- Ankylosing spondylitis
-
Ankylosing spondylitis Classification and external resources 
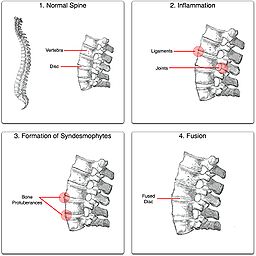
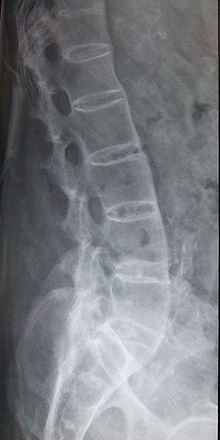
An ankylosing spine in which the vertebrae become fused together.ICD-10 M08.1, M45 ICD-9 720.0 OMIM 106300 DiseasesDB 728 MedlinePlus 000420 eMedicine radio/41 MeSH D013167 Ankylosing spondylitis (AS, from Greek ankylos, stiff; spondylos, vertebrae), previously known as Bekhterev's disease, Bekhterev syndrome, and Marie-Strümpell disease is a chronic inflammatory disease of the axial skeleton with variable involvement of peripheral joints and nonarticular structures. AS is a form of spondyloarthritis, is a chronic, inflammatory arthritis and autoimmune disease.[1] It mainly affects joints in the spine and the sacroiliac joint in the pelvis, and can cause eventual fusion of the spine.
It is a member of the group of the spondyloarthropathies with a strong genetic predisposition. Complete fusion results in a complete rigidity of the spine, a condition known as "bamboo spine".[2]
Contents
Signs and symptoms
The typical patient is a young male,[3] aged 20–40, however the condition also presents in females. The condition is known to be hereditary. Symptoms of the disease first appear, on average, at age 23 years.[4] These first symptoms are typically chronic pain and stiffness in the middle part of the spine or sometimes the entire spine, often with pain referred to one or other buttock or the back of thigh from the sacroiliac joint.
Symptoms appear gradually. Initially they are usually not specific for ankylosing spondylitis. The average onset-to-diagnosis lag time has been estimated to be approximately 8.5 years to 11.4 years.[4]
Men are affected more than women by a ratio about of 3:1,[3] with the disease usually taking a more severe course in men than women.[5]
In 40% of cases, ankylosing spondylitis is associated with an inflammation of the eye (iritis and uveitis), causing redness, eye pain, vision loss, floaters and photophobia. This is thought to be due to the association these two conditions have with inheritance of HLA-B27. Other common symptoms are generalized fatigue and sometimes nausea. Less commonly, aortitis, apical lung fibrosis and ectasia of the sacral nerve root sheaths may occur.
When the condition presents before the age of 18, it is relatively likely to cause pain and swelling of large limb joints, particularly the knee. In prepubescent cases, pain and swelling may also manifest in the ankles and feet, where calcaneal spurs may also develop.
Pain is often severe at rest, but improves with physical activity. However, many experience inflammation and pain to varying degrees regardless of rest and movement.[citation needed]
Ankylosing spondylitis is one of a cluster of conditions known as seronegative spondyloarthropathies, in which rheumatoid factor tests are negative and the characteristic pathological lesion is an inflammation of the enthesis (the insertion of tensile connective tissue into bone).
Pathophysiology
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a systemic rheumatic disease, meaning it affects the entire body. Approximately 90% of AS patients express the HLA-B27 genotype, meaning there is a strong genetic association. However, only 5% of individuals with the HLA-B27 genotype contract the disease.[6] Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF α) and IL-1 are also implicated in ankylosing spondylitis. Autoantibodies specific for AS have not been identified. Antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies ANCA are associated with AS, but do not correlate with disease severity.[citation needed]
The association of AS with HLA-B27 suggests the condition involves CD8 T cells, which interact with HLA-B[citation needed]. This interaction is not proven to involve a self antigen, and at least in the related Reiter's syndrome (reactive arthritis), which follows infections, the antigens involved are likely to be derived from intracellular microorganisms[citation needed]. There is, however, a possibility that CD4 T cells are involved in an aberrant way, since HLA-B27 appears to have a number of unusual properties, including possibly an ability to interact with T cell receptors in association with CD4 (usually only cytotoxic T lymphocytes with CD8 react with HLAB antigen as it is a MHC class 1 antigen).
