- Pharyngitis
-
Pharyngitis Classification and external resources 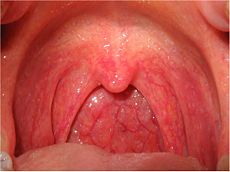
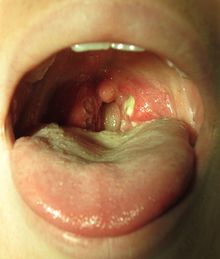
Inflammed oropharynx: swollen and red.ICD-10 J02, J31.2 ICD-9 462, 472.1 DiseasesDB 24580 MedlinePlus 000655 eMedicine emerg/419 MeSH D010612 Pharyngitis (
 /færɨnˈdʒaɪtɨs/) is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx.[1] In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.[2]
/færɨnˈdʒaɪtɨs/) is an inflammation of the throat or pharynx.[1] In most cases it is quite painful, and is the most common cause of a sore throat.[2]Like many types of inflammation, pharyngitis can be acute – characterized by a rapid onset and typically a relatively short course – or chronic. Pharyngitis can result in very large tonsils which cause trouble swallowing and breathing. Pharyngitis can be accompanied by a cough or fever, for example, if caused by a systemic infection.
Most acute cases are caused by viral infections (40–80%), with the remainder caused by bacterial infections, fungal infections, or irritants such as pollutants or chemical substances.[2][3] Treatment of viral causes are mainly symptomatic while bacterial or fungal causes may be amenable to antibiotics and anti-fungal respectively.
Contents
Classification
Pharyngitis is a type of inflammation, most commonly caused by an upper respiratory tract infection. It may be classified as acute or chronic. An acute pharyngitis may be catarrhal, purulent or ulcerative, depending on the virulence of the causative agent and the immune capacity of the affected individual. Chronic pharyngitis is the most common otolaringologic disease and may be catarrhal, hypertrophic or atrophic.
If the inflammation includes tonsillitis, it is called pharyngotonsillitis.[4] Another sub classification is nasopharyngitis (the common cold).[5]
Cause
The majority of cases are due to an infectious organism acquired from close contact with an infected individual.
Infectious
- Viral
These comprise about 40–80% of all infectious cases and can be a feature of many different types of viral infections.[2][3]
- Adenovirus – the most common of the viral causes. Typically the degree of neck lymph node enlargement is modest and the throat often does not appear red, although it is very painful.
- Orthomyxoviridae which cause influenza – present with rapid onset high temperature, headache and generalised ache. A sore throat may be associated.
- Infectious mononucleosis ("glandular fever") caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. This may cause significant lymph gland swelling and an exudative tonsillitis with marked redness and swelling of the throat. The heterophile test can be used if this is suspected.
- Herpes simplex virus can cause multiple mouth ulcers.
- Measles
- Common cold: rhinovirus, coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus can cause infection of the throat, ear, and lungs causing standard cold-like symptoms and often extreme pain.
- Bacterial
A number of different bacteria can infect the human throat. The most common is Group A streptococcus, however others include Corynebacterium diphtheriae, Neisseria gonorrhoeae, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, and Mycoplasma pneumoniae.[6]
-
- Streptococcal pharyngitis
Streptococcal pharyngitis or strep throat is caused by group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus (GAS).[7] It is the most common bacterial cause of cases of pharyngitis (15–30%).[6] Common symptoms include fever, sore throat, and large lymph nodes. It is a contagious infection, spread by close contact with an infected individual. A definitive diagnosis is made based on the results of a throat culture. Antibiotics are useful to both prevent complications and speed recovery.[8]
-
- Fusobacterium necrophorum
Fusobacterium necrophorum are normal inhabitants of the oropharyngeal flora. Occasionally however it can create a peritonsillar abscess. In 1 out of 400 untreated cases Lemierre's syndrome occurs.[9]
-
- Diphtheria
Diphtheria is a potentially life threatening upper respiratory infection caused by Corynebacterium diphtheriae which has been largely eradicated in developed nations since the introduction of childhood vaccination programs, but is still reported in the Third World and increasingly in some areas in Eastern Europe. Antibiotics are effective in the early stages, but recovery is generally slow.[citation needed]
-
- Others
A few other causes are rare, but possibly fatal, and include parapharyngeal space infections: peritonsillar abscess ("quinsy"), submandibular space infection (Ludwig's angina), and epiglottitis.[10][11][12]
- Fungal
Some cases of pharyngitis are caused by fungal infection such as Candida albicans causing oral thrush.[citation needed]
Non-infectious
Pharyngitis may also be caused by mechanical, chemical or thermal irritation, for example cold air or acid reflux. Some medications may produce pharyngitis such as pramipexole and antipsychotics.[13][14]
Diagnostic approach
It is hard to differentiate a viral and a bacterial cause of a sore throat based on symptoms alone. Thus often a throat swab is done to rule out a bacterial cause.[15]
Management
The majority of time treatment is symptomatic. Specific treatments are effective for bacterial, fungal, and herpes simplex infections.
