- Neurosurgery
-
Neurosurgery 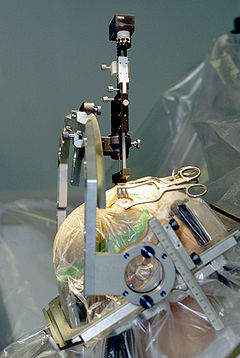
Occupation Activity sectors Surgery Description Education required Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine (U.S. Only), Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery For the journal, see Neurosurgery (journal).Neurosurgery (or neurological surgery) is the medical specialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spine, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and extra-cranial cerebrovascular system.[1][2]
Contents
Education and training
In the US
In the United States, a neurosurgeon must generally complete four years of college, four years of medical school, a year-long internship (PGY-1) that is usually affiliated with their residency program, and five to six years of neurosurgery residency (PGY-2-7).[3] Most, but not all, residency programs have some component of basic science or clinical research. Neurosurgeons may pursue an additional training in a fellowship, after residency or in some cases, as a senior resident. These fellowships include pediatric neurosurgery, trauma/neurocritical care, functional and stereotactic surgery, surgical neuro-oncology, radiosurgery, neurovascular surgery, Interventional neuroradiology, peripheral nerve, spine surgery and skull base surgery.[4] Neurosurgeons can also pursue fellowship training in neuropathology and neuro-ophthalmology.
In the UK
In the UK students must earn A*- C Grades at GCSE (General Certificate of Secondary Education), then they must also achieve A*- C at A levels in Chemistry with at least one other Science or Maths. Also a UKCAT (UK Clinical Aptitude Test) or BMAT (BioMedical Admissions Test) can be used to gain access into some Medical Schools. Students have to study medicine for 5 years and achieve an MBBS qualification (Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery). Then the student must perform Foundation training lasting normally 2 years, this is a paid training job in a hospital or clinical situation setting covers a range of Medical specialties including Surgery. Then students enter the neurosurgical pathway. Unlike other surgical specialties it currently has its own independent training pathway which takes around 8 years (ST1-8) before being able to sit consultant exams.[5]
Neurosurgical methods
Neurosurgery Intervention ICD-10-PCS 00-01 ICD-9-CM 01–05 MeSH D019635 OPS-301 code: 5-01...5-05 Neuroradiology methods are used in modern neurosurgical diagnosis and treatment, including computer assisted imaging computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), positron emission tomography (PET), magnetoencephalography (MEG), and the stereotactic surgery. Some neurosurgical procedures involve the use of MRI and functional MRI intraoperatively.
Microsurgery is utilized in many aspects of neurological surgery. Microvascular anastomosis are required when EC-IC surgery is performed. The clipping of aneurysms is performed using a microscope. Minimally invasive spine surgery utilizes these techniques. Procedures such as microdiscectomy, laminectomy, and artificial discs rely on microsurgery.[6]
Minimally invasive endoscopic surgery is utilized by neurosurgeons. Techniques such as endoscopic endonasal surgery is used for pituitary tumors, craniopharyngiomas, chordomas, and the repair of cerebrospinal fluid leaks. Ventricular endoscopy is used for colloid cysts and neurocysticercosis. Endoscopic techniques can be used to assist in the evaculation of hematomas and trigeminal neuralgia. Repair of craniofacial disorders and disturbance of cerebrospinal fluid circulation is done by neurosurgeons, and depending on the situation, plastic surgeons. Conditions such as chiari malformation, craniosynostosis, and syringomyelia are treated. This is called cranioplasty.
Neurosurgeons are involved in Stereotactic Radiosurgery along with Radiation Oncologists for tumor and AVM[disambiguation needed
 ] treatment. Radiosurgical methods such as Gamma knife, Cyberknife and Novalis Shaped Beam Surgery are used.[7]
] treatment. Radiosurgical methods such as Gamma knife, Cyberknife and Novalis Shaped Beam Surgery are used.[7]Neurosurgeons have begun to utilize endovascular image guided procedures for the treatment of aneurysms, AVMs, carotid stenosis, strokes, and spinal malformations, and vasospasms. Also, nonvascular procedures such as Vertoplasty and Kyphoplasty are used by neurosurgeons. Techniques such as angioplasty, stenting, clot retrieval, embolization, and diagnostic angiography are utilized.[8]
Conditions
Other conditions treated by neurosurgeons include:
- Spinal disc herniation
- Cervical spinal stenosis and Lumbar spinal stenosis
- Hydrocephalus
- Head trauma (brain hemorrhages, skull fractures, etc.)