There has been a longstanding claim that AS arises from a cross-reaction between HLA-B27 and antigens of the Klebsiella bacterial genus (Tiwana et al. 2001).[7] The problem with this idea is no such cross reactivity with B27 has been found (i.e. although antibody responses to Klebsiella may be increased, there is no antibody response to B27, so there seems to be no cross reactivity). Particular authorities argue elimination of the prime nutrients of Klebsiella (starches) would decrease antigenemia and improve the musculoskeletal symptoms. However, as Khan (2002) argues, evidence for a correlation between Klebsiella and AS is circumstantial so far, and the efficacy of low-starch diets has not yet been scientifically evaluated.[8] Studies on low-starch diet and AS could be difficult to fund, while new biologics developed by the pharmaceutical industry may demonstrate efficacy, as well as financial benefit to the industry (whereas changing the diet would not). A randomized controlled trial in Turkey demonstrated that 12-week therapy with moxifloxacin (which would kill Klebsiella) resulted in "significant and sustained improvement" in inflammatory symptoms in patients with ankylosing spondylitis.[9]
Toivanen (1999) found no support for the role of Klebsiella in the etiology of primary AS.[10]
Diagnosis
 Magnetic resonance images of sacroiliac joints, shown are T1-weighted semicoronal magnetic resonance images through the sacroiliac joints (a) before and (b) after intravenous contrast injection. Enhancement is seen at the right sacroiliac joint (arrow, left side of image), indicating active sacroiliitis. This patient had psoriatic arthritis, but similar changes can occur in ankylosing spondylitis.
Magnetic resonance images of sacroiliac joints, shown are T1-weighted semicoronal magnetic resonance images through the sacroiliac joints (a) before and (b) after intravenous contrast injection. Enhancement is seen at the right sacroiliac joint (arrow, left side of image), indicating active sacroiliitis. This patient had psoriatic arthritis, but similar changes can occur in ankylosing spondylitis.
There is no direct test to diagnose AS. A clinical examination, MRI and X-ray studies of the spine, which show characteristic spinal changes and sacroiliitis, and a simple genetic marker blood test are the major diagnostic tools. A drawback of X-ray diagnosis is the signs and symptoms of AS have usually been established as long as 8–10 years prior to X-ray-evident changes occurring on a plain film X-ray, which means a delay of as long as 10 years before adequate therapies can be introduced. Options for earlier diagnosis are tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the sacroiliac joints, but the reliability of these tests is still unclear. The Schober's test is a useful clinical measure of flexion of the lumbar spine performed during examination.[11]
During acute inflammatory periods, AS patients will sometimes show an increase in the blood concentration of C-reactive protein (CRP) and an increase in the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), but there are many with AS whose CRP and ESR rates do not increase, so normal CRP and ESR results do not always correspond with the amount of inflammation a person actually has. Sometimes people with AS have normal level results, yet are experiencing a significant amount of inflammation in their bodies.
Variations of the HLA-B gene increase the risk of developing ankylosing spondylitis, although it is not a diagnostic test. Those with the HLA-B27 variant are at a higher risk than the general population of developing the disorder. HLA-B27, demonstrated in a blood test, can occasionally help with diagnosis, but in itself is not diagnostic of AS in a person with back pain. Over 95% of people that have been diagnosed with AS are HLA-B27 positive, although this ratio varies from population to population (only 50% of African American patients with AS possess HLA-B27, and it is close to 80% among AS patients from Mediterranean countries). In early onset disease HLA-B7/B*2705 heterozygotes exhibited the highest risk for disease.[12]
In 2007, a collaborative effort by an international team of researchers in the U.K., Australia and the United States led to the discovery of two genes, ARTS1 and IL23R, that also contribute to the cause of AS. The findings were published in the November 2007 edition of Nature Genetics, a journal that emphasizes research on the genetic basis for common and complex diseases.[13] Together with HLA-B27, these two genes account for roughly 70 percent of the overall incidence of the disease.
The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), developed in Bath (UK), is an index designed to detect the inflammatory burden of active disease. The BASDAI can help to establish a diagnosis of AS in the presence of other factors such as HLA-B27 positivity, persistent buttock pain which resolves with exercise, and X-ray or MRI evident involvement of the sacroiliac joints. (See: "Diagnostic Tools", below)[14] It can be easily calculated and accurately assesses a patient's need for additional therapy; a patient with a score of four out of a possible 10 points while on adequate NSAID therapy is usually considered a good candidate for biologic therapy.
