- Naproxen
-
Naproxen 

Systematic (IUPAC) name (+)-(S)-2-(6-methoxynaphthalen-2-yl)
propanoic acidClinical data Pregnancy cat. C(AU) B(US) Legal status Pharmacy Only (S2) (AU) P (UK) OTC (US) OTC(Ca) Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability 95% (oral) Protein binding 99% Metabolism Hepatic (to 6-desmethylnaproxen) Half-life 12–24 hours Excretion Renal Identifiers CAS number 22204-53-1 
ATC code G02CC02 M01AE02, M02AA12 PubChem CID 156391 DrugBank APRD01135 ChemSpider 137720 
UNII 57Y76R9ATQ 
KEGG D00118 
ChEBI CHEBI:7476 
ChEMBL CHEMBL154 
Chemical data Formula C14H14O3 Mol. mass 230.259 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Naproxen sodium (INN) (
 /nəˈprɒksən/) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used for the reduction of pain, fever, inflammation and stiffness caused by conditions such as:
/nəˈprɒksən/) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used for the reduction of pain, fever, inflammation and stiffness caused by conditions such as:- osteoarthritis
- kidney stones
- rheumatoid arthritis
- psoriatic arthritis
- gout
- ankylosing spondylitis
- menstrual cramps
- tendinitis
- bursitis
It is also used for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea. It works by inhibiting both the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes. Naproxen and naproxen sodium are marketed under various trade names, including: Aleve, Anaprox, Antalgin, Feminax Ultra, Flanax, Inza, Midol Extended Relief, Nalgesin, Naposin, Naprelan, Naprogesic, Naprosyn, Narocin, Proxen, Synflex and Xenobid.
Naproxen was originally marketed as the prescription drug Naprosyn by Syntex in 1976, and naproxen sodium was first marketed under the trade name Anaprox in 1980. It remains a prescription-only drug in much of the world. In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its use as an over-the-counter (OTC) drug in 1994; OTC preparations in the U.S. are mainly marketed by Bayer HealthCare under the trade name Aleve and generic store brand formulations. In Australia, packets of 275 mg tablets of naproxen sodium are Schedule 2 pharmacy medicines, with a maximum daily dose of 5 tablets or 1375 mg. In the United Kingdom, 250 mg tablets of naproxen were approved for OTC sale under the brand name Feminax Ultra in 2008, for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhoea in women aged 15 to 50.[1] Aleve became available over-the-counter in most provinces in Canada on 14 July 2009, it became available in Quebec during the summer of 2010 but can only be dispensed by a pharmacy employee after an assessment of the patient's needs. It most recently became available in British Columbia in March 2011. [2]
Contents
Risks and adverse effects
COX-2 selective and non-selective NSAIDs have been linked to increases in the number of serious and potentially fatal cardiovascular events such as myocardial infarctions and stroke. A 2011 meta-analysis published in the British Medical Journal states that, of all NSAIDs evaluated, naproxen was associated with the smallest overall cardiovascular risks.[3] The drug had roughly 50% of the associated risk of stroke as compared with ibuprofen and was also associated with a reduced number of myocardial infarctions as compared to control groups.
NSAID Painkillers, such as Naproxen, may interfere and reduce efficiency of SSRI antidepressants [4][5]
Structure and details
Naproxen is a member of the 2-arylpropionic acid (profen) family of NSAIDs. The free acid is an odorless, white to off-white crystalline substance. It is lipid-soluble and practically insoluble in water. It has a melting point of 152-154 °C.
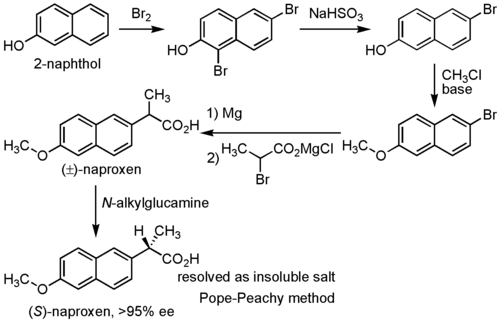
Synthesis
Naproxen has been industrially produced by Syntex as follows:[6]
Other synthetic routes have also been discussed.[6]
See also
References
- ^ Pocock, Nicola (2006). "MHRA approves availability of OTC naproxen (Feminax Ultra)". NHS Press Release. http://www.druginfozone.nhs.uk/Record%20Viewing/viewRecord.aspx?id=591725.
- ^ http://www.bayer.ca/files/Aleve%20Release.July14.FINAL_.pdf
- ^ Trelle S, Reichenbach S, Wandel S, Hildebrand P, Tschannen B, Villiger PM, Egger M, Jüni P. (2011). "Cardiovascular safety of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: network meta-analysis". BMJ 342: c7086. doi:10.1136/bmj.c7086. PMC 3019238. PMID 21224324. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=3019238.
