- Peripheral nerve
-
This article is about the part of the nervous system. For other uses, see nerve (disambiguation).
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons (the long, slender projections of neurons). A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system. In the central nervous system, the analogous structures are known as tracts.[1][2] Neurons are sometimes called nerve cells, though this term is potentially misleading since many neurons do not form nerves, and nerves also include non-neuronal Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin.
Each nerve is a cordlike structure that contains many axons. These axons are often referred to as “fibres”. Within a nerve, each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. Finally, the entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium.
Contents
Anatomy
Nerves are categorized into three groups based on the direction that signals are conducted:
- Afferent nerves conduct signals from sensory neurons to the central nervous system, for example from the mechanoreceptors in skin.
- Efferent nerves conduct signals from the central nervous system along motor neurons to their target muscles and glands.
- Mixed nerves contain both afferent and efferent axons, and thus conduct both incoming sensory information and outgoing muscle commands in the same bundle.
Nerves can be categorized into two groups based on where they connect to the central nervous system:
- Spinal nerves innervate much of the body, and connect through the spinal column to the spinal cord. They are given letter-number designations according to the vertebra through which they connect to the spinal column.
- Cranial nerves innervate parts of the head, and connect directly to the brain (especially to the brainstem). They are typically assigned Roman numerals from 1 to 12, although cranial nerve zero is sometimes included. In addition, cranial nerves have descriptive names.
Each nerve is covered externally by a dense sheath of connective tissue, the epineurium. Underlying this is a layer of flat cells, the perineurium, which forms a complete sleeve around a bundle of axons. Perineurial septae extend into the nerve and subdivide it into several bundles of fibres. Surrounding each such fibre is the endoneurium. This forms an unbroken tube which extends from the surface of the spinal cord to the level at which the axon synapses with its muscle fibers, or ends in sensory receptors. The endoneurium consists of an inner sleeve of material called the glycocalyx and an outer, delicate, meshwork of collagen fibres. Nerves are bundled along with blood vessels, since the neurons of a nerve have fairly high energy requirements. Within the endoneurium, the individual nerve fibres are surrounded by a low protein liquid called endoneurial fluid. The endoneurium has properties analogous to the blood-brain barrier, in that it prevents certain molecules from crossing from the blood into the endoneurial fluid. In this respect, endoneurial fluid is similar to cerebro-spinal fluid in the central nervous system. During the development of nerve edema from nerve irritation or (injury), the amount of endoneurial fluid may increase at the site of irritation. This increase in fluid can be visualized using magnetic resonance neurography, and thus MR neurography can identify nerve irritation and/or injury.
Physiology
A nerve conveys information in the form of electrochemical impulses (known as nerve impulses or action potentials) carried by the individual neurons that make up the nerve. These impulses are extremely fast, with some myelinated neurons conducting at speeds up to 120 m/s. The impulses travel from one neuron to another by crossing a synapse, the message is converted from electrical to chemical and then back to electrical.[1][2]
Nerves can be categorized into two groups based on function:
- Sensory nerves conduct sensory information from their receptors to the central nervous system, where the information is then processed. Thus they are synonymous with afferent nerves.
- Motor nerves conduct signals from the central nervous system to muscles. Thus they are synonymous with efferent nerves.[1][2]
Clinical importance
Damage to nerves can be caused by physical injury or swelling (e.g. carpal tunnel syndrome), autoimmune diseases (e.g. Guillain-Barré syndrome), infection (neuritis), diabetes or failure of the blood vessels surrounding the nerve. A pinched nerve occurs when pressure is placed on a nerve, usually from swelling due to an injury or pregnancy. Nerve damage or pinched nerves are usually accompanied by pain, numbness, weakness, or paralysis. Patients may feel these symptoms in areas far from the actual site of damage, a phenomenon called referred pain. Referred pain occurs because when a nerve is damaged, signalling is defective from all parts of the area from which the nerve receives input, not just the site of the damage. Neurologists usually diagnose disorders of the nerves by a physical examination, including the testing of reflexes, walking and other directed movements, muscle weakness, proprioception, and the sense of touch. This initial exam can be followed with tests such as nerve conduction study and electromyography (EMG).
Cancer
Cancer can spread along nerves; this is known as perineural spread and often is associated with a worse prognosis.