The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index (BASFI) is a functional index which can accurately assess a patient's functional impairment due to the disease, as well as improvements following therapy. (See: "Diagnostic Tools", below)[15] The BASFI is not usually used as a diagnostic tool, but rather as a tool to establish a patient's current baseline and subsequent response to therapy.
Treatment
No cure is known for AS, although treatments and medications are available to reduce symptoms and pain.[16][17]
Physical therapy and exercise, along with medication, are at the heart of therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. Physiotherapy and physical exercises are preceded by medical treatment to reduce the inflammation and pain, and are commonly followed by a physician. This way the movements will help in diminishing pain and stiffness, while exercise in an active inflammatory state would just make the pain worse. Normal occupations may be precluded by the symptoms of the disease.
Some may require the help of walking aids, such as a cane, to help assist in balance and relieve some pressure on affected joints while walking and standing. Many with AS find it very difficult to sit or stand for prolonged periods of time, which can be as little as 20 minutes; therefore, many need to alternate times of sitting and standing, as well as times of rest.
Medical professionals and experts in AS have speculated that maintaining good posture can reduce the likelihood of a fused or curved spine which occurs in a significant percentage of diagnosed persons.[18]
Medication
There are three major types of medications used to treat ankylosing spondylitis.
- Pain-relieving drugs come in two major classes. First, anti-inflammatory drugs, which include NSAIDs such as ibuprofen, phenylbutazone, diclofenac, indomethacin, naproxen and COX-2 inhibitors, which reduce inflammation and pain. Second, some patients require opioid analgesics, which are very effective in alleviating the type of chronic pain commonly experienced by those suffering from AS, especially in extended-release formulations.
- DMARDs such as cyclosporin, methotrexate, sulfasalazine, and corticosteroids, used to reduce the immune system response through immunosuppression;
- TNFα blockers (antagonists) such as etanercept, infliximab, golimumab and adalimumab[19] (also known as biologics), are indicated for the treatment of and are effective immunosuppressants in AS as in other autoimmune diseases.
TNFα blockers have been shown to be the most promising treatment, slowing the progress of AS in the majority of clinical cases, helping many patients receive a significant reduction, though not elimination, of their inflammation and pain. They have also been shown to be highly effective in treating not only the arthritis of the joints but also the spinal arthritis associated with AS. A drawback, besides the often high cost, is the fact these drugs increase the risk of infections. So, the protocol for any of the TNF-α blockers includes a test for tuberculosis (like Mantoux or Heaf) before starting treatment. In case of recurrent infections, even recurrent sore throats, the therapy may be suspended because of the involved immunosuppression. Patients taking the TNF medications are advised to limit their exposure to others who are or may be carrying a virus (such as a cold or influenza) or who may have a bacterial or fungal infection.
Tocilizumab, an IL-6 inhibitor currently approved for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, may also show promise for the treatment of ankylosing spondylitis.[20] Rituximab, a monoclonal antibody against CD20, has also reportedly been effective.[21] Both of these drugs require further investigation, but may one day be viable alternatives for patients who are not responsive to TNF-alpha antagonists.
Surgery
In severe cases of AS, surgery can be an option in the form of joint replacements, particularly in the knees and hips. Surgical correction is also possible for those with severe flexion deformities (severe downward curvature) of the spine, particularly in the neck, although this procedure is considered very risky.
In addition, AS can have some manifestations which make anaesthesia more complex.
Changes in the upper airway can lead to difficulties in intubating the airway, spinal and epidural anaesthesia may be difficult owing to calcification of ligaments, and a small number have aortic regurgitation. The stiffness of the thoracic ribs results in ventilation being mainly diaphragm-driven, so there may be a decrease in pulmonary function.
Physical therapy
Some of the therapies that have been shown to benefit AS patients include:
- Physical therapy/osteopathy/physiotherapy, shown to be of great benefit to AS patients;
- Swimming, one of the preferred exercises since it involves all muscles and joints in a low-impact, buoyant environment;
- Slow movement muscle extending exercises like stretching, yoga, climbing, t'ai chi, Pilates method, etc.
Moderate-to-high impact exercises like jogging are generally not recommended or recommended with restrictions due to the jarring of affected vertebrae that can worsen pain and stiffness in some patients.