Medications
- Analgesics such as NSAIDs and acetaminophen can help reduce the pain associated with a sore throat.[16]
- Steroids (such as dexamethasone) have been found to be useful for severe pharyngitis.[17][18]
- Viscous lidocaine relieves pain by numbing the mucus membranes.[19]
- Antibiotics are useful if group A streptococcus is the cause of the sore throat. For viral infections, antibiotics have no effect.[20]
Alternative
See also: Alternative treatments used for the common coldAlternative medicines are promoted and used for the treatment of sore throats.[21] They are however poorly supported by evidence, and UpToDate, an evidence-based peer-reviewed resource, recommends that they not be used to treat pharyngitis.[21][22]
Epidemiology
Acute pharyngitis is the most common cause of a sore throat and is diagnosed in more than 1.9 million people a year in the United States.[2]
References
- ^ "pharyngitis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ a b c d Marx, John (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice (7th ed.). Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: Mosby/Elsevier. Chapter 30. ISBN 9780323054720.
- ^ a b Acerra JR. "Pharyngitis". eMedicine. http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/764304-overview. Retrieved 28 April 2010.
- ^ Rafei K, Lichenstein R (April 2006). "Airway infectious disease emergencies". Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 53 (2): 215–42. doi:10.1016/j.pcl.2005.10.001. PMID 16574523.
- ^ "www.nlm.nih.gov". http://www.nlm.nih.gov/cgi/mesh/2010/MB_cgi?field=uid&term=D014069.
- ^ a b Bisno AL (January 2001). "Acute pharyngitis". N Engl J Med 344 (3): 205–11. doi:10.1056/NEJM200101183440308. PMID 11172144.
- ^ Baltimore RS (February 2010). "Re-evaluation of antibiotic treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis". Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 22 (1): 77–82. doi:10.1097/MOP.0b013e32833502e7. PMID 19996970.
- ^ Choby BA (March 2009). "Diagnosis and treatment of streptococcal pharyngitis". Am Fam Physician 79 (5): 383–90. PMID 19275067.
- ^ Centor RM (2009-12-01). "Expand the pharyngitis paradigm for adolescents and young adults". Ann Intern Med 151 (11): 812–5. doi:10.1059/0003-4819-151-11-200912010-00011. PMID 19949147.
- ^ "UpToDate Inc.". http://www.uptodate.com/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=pc_id/4421&selectedTitle=1~150&source=search_result. (registration required)
- ^ Reynolds SC, Chow AW (2009 Sep-Oct). "Severe soft tissue infections of the head and neck: a primer for critical care physicians". Lung 187 (5): 271–9. doi:10.1007/s00408-009-9153-7. PMID 19653038.
- ^ Bansal A, Miskoff J, Lis RJ (2003 Jan). "Otolaryngologic critical care". Crit Care Clin 19 (1): 55–72. doi:10.1016/S0749-0704(02)00062-3. PMID 12688577.
- ^ "Mirapex product insert" (PDF). Boehringer Ingelheim. 2009. http://bidocs.boehringer-ingelheim.com/BIWebAccess/ViewServlet.ser?docBase=renetnt&folderPath=/Prescribing+Information/PIs/Mirapex/Mirapex.pdf. Retrieved 2010-06-30.
- ^ "Mosby's Medical Dictionary, 8th edition". Elsevier. 2009. http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/olanzapine. Retrieved 2010-06-30.
- ^ Del Mar C (1992). "Managing sore throat: a literature review. I. Making the diagnosis". Med J Aust 156 (8): 572–5. PMID 1565052.
