- Thebacon
-
Thebacon 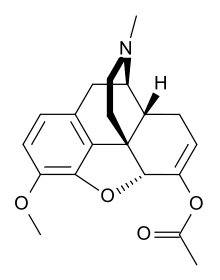

Systematic (IUPAC) name 6,7-didehydro- 4,5α-epoxy- 3-methoxy- 17-methylmorphinan- 6-ol acetate Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status Schedule I (US) Identifiers CAS number 466-90-0 ATC code R05DA10 PubChem CID 10075 UNII 520D430GDK 
KEGG D07386 
Chemical data Formula C20H23NO4 Mol. mass 341.401 g/mol  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Thebacon (INN[1]) or dihydrocodeinone enol acetate is a semisynthetic opioid that is similar to hydrocodone and manufactured from Thebaine. It is marketed as its hydrochloride salt under the trade name Acedicon and as the bitartrate as Diacodin and possibly other trade names. Other salts used in medicine include the hydroiodide and sulphate.
It is a narcotic analgesic of the middle range and an antitussive, primarily in Europe, although it is no longer in common use. It was invented in Germany in 1924.
It is the esterification product of the enol tautomer of hydrocodone (dihydrocodeineone) with acetic acid.
Dihydrocodeinone enol acetate's analgesic and antitussive potency is slightly higher than that of its parent compound hydrocodone.
Like all of its chemical relatives in this therapeutic class (codeine-based narcotic antitussives and midrange analgesics), Dihydrocodeinone enol acetate exerts some of its effect by being a prodrug for a stronger opioid, namely hydromorphone, which is formed in the liver by the Cytochrome P450 2D6 (CYP2D6) enzyme pathway, meaning that effectiveness of a given dose will vary amongst patients and other drugs taken at the same time can antagonise or cause potentiation.
Dihydrocodeinone enol acetate is a Schedule I controlled substance in the US.[2]
References
- ^ Sean C. Sweetman, ed (2009). Martindale: The Complete Drug Reference (36th ed.). London: Pharmaceutical Press. ISBN 0853698406.
- ^ "Controlled Substance Schedules". US Department of Justice. http://www.justice.gov/dea/pubs/scheduling.html.
Analgesics (N02A, N02B) Opioids
See also: Opioids templateOpium & alkaloids thereofSemi-synthetic opium
derivativesSynthetic opioidsAlphaprodine • Anileridine • Butorphanol • Dextromoramide • Dextropropoxyphene • Dezocine • Fentanyl • Ketobemidone • Levorphanol • Methadone • Meptazinol • Nalbuphine • Pentazocine • Propoxyphene • Propiram • Pethidine • Phenazocine • Piminodine • Piritramide • Tapentadol • Tilidine • Tramadol
Pyrazolones Cannabinoids Anilides Non-steroidal
anti-inflammatories
See also: NSAIDs templatePropionic acid classFenoprofen • Flurbiprofen • Ibuprofen# • Ketoprofen • Naproxen • Oxaprozin
Oxicam classAcetic acid classDiclofenac • Indometacin • Ketorolac • Nabumetone • Sulindac • Tolmetin
Celecoxib • Rofecoxib • Valdecoxib • Parecoxib • Lumiracoxib
Anthranilic acid
(fenamate) classMeclofenamate • Mefenamic acid
SalicylatesAspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)# • Benorylate • Diflunisal • Ethenzamide • Magnesium salicylate • Salicin • Salicylamide • Salsalate • Trisalate • Wintergreen (Methyl salicylate)
Atypical, adjuvant and potentiators,
Metabolic agents and miscellaneousAmitryptiline • Befiradol • Bicifadine • Carisoprodol • Camphor • Cimetidine • Clonidine • Chlorzoxazone • Cyclobenzaprine • Duloxetine • Esreboxetine • Flupirtine • Gabapentin • Glafenine • Hydroxyzine • Ketamine • Menthol • Mephenoxalone • Methocarbamol • Nefopam • Orphenadrine • Pregabalin • Proglumide • Scopolamine • Tebanicline • Trazodone • Gabapentin enacarbil • ZiconotideCough and cold preparations (R05) Expectorants Mucolytics Acetylcysteine • Ambroxol • Bromhexine • Carbocisteine • Domiodol • Dornase alfa • Eprazinone • Erdosteine • Letosteine • Mesna • Neltenexine • Sobrerol • Stepronin • TioproninCough suppressants Acetyldihydrocodeine • Benzylmorphine • Codeine • Dextromethorphan • Diacetylmorphine • Dihydrocodeine • Dimemorfan • Droxypropine • Ethylmorphine • Hydrocodone • Hydromorphone • Isoaminile • Laudanum • Levomethadone • Levopropoxyphene • Methadone • Nicocodeine • Nicodicodeine • Normethadone • Noscapine • Pholcodine • Thebacon • Tipepidine • ZipeprolOtherBenzonatate • Benproperine • Bibenzonium bromide • Butamirate • Clobutinol • Clofedanol • Cloperastine • Diphenhydramine • Dibunate • Dimethoxanate • Dropropizine • Fedrilate • Glaucine • Levodropropizine • Meprotixol • Morclofone • Nepinalone • Oxolamine • Oxeladin • Pentoxyverine • Pipazetate • Prenoxdiazine • Piperidione
This drug article relating to the respiratory system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. This analgesic-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