Prognosis
AS can range from mild to progressively debilitating and from medically controlled to refractive. Some have times of active inflammation followed by times of remission, while others never have times of remission and have acute inflammation and pain.
Unattended cases of AS accompanied by dactylitis or enthesitis, especially when spine inflammation is not yet active, may result in a misdiagnosis of normal rheumatism. In a long-term undiagnosed period, osteopenia or osteoporosis of the AP spine may occur, causing eventual compression fractures and a back "hump". Typical signs of progressed AS are the visible formation of syndesmophytes on X-rays and abnormal bone outgrowths similar to osteophytes affecting the spine. The fusion of the vertebrae paresthesia is a complication due to the inflammation of the tissue surrounding nerves.
Organs commonly affected by AS, other than the axial spine and other joints, are the heart, lungs, eyes, colon, and kidneys. Other complications are aortic regurgitation, Achilles tendinitis, AV node block and amyloidosis.[22] Owing to lung fibrosis, chest X-rays may show apical fibrosis, while pulmonary function testing may reveal a restrictive lung defect. Very rare complications involve neurologic conditions such as the cauda equina syndrome.[22][23]
Factors that may affect recovery
Prognosis may not be favorable if the following symptoms continue:
- Hip involvement
- Plus 3 of the following in the first 2 years of disease:
- ESR >30 mm/h
- Unresponsive to NSAIDs
- Limitation of lumbar spine
- Sausage-like fingers or toes
- Oligoarthritis
- Onset <16 years old
Epidemiology
Three men are diagnosed with AS for every one woman; the overall prevalence is 0.25%. Many rheumatologists believe the number of women with AS is underdiagnosed, as most women tend to experience milder symptoms.[5]
History
AS has been suggested as the first recognized disease which was different from rheumatoid arthritis by Galen as early as the second century A.D.;[24] however, skeletal evidence of the disease (ossification of joints and entheses primarily of the axial skeleton, known as "bamboo spine") was first discovered in an archaeological dig that unearthed the skeletal remains of a 5000-year–old Egyptian mummy with evidence of bamboo spine.[25]
The anatomist and surgeon Realdo Colombo described what could have been the disease in 1559,[26] and the first account of pathologic changes to the skeleton possibly associated with AS was published in 1691 by Bernard Connor.[27] In 1818, Benjamin Brodie became the first physician to document a patient believed to have active AS who also had accompanying iritis.[28]
In 1858, David Tucker published a small booklet which clearly described a patient, Leonard Trask, who suffered from severe spinal deformity subsequent to AS.[29] In 1833, Trask fell from a horse, exacerbating the condition and resulting in severe deformity. Tucker reported:
“ It was not until he [Trask] had exercised for some time that he could perform any labor.... {H]is neck and back have continued to curve drawing his head downward on his breast. ” This account became the first documented case of AS in the United States, owing to its indisputable description of inflammatory disease characteristics of AS and the hallmark of deforming injury in AS.
It was not until the late nineteenth century, however, when the neurophysiologist Vladimir Bekhterev of Russia in 1893,[30] Adolph Strümpell of Germany in 1897,[31] and Pierre Marie of France in 1898[32] were the first to give adequate descriptions which permitted an accurate diagnosis of AS prior to severe spinal deformity. For this reason, AS is also known as Bechterew Disease or Marie–Strümpell Disease.
Research
The majority of patients with AS exhibit the HLA-B27 antigen and high levels of immunoglobulin A (IgA) in the blood. The HLA-B27 antigen is also expressed by Klebsiella bacteria, which are found in high levels in the feces of AS patients. A theory suggests the presence of the bacteria may be a trigger of the disease, and reducing the amount of starch in the diet (which these bacteria require to grow) may be of benefit to AS patients. A test of this diet resulted in reduced symptoms and inflammation in patients with AS as well as IgA levels in individuals with and without AS.[33] Further research is required to determine if diet changes may have a clinical effect on the course of the disease. While there are anecdotal accounts from people who have reduced their symptoms of inflammation and pain by using a low starch diet, the efficacy has not been confirmed by a clinical study.[34]
See also
- NIAMS, the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases
- SAA, Spondylitis Association of America
- AF, Arthritis Foundation
References
- ^ "Ankylosing Spondylitis: MedlinePlus". U.S. National Library of Medicine. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ankylosingspondylitis.html. Retrieved 2011-04-26.
