- Tibia
-
This article is about the vertebrate bone. For other uses, see Tibia (disambiguation).
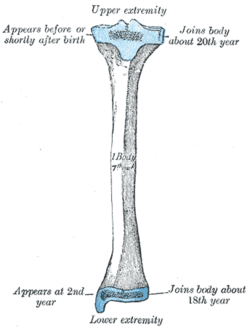
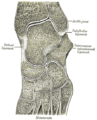
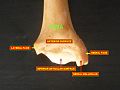
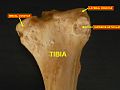
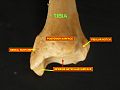
Bone: Tibia Plan of ossification of the tibia. From three centers. Gray's subject #61 256 MeSH Tibia The tibia (English pronunciation: /ˈtɪbɪə/), shinbone, or shankbone is the larger and stronger of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula), and connects the knee with the ankle bones. The tibia is named for the Greek aulos flute, also known as a tibia. It is commonly recognized as the strongest weight bearing bone in the body.
Contents
In humans
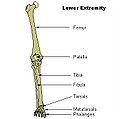
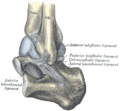
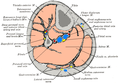
The tibia is found next to the fibula. It is the second largest bone in the human body, the largest being the femur. The tibia articulates with the femur superiorly, the fibula laterally and with the talus inferiorly.
Sex differences
In the male, its direction is vertical, and parallel with the bone of the opposite side. In the female, it has a slightly oblique direction downward and laterally, to compensate for the greater obliqueness of the femur. Studies are inconclusive, however.
Structure
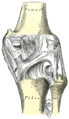
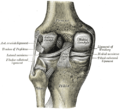
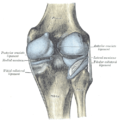
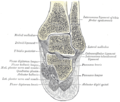
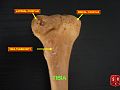
It is prismoid in form, expanded above, where it enters into the knee-joint, contracted in the lower third, and again enlarged but to a lesser extent towards the ankle joint.
The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end of the fibula, and a rough concave surface on the lateral side of the tibia. The tibia is connected to the fibula by an interosseous membrane, forming a type of joint called a syndesmosis. The forward flat part of the tibia is called the fibia, often confused with the fibula.
Blood supply
The tibia derives its arterial blood supply from two sources:[1]
- the nutrient artery (main source)
- periosteal vessels derived from the anterior tibial artery
Strength
The tibia has been modeled as taking an axial force during walking that is up to 4.7 bodyweight. Its bending moment in the sagittal plane in the late stance phase is up to 71.6 bodyweight times millimetre.[2]
In other animals
The structure of the tibia in most other tetrapods is essentially similar to that in humans. The tuberosity of the tibia, a crest to which the patellar ligament attaches in mammals, is instead the insertion point for the tendon of the quadriceps muscle in reptiles, birds, and amphibians, which have no patella.[3]
Additional images
-
Bones of the right leg. Posterior surface.
See also
- Bone terminology
- Terms for anatomical location
- Ossification of tibia
- Upper extremity of tibia
- Body of tibia
- Lower extremity of tibia
- Shin Splints
- Squatting facets
References
- ^ Nelson G, Kelly P, Peterson L, Janes J (1960). "Blood supply of the human tibia". J Bone Joint Surg Am 42-A: 625–36. PMID 13854090.
- ^ Wehner T, Claes L, Simon U. (2009). Internal loads in the human tibia during gait. Clin Biomech 24(3):299-302. PMID 19185959 doi:10.1016/j.clinbiomech.2009.01.002
- ^ Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. p. 205. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of lower limbs (TA A02.5.04–18, GA 2.242–277) Femur head (fovea) · neck · greater trochanter (trochanteric fossa) · lesser trochanter · intertrochanteric line · intertrochanteric crest · quadrate tubercleadductor tubercle · patellar surface · epicondyles (lateral, medial) · condyles (lateral, medial) · intercondylar fossaCrus TibiaOtherpatella (apex of patella)Foot calcaneus (sustentaculum tali, trochlear process) · talus (body, neck, head) · navicular · cuboid · cuneiform (medial, intermediate, lateral)OtherCategories:- Bones of the lower limb
- Long bones
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.