- Spinal cord trauma
- Traumatic injuries of peripheral nerves
- Infections
- Tumours of the spine, spinal cord and peripheral nerves
- Intracerebral hemorrhage, such as subarachnoid hemorrhage, intraparenchymal, and intraventricular hemorrhages
- Some forms of drug-resistant epilepsy
- Some forms of movement disorders (advanced Parkinson's disease, chorea) – this involves the use of specially developed minimally invasive stereotactic techniques (functional, stereotactic neurosurgery) such as ablative surgery and deep brain stimulation surgery
- Intractable pain of cancer or trauma patients and cranial/peripheral nerve pain
- Some forms of intractable psychiatric disorders
- Vascular malformations (i.e., arteriovenous malformations, venous angiomas, cavernous angiomas, capillary telangectasias) of the brain and spinal cord
- Peripheral neuropathies such as carpal tunnel syndrome and ulnar neuropathy
- Moyamoya disease
See also
- Gazi Yasargil – Known as the father of microneurosurgery
- Harvey Cushing – Known as the father of neurosurgery
- Walter Dandy – Known as one of the founding fathers of neurosurgery
- Wilder Penfield – Known as one of the founding fathers of neurosurgery, and pioneer of epilepsy neurosurgery
- Lars Leksell – Swedish Neurosurgeon who developed the Gamma Knife
- Benjamin Carson – Renowned pediatric neurosurgeon at Johns Hopkins Hospital, pioneer in hemispherectomy, and pioneer in the separation of conjoined twins, joined at the head
- John R. Adler – Stanford University neurosurgeon who invented the CyberKnife
- Wirginia Maixner - Pediatric Neurosurgeon at Melbourne's Royal Children's Hospital. Primarily known for separating conjoined Bangladeshi twins, Trishna and Krishna.
- Sid Watkins – World renowned neurosurgeon who served for 26 years as the Formula One Safety and Medical Delegate (race doctor)
- American Association of Neurological Surgeons
- Congress of Neurological Surgeons
References
- ^ http://www.casattexas.com/NEURObody.cfm
- ^ http://www.neurosurgerytoday.org/
- ^ http://www.abns.org/content/primary_certification_process.asp
- ^ http://www.aans.org/medical_students/questions.asp
- ^ "The society of british neurological surgeons". http://www.sbns.org.uk/site/1090/default.aspx. Retrieved 11/03/2011.
- ^ http://www.neurosurgery.org/cybermuseum/microneurohall/arhoton.html
- ^ http://neurosurgery.ucla.edu/body.cfm?id=952
- ^ http://www.mir.wustl.edu/neurorad/internal.asp?NavID=74
Surgery, Nervous system: neurosurgical and other procedures (ICD-9-CM V3 01–05+89.1, ICD-10-PCS 00-01) Skull CNS thalamus and globus pallidus: Thalamotomy · Thalamic stimulator · Pallidotomy
ventricular system: Ventriculostomy · Suboccipital puncture · Intracranial pressure monitoring
cerebrum: Psychosurgery (Lobotomy, Bilateral cingulotomy) · Hemispherectomy · Anterior temporal lobectomy
pituitary: Hypophysectomy
hippocampus: Amygdalohippocampectomy
Brain biopsyCerebral meningesSpinal cord and roots (Cordotomy, Rhizotomy)
Vertebrae and intervertebral discs: see Template:Bone, cartilage, and joint proceduresCT head · Cerebral angiography · Pneumoencephalography · Echoencephalography/Transcranial doppler · MRI of brain and brain stem · Brain PET · SPECT of brain · MyelographyDiagnosticPNS Sympathetic nerves or gangliaNerves (general)DiagnosticNeuroscience Affective neuroscience · Behavioral neurology · Behavioral genetics · Behavioral neuroscience · Brain–computer interface · Chronobiology · Clinical neurophysiology · Clinical neuroscience · Cognitive neuroscience · Computational neuroscience · Connectomics · Evolution of nervous systems · Imaging genetics · Integrative neuroscience · Molecular cellular cognition · Neural development · Neural engineering · Neural network (both artificial and biological) · Neural signal processing · Neural tissue regeneration · Neuroanatomy · Neurobioengineering · Neurobiology · Neurobiotics · Neurocardiology · Neurochemistry · Neurochip · Neurodegeneration · Neurodevelopmental disorders · Neurodiversity · Neuroembryology · Neuroendocrinology · Neuroepidemiology · Neuroethics · Neuroethology · Neurogastroenterology · Neurogenetics · Neuroimaging · Neuroimmunology · Neuroinformatics · Neurointensive care · Neurolinguistics · Neurology · Neurometrics · Neuromodulation · Neuromonitoring · Neurooncology · Neuro-ophthalmology · Neuropathology · Neuropharmacology · Neurophilosophy · Neurophysics · Neurophysiology · Neuroplasticity · Neuroprosthetics · Neuropsychiatry · Neuropsychology · Neuroradiology · Neurorehabilitation · Neurorobotics · Neurosurgery · Neurotechnology · Neurotology · Neurotoxin · Neurotransmitter · Neurovirology · Psychiatry · Sensory neuroscience · Social neuroscience · Systems neuroscience
Categories:- Neurosurgery
- Surgical specialties
- Medical specialties
- Medical doctors by specialty
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