- ^ Thomas M, Del Mar C, Glasziou P (October 2000). "How effective are treatments other than antibiotics for acute sore throat?". Br J Gen Pract 50 (459): 817–20. PMC 1313826. PMID 11127175. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1313826.
- ^ Hayward G, Thompson M, Heneghan C, Perera R, Del Mar C, Glasziou P (2009). "Corticosteroids for pain relief in sore throat: systematic review and meta-analysis". BMJ 339: b2976. doi:10.1136/bmj.b2976. PMC 2722696. PMID 19661138. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2722696.
- ^ "Do steroids reduce symptoms in acute pharyngitis?". BestBets.org. http://www.bestbets.org/bets/bet.php?id=740. Retrieved 2009-01-14.
- ^ "LIDOCAINE VISCOUS (Xylocaine Viscous) side effects, medical uses, and drug interactions.". http://www.medicinenet.com/lidocaine_viscous/article.htm.
- ^ Del Mar CB, Glasziou PP, Spinks AB (2004). Del Mar, Chris. ed. "Antibiotics for sore throat". Cochrane Database Syst Rev (2): CD000023. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000023.pub2. PMID 15106140. - Meta-analysis of published research
- ^ a b "Sore throat: Self-care". Mayo Clinic. http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/sore-throat/DS00526/DSECTION=10. Retrieved 2007-09-17.
- ^ "UpToDate Inc.". Uptodate. http://www.uptodate.com/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=c_health/6691.
Inflammation Acute preformed: Lysosome granules · vasoactive amines (Histamine, Serotonin)
synthesized on demand: cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-1) · eicosanoids (Leukotriene B4, Prostaglandins) · Nitric oxide · KininsChronic Processes Traditional: Rubor · Calor · Tumor · Dolor (pain) · Functio laesa
Modern: Acute-phase reaction/Fever · Vasodilation · Increased vascular permeability · Exudate · Leukocyte extravasation · ChemotaxisSpecific locations CNS (Encephalitis, Myelitis) · Meningitis (Arachnoiditis) · PNS (Neuritis) · eye (Dacryoadenitis, Scleritis, Keratitis, Choroiditis, Retinitis, Chorioretinitis, Blepharitis, Conjunctivitis, Iritis, Uveitis) · ear (Otitis, Labyrinthitis, Mastoiditis)CardiovascularCarditis (Endocarditis, Myocarditis, Pericarditis) · Vasculitis (Arteritis, Phlebitis, Capillaritis)upper (Sinusitis, Rhinitis, Pharyngitis, Laryngitis) · lower (Tracheitis, Bronchitis, Bronchiolitis, Pneumonitis, Pleuritis) · MediastinitisDigestivemouth (Stomatitis, Gingivitis, Gingivostomatitis, Glossitis, Tonsillitis, Sialadenitis/Parotitis, Cheilitis, Pulpitis, Gnathitis) · tract (Esophagitis, Gastritis, Gastroenteritis, Enteritis, Colitis, Enterocolitis, Duodenitis, Ileitis, Caecitis, Appendicitis, Proctitis) · accessory (Hepatitis, Cholangitis, Cholecystitis, Pancreatitis) · PeritonitisArthritis · Dermatomyositis · soft tissue (Myositis, Synovitis/Tenosynovitis, Bursitis, Enthesitis, Fasciitis, Capsulitis, Epicondylitis, Tendinitis, Panniculitis)
Osteochondritis: Osteitis (Spondylitis, Periostitis) · Chondritisfemale: Oophoritis · Salpingitis · Endometritis · Parametritis · Cervicitis · Vaginitis · Vulvitis · Mastitis
male: Orchitis · Epididymitis · Prostatitis · Balanitis · Balanoposthitis
pregnancy/newborn: Chorioamnionitis · OmphalitisCommon cold Viruses Symptoms Sore throat - Rhinorrhea - Nasal congestion - Sneezing - Cough - Muscle aches - Fatigue - Malaise - Headache - Weakness - Loss of appetiteComplications Acute bronchitis - Bronchiolitis - Croup - Pharyngitis - Pneumonia - Sinusitis - Otitis media - Strep throatAntiviral drugs Pleconaril (experimental)Categories:- Infectious diseases
- Inflammations
- Upper respiratory tract diseases
- GI tract disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.