- Cuboid bone
-
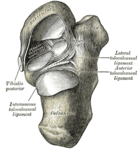
Bone: Cuboid bone The left cuboid. Antero-medial view. The left cuboid. Postero-lateral view Latin os cuboideum Gray's subject #63 269 MeSH Cuboid+Bone In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot.
Contents
Surfaces
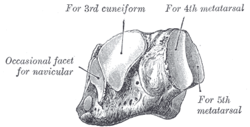
The dorsal surface, directed upward and lateralward, is rough, for the attachment of ligaments.
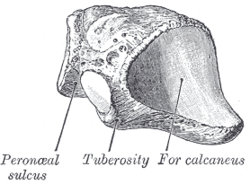
The plantar surface presents in front a deep groove, the peroneal sulcus, which runs obliquely forward and medialward; it lodges the tendon of the peroneus longus, and is bounded behind by a prominent ridge, to which the long plantar ligament is attached.
The ridge ends laterally in an eminence, the tuberosity, the surface of which presents an oval facet; on this facet glides the sesamoid bone or cartilage frequently found in the tendon of the peroneus longus. The surface of bone behind the groove is rough, for the attachment of the plantar calcaneocuboid ligament, a few fibers of the flexor hallucis brevis, and a fasciculus from the tendon of the tibialis posterior.
The lateral surface presents a deep notch formed by the commencement of the peroneal sulcus.
The posterior surface is smooth, triangular, and concavo-convex, for articulation with the anterior surface of the calcaneus (the calcaneocuboid joint); its infero-medial angle projects backward as a process which underlies and supports the anterior end of the calcaneus.
The anterior surface, of smaller size, but also irregularly triangular, is divided by a vertical ridge into two facets, forming the fourth and fifth tarsometatarsal joints: the medial facet, quadrilateral in form, articulates with the fourth metatarsal; the lateral, larger and more triangular, articulates with the fifth.
The medial surface is broad, irregularly quadrilateral, and presents at its middle and upper part a smooth oval facet, for articulation with the third cuneiform; and behind this (occasionally) a smaller facet, for articulation with the navicular bone; it is rough in the rest of its extent, for the attachment of strong interosseous ligaments.
Injuries
In a condition known as cuboid syndrome, the cuboid can be subluxated downward causing a swollen kind of ache along the central portion of the lateral border of the foot.
See also
- Bone terminology
- Terms for anatomical location
- Knucklebones (precursor of gaming dice)
Additional images
CuboidBones of the right foot. Plantar surface.Skeleton of foot. Lateral aspect.Talocalcaneal and talocalcaneonavicular articulations exposed from above by removing the talus.Oblique section of left intertarsal and tarsometatarsal articulations, showing the synovial cavities.Bones of foot, in German and LatinReferences
- ^ Gray's Anatomy, (See infobox.)
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of lower limbs (TA A02.5.04–18, GA 2.242–277) Femur head (fovea) · neck · greater trochanter (trochanteric fossa) · lesser trochanter · intertrochanteric line · intertrochanteric crest · quadrate tubercleadductor tubercle · patellar surface · epicondyles (lateral, medial) · condyles (lateral, medial) · intercondylar fossaCrus OtherFoot calcaneus (sustentaculum tali, trochlear process) · talus (body, neck, head) · navicular · cuboid · cuneiform (medial, intermediate, lateral)OtherCategories:- Musculoskeletal system stubs
- Bones of the lower limb
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.