- Oropharynx
-
Oropharynx 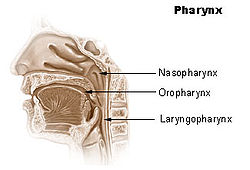
Pharynx 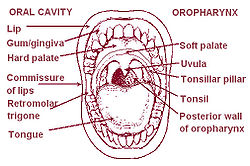
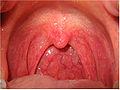
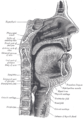
Mouth Latin pars oralis pharyngis Gray's subject #244 1142 Nerve pharyngeal plexus MeSH Oropharynx The Oropharynx (oral part of the pharynx) reaches from the Uvula to the level of the hyoid bone.
It opens anteriorly, through the isthmus faucium, into the mouth, while in its lateral wall, between the two palatine arches, is the palatine tonsil.
Contents
Normal oropharyngeal flora
Fusobacterium
Although older resources have stated that Fusobacterium is a common occurrence in the human oropharynx, the current consensus is that Fusobacterium should always be treated as a pathogen. [1]
HACEK organisms
The name is formed from their initials:[2]
- Haemophilus
- Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans
- Cardiobacterium hominis
- Eikenella corrodens
- Kingella
All of these organisms are part of the normal oropharyngeal flora, which grow slowly, prefer a carbon dioxide–enriched atmosphere and share an enhanced capacity to produce endocardial infections, especially in young children.
Actinomyces
Actinomyces species that cause human disease do not exist freely in nature but are normal flora of the oropharynx.
Additional images
References
- ^ Aliyu SH, Marriott RK, Curran MD, et al. (2004). "Real-time PCR investigation into the importance of Fusobacterium necrophorum as a cause of acute pharyngitis in general practice". J Med Microbiol 53 (Pt 10): 1029–35. doi:10.1099/jmm.0.45648-0. PMID 15358827.
- ^ Morpeth S, Murdoch D, Cabell CH, et al. (December 2007). "Non-HACEK gram-negative bacillus endocarditis". Ann. Intern. Med. 147 (12): 829–35. PMID 18087053.
External links
Human systems and organs TA 2–4:
MSBone (Carpus · Collar bone (clavicle) · Thigh bone (femur) · Fibula · Humerus · Mandible · Metacarpus · Metatarsus · Ossicles · Patella · Phalanges · Radius · Skull (cranium) · Tarsus · Tibia · Ulna · Rib · Vertebra · Pelvis · Sternum) · CartilageTA 5–11:
splanchnic/
viscusMouth (Salivary gland, Tongue) · upper GI (Oropharynx, Laryngopharynx, Esophagus, Stomach) · lower GI (Small intestine, Appendix, Colon, Rectum, Anus) · accessory (Liver, Biliary tract, Pancreas)TA 12–16 Blood
(Non-TA)General anatomy: systems and organs, regional anatomy, planes and lines, superficial axial anatomy, superficial anatomy of limbsHead and neck anatomy, digestive system: Mouth anatomy (TA A05.1–2, TH H3.04.01, GA 11.1110–2, 1125–1141) Mouth Lip (Upper, Lower, Vermilion border, Frenulum of lower lip, Labial commissure of mouth, Philtrum)
Cheek (Buccal fat pad)Interdental papilla · Gingival sulcus · Gingival margin · Free gingival margin · Gingival fibers · Junctional epithelium · Mucogingival junction · Sulcular epithelium · Stippling
Periodontium: Cementum · Gingiva · Periodontal ligamentTeethsee tooth anatomydorsum (Taste bud, Median sulcus, Terminal sulcus, Foramen cecum, Lingual tonsils) · underside (Frenulum, Fimbriated fold, Sublingual caruncle) · Anterior · Posterior · Glossoepiglottic folds · Lingual septumOro-pharynx/
faucesCategories:- Head and neck
- Digestive system
- Digestive system stubs
- Respiratory system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.