- ^ Why Painkillers Interfere with Anti-depressants
- ^ J.L. Warner-Schmidt et.al "Antidepressant effects of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) are attenuated by antiinflammatory drugs in mice and humans" PNAS 2011
- ^ a b Peter J. Harrington and Eric Lodewijk (1997). "Twenty Years of Naproxen Technology". Org. Process Res. Dev. 1 (1): 72–76. doi:10.1021/op960009e.
External links
- CID 1302 from PubChem
- EINECS number 244-838-7
- MedlinePlus Information on naproxen
- FDA Statement on Naproxen, released 20 December 2004
- Alzheimer's Disease Anti-Inflammatory Prevention Trial
- Forbes article (expressing the point of view that the risk of heart attack or stroke was overstated)
- Which NSAID for Heart Disease Patients? - Medscape
- U.S. National Library of Medicine: Drug Information Portal - Naproxen
Anti-inflammatory products (M01A) Pyrazolidine/Butylpyrazolidines Ampyrone • Clofezone • Kebuzone • Metamizole • Mofebutazone • Oxyphenbutazone • Phenazone • Phenylbutazone • Sulfinpyrazone • Feprazone •Acetic acid derivatives
and related substancesAceclofenac • Acemetacin • Alclofenac • Bromfenac • Bumadizone • Bufexamac • Diclofenac • Difenpiramide • Etodolac • Fentiazac • Indometacin • Ketorolac • Lonazolac • Oxametacin • Proglumetacin • Sulindac • Tolmetin • Zomepirac • AmfenacOxicams Propionic acid derivatives Alminoprofen • Benoxaprofen • Dexibuprofen • Dexketoprofen • Fenbufen • Fenoprofen • Flunoxaprofen • Flurbiprofen • Ibuprofen • Ibuproxam • Indoprofen • Ketoprofen • Naproxen • Oxaprozin • Pirprofen • Suprofen • Tiaprofenic acidFenamates Coxibs Other Topical products for joint and muscular pain (M02) Anti-inflammatory preparations,
non-steroidsAcetic acid derivativesOtherBenzydamine • Etofenamate • Piroxicam • Felbinac • Bufexamac • Ketoprofen • Bendazac • Naproxen • Ibuprofen • Feprazone • Niflumic acid • Meclofenamic acid • Flurbiprofen • Suxibuzone • Indometacin • NifenazoneCapsaicin derivatives Other Analgesics (N02A, N02B) Opioids
See also: Opioids templateOpium & alkaloids thereofSemi-synthetic opium
derivativesSynthetic opioidsAlphaprodine • Anileridine • Butorphanol • Dextromoramide • Dextropropoxyphene • Dezocine • Fentanyl • Ketobemidone • Levorphanol • Methadone • Meptazinol • Nalbuphine • Pentazocine • Propoxyphene • Propiram • Pethidine • Phenazocine • Piminodine • Piritramide • Tapentadol • Tilidine • Tramadol
Pyrazolones Cannabinoids Anilides Non-steroidal
anti-inflammatories
See also: NSAIDs templatePropionic acid classFenoprofen • Flurbiprofen • Ibuprofen# • Ketoprofen • Naproxen • Oxaprozin
Oxicam classAcetic acid classDiclofenac • Indometacin • Ketorolac • Nabumetone • Sulindac • Tolmetin
Celecoxib • Rofecoxib • Valdecoxib • Parecoxib • Lumiracoxib
Anthranilic acid
(fenamate) classMeclofenamate • Mefenamic acid
SalicylatesAspirin (Acetylsalicylic acid)# • Benorylate • Diflunisal • Ethenzamide • Magnesium salicylate • Salicin • Salicylamide • Salsalate • Trisalate • Wintergreen (Methyl salicylate)
Atypical, adjuvant and potentiators,
Metabolic agents and miscellaneousAmitryptiline • Befiradol • Bicifadine • Carisoprodol • Camphor • Cimetidine • Clonidine • Chlorzoxazone • Cyclobenzaprine • Duloxetine • Esreboxetine • Flupirtine • Gabapentin • Glafenine • Hydroxyzine • Ketamine • Menthol • Mephenoxalone • Methocarbamol • Nefopam • Orphenadrine • Pregabalin • Proglumide • Scopolamine • Tebanicline • Trazodone • Gabapentin enacarbil • ZiconotideProlactin inhibitors Anti-inflammatory products
for vaginal administrationCategories:- Analgesics
- Antipyretics
- Propionic acids
- Equine medications
- Naphthol ethers
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.