Nerve Growth & stimulation
Nerve growth normally ends in adolescence, but can be re-stimulated with a molecular mechanism known as "Notch signaling", working on a Notch receptor:
Yale Study Shows Way To Re-Stimulate Brain Cell Growth ScienceDaily (Oct. 22, 1999) — Results Could Boost Understanding Of Alzheimer's, Other Brain Disorders http://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/1999/10/991022005127.htm
See also
- Nerve fiber
- Peripheral nerve injury (Nerve injury)
- Connective tissue in the peripheral nervous system
- Neuropathy
- Peripheral nerve injury classification
- Nervous system
- Dermatome (Anatomy)
Additional images
References
Human systems and organs TA 2–4:
MSBone (Carpus · Collar bone (clavicle) · Thigh bone (femur) · Fibula · Humerus · Mandible · Metacarpus · Metatarsus · Ossicles · Patella · Phalanges · Radius · Skull (cranium) · Tarsus · Tibia · Ulna · Rib · Vertebra · Pelvis · Sternum) · CartilageTA 5–11:
splanchnic/
viscusmostly
Thoracicmostly
AbdominopelvicDigestive system+
adnexaMouth (Salivary gland, Tongue) · upper GI (Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx, Esophagus, Stomach) · lower GI (Small intestine, Appendix, Colon, Rectum, Anus) · accessory (Liver, Biliary tract, Pancreas)TA 12–16 Blood
(Non-TA)General anatomy: systems and organs, regional anatomy, planes and lines, superficial axial anatomy, superficial anatomy of limbs Nerves: spinal nerves (TA A14.2, GA 9.916) Cervical (8) Thoracic (12) T1, T2, T3, T4, T5, T6, T7, T8, T9, T10, T11, T12
anterior (Intercostal, Intercostobrachial – T2, Thoraco-abdominal nerves – T7–T11, Subcostal – T12) – posterior (Posterior branches of thoracic nerves)Lumbar (5)
anterior (Lumbar plexus, Lumbosacral trunk) · posterior (Posterior branches of the lumbar nerves, Superior cluneal L1–L3)Sacral (5) Coccygeal (1) Nerves of head and neck: the cranial nerves and nuclei (TA A14.2.01, GA 9.855) olfactory (AON->I) optic (LGN->II) oculomotor
(ON, EWN->III)trochlear (TN->IV) no significant branchestrigeminal
(PSN, TSN, MN, TMN->V)abducens (AN->VI) no significant branchesfacial (FMN, SN, SSN->VII) near origininside
facial canalvestibulocochlear
(VN, CN->VIII)glossopharyngeal
(NA, ISN, SN->IX)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossavagus
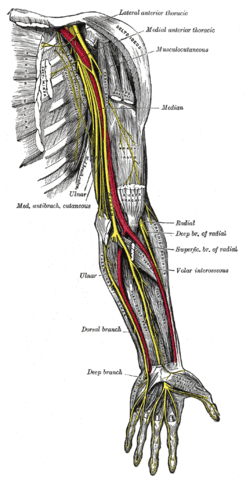
(NA, DNVN, SN->X)before jugular fossaafter jugular fossaaccessory (NA, SAN->XI) hypoglossal (HN->XII) Nerves of head and neck: the cervical plexus (C1–C4) (TA A14.2.02, GA 9.926) superficial deep Nerves of upper limbs (primarily): the brachial plexus (C5–T1) (TA A14.2.03, GA 9.930) Supraclavicular Infraclavicular cutaneous: medial cutaneous of forearm · medial cutaneous of arm
ulnar: muscular · palmar · dorsal (dorsal digital nerves) · superficial (common palmar digital, proper palmar digital) · deep
median/medial root: see abovesubscapular (upper, lower) · thoracodorsal
axillary (superior lateral cutaneous of arm)
radial: muscular · cutaneous (posterior of arm, inferior lateral of arm, posterior of forearm) · superficial (dorsal digital nerves) · deep (posterior interosseous)Other Nerves of lower limbs and lower torso: the lumbosacral plexus (L1–Co) (TA A14.2.05–07, GA 9.948) lumbar
plexus
(L1–L4)sacral
plexus
(L4–S4)othercoccygeal
plexus
(S4–Co)Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.