state.edu/dspace/bitstream/2068/814/3/Article%2B1-Bethea%2B_Broadband_.pdf. "Growth of Broadband Users:June 2000:total:4,367,434"[dead link]
- ^ Sharma, Dinesh (August 2, 2005). "Study: Broadband penetration to surge by 2010". CNET News.com. http://news.com.com/Study+Broadband+penetration+to+surge+by+2010/2100-1034_3-5815756.html.
- ^ "US Broadband Penetration Breaks 80% Among Active Internet Users". WebSiteOptimization.com. May 2007. http://www.websiteoptimization.com/bw/0703/.
- ^ Alex Woodson (July 8, 2007). "Wikipedia remains go-to site for online news". Reuters. http://www.reuters.com/article/internetNews/idUSN0819429120070708. Retrieved December 16, 2007. "Online encyclopedia Wikipedia has added about 20 million unique monthly visitors in the past year, making it the top online news and information destination, according to Nielsen//NetRatings."
- ^ "Top 500". Alexa. http://www.alexa.com/site/ds/top_sites?ts_mode=global&lang=none. Retrieved October 13, 2009.
- ^ PCmag.com
- ^ Yahoo News
- ^ Examiner.net
- ^ United Nations The World at Six Billion U.N. Department of Economic and Social Affairs (Population Division)
- ^ U.S. Census Bureau World POPClock Projection Archived 31 January 2008 at WebCite
- ^ Statistical Handbook of Japan Archived 4 March 2008 at WebCite
- ^ Hanley, Charles J. (December 8, 2009). "UN: 2000–2009 likely warmest decade on record". Associated Press. Google News. http://www.webcitation.org/5m7FhrAlX. Retrieved December 20, 2009. "This decade is on track to become the warmest since records began in 1850, and 2009 could rank among the top-five warmest years, the U.N. weather agency reported Tuesday on the second day of a pivotal 192-nation climate conference."
- ^ Beament, Emily (December 8, 2009). "Temperature records released to debunk climate change claims". The Independent. Press Association (London). Archived from the original on December 20, 2009. http://www.webcitation.org/5mAN6SEtB. Retrieved December 20, 2009.
- ^ Broder, John M. (January 21, 2010). "Past Decade Warmest on Record, NASA Data Shows". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2010/01/22/science/earth/22warming.html?hpw. Retrieved January 23, 2010.
- ^ Earth-policy.org, Janet Larsen, Record Heat Wave in Europe Takes 35,000 Lives: Far Greater Losses May Lie Ahead. Retrieved December 10, 2009.
- ^ "Kyoto Protocol: Status of Ratification" (PDF). United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change. January 14, 2009. http://unfccc.int/files/kyoto_protocol/status_of_ratification/application/pdf/kp_ratification.pdf. Retrieved May 6, 2009.
- ^ Eastley, Tony (March 4, 2005). "Steve Fossett sets solo aviation record". Australian Broadcasting Corporation. http://www.abc.net.au/am/content/2005/s1315740.htm. Retrieved October 16, 2009.
- ^ "Official says pirates have seized a German ship off Somalia, the third in a day". http://www.micportal.com/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=859:official-says-pirates-have-seized-a-german-ship-off-somalia-the-third-in-a-day&catid=25:security-measures&Itemid=38.
- ^ Munro, Ian; York, New (January 16, 2009). "Passenger jet plunges into Hudson River". The Age (Melbourne). http://www.theage.com.au/world/passenger-jet-plunges-into-hudson-river-20090116-7ie3.html?page=-1.
- ^ a b IMDb.com
- ^ http://sports.espn.go.com/espn/page3/story?page=boyd/040818
- ^ Caramanica, Jon (2009-11-09). "MYTH No. 4: Biggie & Tupac Are Hip-Hop's Pillars". http://www.spin.com/articles/myth-no-4-biggie-tupac-are-hip-hops-pillars (SPIN).
- ^ MTV. Eminem Is The Best-Selling Artist Of The Decade
- ^ Rolling Stone. Eminem and the Beatles: The top-selling artists of the 2000s.'.' Retrieved December 22, 2009.
- ^ Nationalpost.com
- ^ RTTnews.com
- ^ Allen, Nick. "Michael Jackson memorial service: the biggest celebrity send-off of all time". The Daily Telegraph, July 7, 2009.
- ^ Scott, Jeffry. "Jackson memorial second most-watched in TV history". The Atlanta Journal-Constitution, July 8, 2009.