- ^ Jiménez-Balderas FJ, Mintz G. (1993). "Ankylosing spondylitis: clinical course in women and men". J Rheumatol 20 (12): 2069–72. PMID 7516975.
- ^ a b Porter, Robert; Beers, Mark H.; Berkow, Robert (2006). The Merck manual of diagnosis and therapy. Rahway, NJ: Merck Research Laboratories. p. 290. ISBN 0-911910-18-2.
- ^ a b Feldtkeller, E.; Khan, M.; Van Der Heijde, D.; Van Der Linden, S.; Braun, J. (2003). "Age at disease onset and diagnosis delay in HLA-B27 negative vs. Positive patients with ankylosing spondylitis". Rheumatology international 23 (2): 61–66. doi:10.1007/s00296-002-0237-4. PMID 12634937.
- ^ a b "Arthritis Research Campaign - Ankylosing Spondylitis Case History". Arthritis Research Campaign. 2009. http://www.arc.org.uk/arthinfo/patpubs/6001/6001.asp. Retrieved 2009-08-25.
- ^ Reveille JD (2006). "Major histocompatibility genes and ankylosing spondylitis". Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology 20 (3): 601–609. doi:10.1016/j.berh.2006.03.004. PMID 16777585.
- ^ Tiwana H, Natt R, Benitez-Brito R, Shah S, Wilson C, Bridger S, Harbord M, Sarner M, Ebringer A (2001). "Correlation between the immune responses to collagens type I, III, IV and V and Klebsiella pneumoniae in patients with Crohn's disease and ankylosing spondylitis". Rheumatology (Oxford) 40 (1): 15–23. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/40.1.15. PMID 11157137.
- ^ Khan MA. (2002). Ankylosing spondylitis: The facts. Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-263282-5.
- ^ Ogrendik, M (2007). "Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis with moxifloxacin.". Southern medical journal 100 (4): 366–70. PMID 17458395.
- ^ Toivanen P, Hansen D, Mestre F, Lehtonen L, Vaahtovuo J, Vehma M, Möttönen T, Saario R, Luukkainen R, Nissilä M (1 September 1999). "Somatic serogroups, capsular types, and species of fecal Klebsiella in patients with ankylosing spondylitis". J Clin Microbiol 37 (9): 2808–12. PMC 85385. PMID 10449457. http://jcm.asm.org/cgi/content/full/37/9/2808?view=long&pmid=10449457.
- ^ Thomas E, Silman AJ, Papageorgiou AC, Macfarlane GJ, Croft PR. (1998). "Association between measures of spinal mobility and low back pain. An analysis of new attenders in primary care". Spine 23 (2): 343–7. doi:10.1097/00007632-199802010-00011. PMID 9507623.
- ^ Harjacek M, Margetić T, Kerhin-Brkljacić V, Martinez N, Grubić Z (2008). "HLA-B*27/HLA-B*07 in combination with D6S273-134 allele is associated with increased susceptibility to juvenile spondyloarthropathies". Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 26 (3): 498–504. PMID 18578977.
- ^ Brionez TF, Reveille JD (July 2008). "The contribution of genes outside the major histocompatibility complex to susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis". Curr Opin Rheumatol 20 (4): 384–91. doi:10.1097/BOR.0b013e32830460fe. PMID 18525349.
- ^ Garrett S, Jenkinson T, Kennedy L, Whitelock H, Gaisford P, Calin A (1994). "A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index". J Rheumatol 21 (12): 2286–91. PMID 7699630.
- ^ Calin A, Garrett S, Whitelock H, Kennedy L, O'Hea J, Mallorie P, Jenkinson T (1994). "A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index". J Rheumatol 21 (12): 2281–5. PMID 7699629.
- ^ Toivanen A, Möttönen T. (1998). "Ankylosing spondylitis: current approaches to treatment". BioDrugs 10 (3): 193–200. doi:10.2165/00063030-199810030-00003. PMID 18020595.
- ^ Williams RO, Paleolog E, Feldmann M. (2007). "Cytokine inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases". Curr Opin Pharmacol 7 (4): 412–7. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2007.06.001. PMID 17627887.
