- Dimethylthiambutene
-
Dimethylthiambutene 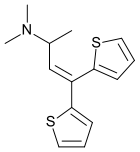
Systematic (IUPAC) name (RS)-N,N-dimethyl-4,4-dithiophen-2-yl-but-3-en-2-amine Clinical data Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status Schedule I (US) Identifiers CAS number 524-84-5 ATC code None PubChem CID 10668 DrugBank DB01444 ChemSpider 10218 
UNII 915D88LM9O 
ChEBI CHEBI:59781 
Chemical data Formula C14H17NS2 Mol. mass 263.424 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem Physical data Melt. point 169–170 °C (336–338 °F)  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Dimethylthiambutene (N,N-Dimethyl-1-methyl-3,3-di-2-thienylallylamine, Ohton, Aminobutene, Dimethibutin, Kobaton, Takaton, Dimethibutin) is an opioid analgesic drug, most often used in veterinary medicine in Japan and to a lesser extent in other countries in the region and around the world. It is the most prominent and widely-used of the thiambutenes, a series of open-chain opioids structurally related to methadone which are also called the thienyl derivative opioids which also includes diethylthiambutene and ethylmethylthiambutene as well as the cough suppressant tipepidine, which is weaker and not a controlled substance in most of the world.
Dimethylthiambutene was developed in the United States in the early 1950s and introduced to the market by Burroughs-Wellcome in the United Kingdom in 1951. Dimethylthiambutene is now under international control under the UN Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961, the laws governing habit-forming substances in virtually all countries and Schedule I of the US Controlled Substances Act of 1970 due to high abuse potential and never being introduced clinically in the United States; other countries regulate it much as morphine or diamorphine.

This analgesic-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