- ^ Hinckley, David and Richard Huff. "Michael Jackson's memorial 2nd most-watched funeral ever, after Princess Di, say Nielsen ratings". New York Daily News, July 8, 2009.
- ^ "'Nevermind,' never again?". CNN. 2011-09-23. http://www.cnn.com/2011/09/23/showbiz/music/nirvana-nevermind/index.html. Retrieved 2011-10-27.
- ^ McCormick, Neil (2009-08-05). "La Roux, Lady Gaga, Mika, Little Boots: the 80s are back". The Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/culture/music/rockandpopfeatures/5978573/La-Roux-Lady-Gaga-Mika-Little-Boots-the-80s-are-back.html.
- ^ Reynolds, Simon (2009-11-26). "Simon Reynolds's Notes on the noughties: When will hip-hop hurry up and die?". The Guardian. http://www.guardian.co.uk/music/musicblog/2009/nov/26/notes-noughties-hip-hop. Retrieved 2011-08-25.
- ^ "Review of the decade: Alexis Petridis on pop". The Guardian (London). December 7, 2009. http://www.guardian.co.uk/world/2009/dec/06/review-of-the-decade-pop. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
- ^ "TIME.com – TECH TIME: Sound Advice – Too Legit". Time. July 4, 2003. http://www.time.com/time/techtime/200304/sites_angel.html. Retrieved April 21, 2010.[dead link]
- ^ Leeds, Jeff (March 4, 2008). "Nine Inch Nails Fashions Innovative Web Pricing Plan". The New York Times. http://www.nytimes.com/2008/03/04/arts/music/04nine.html. Retrieved April 21, 2010.
- ^ Billboard.com
- ^ France, Lisa (2010-07-20). "Is the death of the CD looming?". CNN. http://edition.cnn.com/2010/SHOWBIZ/Music/07/19/cd.digital.sales/index.html. Retrieved 2011-11-03.
- ^ Blogspot.com
- ^ Pamela Barone (August 17, 2008). "5 things we learned about Michael Phelps". http://www.nbcolympics.com/swimming/news/newsid=229303.html. Retrieved July 30, 2009.
- ^ Mike Celizic (August 16, 2008). "Phelps officially world's greatest athlete ever". msnbc. http://www.msnbc.msn.com/id/26194188. Retrieved July 30, 2009.
- ^ Pat Forde (August 13, 2008). "It's over, there are no arguments … Phelps is the best ever". ESPN. http://sports.espn.go.com/oly/summer08/columns/story?columnist=forde_pat&id=3532594. Retrieved July 30, 2009.
- ^ Smith, Ray A. (6 July 2009). "Tight Squeeze: Making Room For a New Men's Fashion". The Wall Street Journal (New York). http://online.wsj.com/article/SB124683780090998061.html.
- ^ NY TimesSteady Decline of Newspaper Circulation. Retrieved December 4, 2009.
- ^ USA Today, Rachel Metz, Newspaper circulation decline picks up speed. Retrieved December 4, 2009.
- ^ Newspaperdeathwatch.com, The Death of Newspapers. Retrieved December 4, 2009.
- ^ The New Yorker Caleb Crain, Twilight of the Books. Retrieved December 4, 2009.
- ^ Times Online, The decline and fall of books. Retrieved December 4, 2009.
- ^ NEA.gov
21st century
19th century←20th century← ↔ →22nd century→23rd century1990s 1990 1991 1992 1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000–2009 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005 2006 2007 2008 2009 2010s 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020s 2020 2021 2022 2023 2024 2025 2026 2027 2028 2029 2030s 2030 2031 2032 2033 2034 2035 2036 2037 2038 2039 2040s 2040 2041 2042 2043 2044 2045 2046 2047 2048 2049 2050s 2050 2051 2052 2053 2054 2055 2056 2057 2058 2059 2060s 2060 2061 2062 2063 2064 2065 2066 2067 2068 2069 2070s 2070 2071 2072 2073 2074 2075 2076 2077 2078 2079 2080s 2080 2081 2082 2083 2084 2085 2086 2087 2088 2089 2090s 2090 2091 2092 2093 2094 2095 2096 2097 2098 2099 2100–2109 2100 2101 2102 2103 2104 2105 2106 2107 2108 2109 External links
- The fashions, trends and people that defined the decade, VOGUE.COM UK
- 100 Top Pictures of the Decade – slideshow by Reuters
- "A portrait of the decade", BBC, December 14, 2009
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.