- Nasopharynx
-
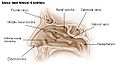
Nasopharynx 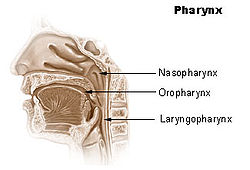
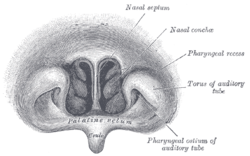
Front of nasal part of pharynx, as seen with the laryngoscope. Latin pars nasalis pharyngis Gray's subject #244 1141 Nerve maxillary nerve (pharyngeal nerve) MeSH Nasopharynx The nasopharynx (nasal part of the pharynx) is the uppermost part of the pharynx. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate;[1] it differs from the oral and laryngeal parts of the pharynx in that its cavity always remains patent (open).
Contents
Anterior
In front it communicates through the choanae with the nasal cavities.
Lateral
On its lateral wall is the pharyngeal ostium of the auditory tube, somewhat triangular in shape, and bounded behind by a firm prominence, the torus tubarius or cushion, caused by the medial end of the cartilage of the tube which elevates the mucous membrane.
Two folds arise from the cartilaginous opening:
- vertical fold of mucous membrane, the salpingopharyngeal fold, stretches from the lower part of the torus; it contains the Salpingopharyngeus muscle.
- second and smaller fold, the salpingopalatine fold, stretches from the upper part of the torus to the palate; it contains the levator veli palatini muscle. The tensor veli palatini is lateral to the levator and does not contribute the fold, since the origin is deep to the cartilaginous opening.
Behind the ostium of the auditory tube is a deep recess, the pharyngeal recess (fossa of Rosenmüller).
Posterior
On the posterior wall is a prominence, best marked in childhood, produced by a mass of lymphoid tissue, which is known as the pharyngeal tonsil.
Above the pharyngeal tonsil, in the middle line, an irregular flask-shaped depression of the mucous membrane sometimes extends up as far as the basilar process of the occipital bone; it is known as the pharyngeal bursa.
Additional images
Notes and references
- ^ Clinical Head and Neck and Functional Neuroscience Course Notes, 2008-2009, Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences School of Medicine, Bethesda, Maryland
See also
- nasopharyngeal carcinoma - cancer of the nasopharynx
- Pharyngitis
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.Human systems and organs TA 2–4:
MSBone (Carpus · Collar bone (clavicle) · Thigh bone (femur) · Fibula · Humerus · Mandible · Metacarpus · Metatarsus · Ossicles · Patella · Phalanges · Radius · Skull (cranium) · Tarsus · Tibia · Ulna · Rib · Vertebra · Pelvis · Sternum) · CartilageTA 5–11:
splanchnic/
viscusMouth (Salivary gland, Tongue) · upper GI (Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx, Esophagus, Stomach) · lower GI (Small intestine, Appendix, Colon, Rectum, Anus) · accessory (Liver, Biliary tract, Pancreas)TA 12–16 Blood
(Non-TA)General anatomy: systems and organs, regional anatomy, planes and lines, superficial axial anatomy, superficial anatomy of limbs Head and neck, upper RT: Nose (TA A06.1, TH H3.05.01, GA 10.992) External nose Ala of nose
nasal cartilages (of the septum, Greater alar, Lesser alar, Lateral nasal, Accessory nasal, Vomeronasal)Nasal cavity OpeningsLateral wallNasal concha/meati: Superior nasal concha · Middle nasal concha · Inferior nasal concha · Superior nasal meatus · Middle nasal meatus · Inferior nasal meatus
Sphenoethmoidal recess · Ethmoid bulla · Agger nasi · Ethmoidal infundibulum · Semilunar hiatus · Maxillary hiatusMedial wallParanasal sinuses Naso-pharynx Categories:- Respiratory system stubs
- Head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.