- ^ "Ankylosing Spondylitis, Treatment Options". Arthritis Foundation (arthritis.org). 2010. http://www.arthritis.org/disease-center.php?disease_id=2&df=treatments. Retrieved August 2010
- ^ "Ankylosing Spondylitis". Humira (adalimumab) drug information website. Abbott Laboratories. http://www.humira.com/as/default.aspx. Retrieved 29 October 2011.
- ^ Henes, Joerg; Horger, Guenaydin, Kanz, Koetter (February 2010). "Mixed response to tocilizumab for ankylosing spondylitis". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 69 (12): 2217–2218. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.126706. PMID 20851032.
- ^ Rodriguez-Escalera, C.; Fernandez-Nebro, A. (2008). "The use of rituximab to treat a patient with ankylosing spondylitis and hepatitis B". Rheumatology 47 (11): 1732–1733. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/ken362. PMID 18786966.
- ^ a b Alpert, Joseph S. (2006). The AHA Clinical Cardiac Consult. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0781764904.
- ^ Nicholas U. Ahn, Uri M. Ahn, Elizabeth S. Garrett et al. (2001). "Cauda Equina Syndrome in AS (The CES-AS Syndrome): Meta-analysis of outcomes after medical and surgical treatments". J of Spinal Disorders 14 (5): 427–433. doi:10.1097/00002517-200110000-00009. PMID 11586143.
- ^ Dieppe P (1988). "Did Galen describe rheumatoid arthritis?". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 47 (1): 84–87. doi:10.1136/ard.47.1.84-b. PMC 1003452. PMID 3278697. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1003452.
- ^ Calin A (April 1985). "Ankylosing spondylitis". Clin Rheum Dis 11 (1): 41–60. PMID 3158467.
- ^ Benoist M (April 1995). "Pierre Marie. Pioneer investigator in ankylosing spondylitis". Spine 20 (7): 849–52. doi:10.1097/00007632-199504000-00022. PMID 7701402.
- ^ BLUMBERG BS (December 1958). "Bernard Connor's description of the pathology of ankylosing spondylitis". Arthritis Rheum. 1 (6): 553–63. doi:10.1002/art.1780010609. PMID 13607268.
- ^ Leden I (1994). "Did Bechterew describe the disease which is named after him? A question raised due to the centennial of his primary report". Scand J Rheumatol 23 (1): 42–5. doi:10.3109/03009749409102134. PMID 8108667.
- ^ "Life and sufferings of Leonard Trask" (PDF). Ankylosing Spondylitis Information Matrix.. http://www.HLAB27.com.com/members/life%20and%20sufferings%20of%20leonard%20trask.pdf.
- ^ Bechterew W. (1893). "Steifigkeit der Wirbelsaule und ihre Verkrummung als besondere Erkrankungsform". Neurol Centralbl 12: 426–434.
- ^ Strumpell A. (1897). "Bemerkung uber die chronische ankylosirende Entzundung der Wirbelsaule und der Huftgelenke". Dtsch Z Nervenheilkd 11 (3–4): 338–342. doi:10.1007/BF01674127.
- ^ Marie P. (1898). "Sur la spondylose rhizomelique". Rev Med 18: 285–315.
- ^ Ebringer A, Wilson C (Jan 15 1996). "The use of a low starch diet in the treatment of patients suffering from ankylosing spondylitis". Clin Rheumatol 15 Suppl 1: 62–66. PMID 8835506.
- ^ No/Low Starch Diet Success Stories
External links
- Ankylosing spondylitis at the Open Directory Project
- NASS - National Anklosying Spondylitis Society
Diagnostic tools
- Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index Calculator (BASDAI)
- Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index Calculator (BASFI)
Musculoskeletal disorders: Arthropathies (M00–M19, 711–719) Arthritis
(monoarthritis/
polyarthritis)NoninfectiousRheumatoid arthritis: Juvenile idiopathic arthritis · Adult-onset Still's disease · Felty's syndromeNoninflammatoryOther hemorrhage (Hemarthrosis) · pain (Arthralgia) · Osteophyte · villonodular synovitis (Pigmented villonodular synovitis) · Joint stiffnessM: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Dorsopathies / spinal disease (M40–M54, 720–724, 737) Deforming dorsopathies OtherSpondylopathy inflammatory: Spondylitis (Ankylosing spondylitis) · Sacroiliitis · Discitis · Spondylodiscitis · Pott diseaseBack pain Intervertebral disc disorder M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Rheumatology
- Arthritis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Autoimmune diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.