- Calcaneus
-
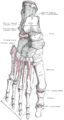
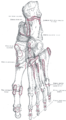
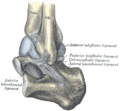
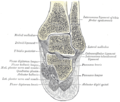
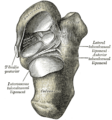
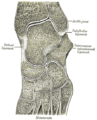
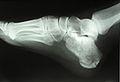
Bone: Calcaneus Subtalar Joint Left calcaneus, lateral surface. Latin Os calcis Gray's subject #63 263 MeSH Calcaneus In humans, the calcaneus (from the Latin calcaneum, meaning heel[1]) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitute the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
Contents
Human anatomy
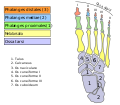
In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. In it, several important structures can be distinguished:[2]
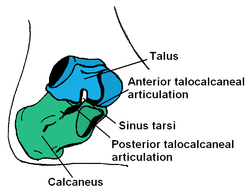
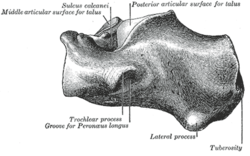
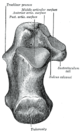
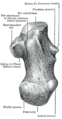
The posterior half of the bone is the tuber calcanei. On its lower edge on either sides are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the abductor hallucis and abductor digit minimi). The Achilles tendon is inserted into a roughened area on its superior side, the cuboid bone articulates with its anterior side, and on its superior side are three articular surfaces for the articulation with the talus bone. Between these superior articulations and the equivalents on the talus is the tarsal sinus (a canal occupied by the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament). On the medial side of the bone, below the middle talar facet, is the sustentaculum tali (which serves for the attachment of several other ligaments). On the lateral side is commonly a tubercle called the peroneal trochlea, under which is a groove for the tendon of the peroneus longus. [2]
In the calcaneus, an ossification center is developed during the 4-7th intrauterine month. [2]
With normal axial alignment in the hindfoot, the axes of the tibia and calcaneus lie on a vertical line (pes rectus). If the calcaneal axis is turned medially the foot is in an everted position (pes valgus), and if it is turned laterally the foot is in an inverted position (pes varus). [3]
Horse
The calcaneus has two articulations, being part of the Proximal intertarsal joint and the Talocalcaneal joint. As in humans it is the insertion of the gastrocnemius and superficial digital flexor tendons. The point of the calcaneus is covered by the calcanean bursa.
See also
- Calcar
- Bone terminology
- Calcaneal fracture, also known as Lover's fracture and Don Juan fracture
- Terms for anatomical location
Additional images
Notes
References
- Platzer, Werner (2004). Color Atlas of Human Anatomy, Vol. 1: Locomotor System (5th ed.). Thieme. ISBN 3-13-533305-1.
- Thieme Atlas of Anatomy: General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System. Thieme. 2006. ISBN 1-58890-419-9.
External links
- lljoints at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (posterioranklejoint)
Bones of lower limbs (TA A02.5.04–18, GA 2.242–277) Femur head (fovea) · neck · greater trochanter (trochanteric fossa) · lesser trochanter · intertrochanteric line · intertrochanteric crest · quadrate tubercleadductor tubercle · patellar surface · epicondyles (lateral, medial) · condyles (lateral, medial) · intercondylar fossaCrus Otherpatella (apex of patella)Foot calcaneus (sustentaculum tali, trochlear process) · talus (body, neck, head) · navicular · cuboid · cuneiform (medial, intermediate, lateral)OtherCategories:- Bones of the lower limb
- Vertebrate anatomy
- Musculoskeletal system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.