- Mefenamic acid
-
Mefenamic acid 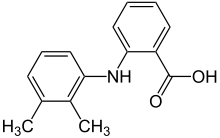
Systematic (IUPAC) name 2-(2,3-dimethylphenyl)aminobenzoic acid Clinical data Trade names Ponstel AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a681028 Pregnancy cat. C (Australia, United States) Legal status ℞-only (U.S.), POM in UK Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 90% Protein binding 90% Metabolism Hepatic (CYP2C9) Half-life 2 hours Excretion Renal and fecal Identifiers CAS number 61-68-7 
ATC code M01AG01 PubChem CID 4044 DrugBank APRD0073 ChemSpider 3904 
UNII 367589PJ2C 
KEGG D00151 
ChEMBL CHEMBL686 
Chemical data Formula C15H15NO2 Mol. mass 241.285 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) acid (verify)
(what is this?) acid (verify)Mefenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug used to treat pain, including menstrual pain. It is typically prescribed for oral administration. Mefenamic acid is marketed in the USA as Ponstel.
Mefenamic acid decreases inflammation (swelling) and uterine contractions by a still unknown mechanism. However it is thought to be related to the inhibition of prostaglandin synthesis. There is also evidence that supports the use of mefenamic acid for perimenstrual migraine headache prophylaxis, with treatment starting 2 days prior to the onset of flow or 1 day prior to the expected onset of the headache and continuing for the duration of menstruation.[1]
Since hepatic metabolism plays a significant role in mefenamic acid elimination, patients with known liver deficiency may be prescribed lower doses. Kidney deficiency may also cause accumulation of the drug and its metabolites in the excretory system. Therefore patients suffering from renal conditions should not be prescribed mefenamic acid.
Brand Names Mefalth, Mefalth T, Ponstel, Ponstan, Ponstal, Parkemed, Mafepain, Mefamed, Mephadolor, Meftal, Dyfenamic, Potarlon, Dolfenal, Meyerdonal, Alfoxan, Fenagesic, Spiralgin. Contents
Side effects
Known mild side effects of mefenamic acid include headaches, nervousness and vomiting. Serious side effects may include diarrhea, hematemesis (vomiting blood), haematuria (blood in urine), blurred vision, skin rash, itching and swelling, sore throat and fever. It is advised to consult a doctor immediately if these symptoms appear while taking this medication.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may worsen hypertension. Persons with hypertension, left ventricular dysfunction, and heart failure may wish to avoid NSAIDs.
Mefenamic acid is recommended to be taken with food.[2]
Mefenamic acid usage has been discontinued in Germany in 2007 because no study to date could prove any advantage over other NSAIDs, but some severe side-effects have been observed. [3]
Overdose
Overdose can lead to a range of symptoms including convulsions, nausea, vomiting, vomiting blood, shallow breathing, coma. Onset of symptoms is usually between 30 minutes and 4 hours, but signs of renal failure may appear several days after an overdose. Seek medical attention immediately in the case of overdose. The lethal dose can be as low as 2.5g.
Synthesis
Analogous to fenamic acid, this compound may be synthesized from 2-chlorobenzoic acid and 2,3-dimethylaniline.[4]
References
- ^ Pringsheim T, Davenport WJ, Dodick D. Acute treatment and prevention of menstrually related migraine headache: evidence-based review. Neurology. 2008;70(17):1555-1563.
- ^ National Institutes of Health side effects for Mefenamic Acid
- ^ http://www.qualimedic.de/Sprechstunde/arzneimittel_nebenwirkung/7182967
- ^ Trinus, F. P.; Mokhort, N. A.; Yagupol'skii, L. M.; Fadeicheva, A. G.; Danilenko, V. S.; Ryabukha, T. K.; Fialkov, Yu. A.; Kirichek, L. M. et al. (1977). "Mefenamic acid — A nonsteroid antiinflammatory agent". Pharmaceutical Chemistry Journal 11 (12): 1706. doi:10.1007/BF00778304.
Sources
- MedlinePlus Drug Information: Mefenamic Acid. Last accessed September 28, 2005.
- Ponstel Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics, Studies, Metabolism - Mefenamic Acid - RxList Monographs. Last accessed September 28, 2005.
- Consumption of NSAIDs and the Development of Congestive Heart Failure in Elderly Patients
- NSAIDs May Increase Risk for Worsening Heart Failure
Anti-inflammatory products (M01A) Pyrazolidine/Butylpyrazolidines Ampyrone • Clofezone • Kebuzone • Metamizole • Mofebutazone • Oxyphenbutazone • Phenazone • Phenylbutazone • Sulfinpyrazone • Feprazone •Acetic acid derivatives
and related substancesAceclofenac • Acemetacin • Alclofenac • Bromfenac • Bumadizone • Bufexamac • Diclofenac • Difenpiramide • Etodolac • Fentiazac • Indometacin • Ketorolac • Lonazolac • Oxametacin • Proglumetacin • Sulindac • Tolmetin • Zomepirac • AmfenacOxicams Propionic acid derivatives Alminoprofen • Benoxaprofen • Dexibuprofen • Dexketoprofen • Fenbufen • Fenoprofen • Flunoxaprofen • Flurbiprofen • Ibuprofen • Ibuproxam • Indoprofen • Ketoprofen • Naproxen • Oxaprozin • Pirprofen • Suprofen • Tiaprofenic acidFenamates Flufenamic acid • Meclofenamic acid • Mefenamic acid • Tolfenamic acid • Niflumic acid • Morniflumate • Azapropazone •Coxibs Other Analgesics (N02A, N02B) Opioids
See also: Opioids templateOpium & alkaloids thereofSemi-synthetic opium
derivativesSynthetic opioidsAlphaprodine • Anileridine • Butorphanol • Dextromoramide • Dextropropoxyphene • Dezocine • Fentanyl • Ketobemidone • Levorphanol • Methadone • Meptazinol • Nalbuphine • Pentazocine • Propoxyphene • Propiram • Pethidine • Phenazocine • Piminodine • Piritramide • Tapentadol • Tilidine • Tramadol
Pyrazolones Cannabinoids Anilides Non-steroidal
anti-inflammatories
See also: NSAIDs templatePropionic acid classFenoprofen • Flurbiprofen • Ibuprofen# • Ketoprofen • Naproxen • Oxaprozin
Oxicam classAcetic acid classDiclofenac • Indometacin • Ketorolac • Nabumetone • Sulindac • Tolmetin
Celecoxib • Rofecoxib • Valdecoxib • Parecoxib • Lumiracoxib
Anthranilic acid
(fenamate) classMeclofenamate • Mefenamic acid
SalicylatesAspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)# • Benorylate • Diflunisal • Ethenzamide • Magnesium salicylate • Salicin • Salicylamide • Salsalate • Trisalate • Wintergreen (Methyl salicylate)
Atypical, adjuvant and potentiators,
Metabolic agents and miscellaneousAmitryptiline • Befiradol • Bicifadine • Carisoprodol • Camphor • Cimetidine • Clonidine • Chlorzoxazone • Cyclobenzaprine • Duloxetine • Esreboxetine • Flupirtine • Gabapentin • Glafenine • Hydroxyzine • Ketamine • Menthol • Mephenoxalone • Methocarbamol • Nefopam • Orphenadrine • Pregabalin • Proglumide • Scopolamine • Tebanicline • Trazodone • Gabapentin enacarbil • ZiconotideCategories:- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Anthranilic acids
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
