- Interstitial lung disease
-
Interstitial lung disease Classification and external resources 
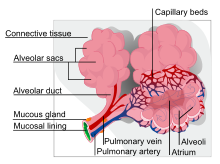
End-stage pulmonary fibrosis of unknown origin, taken from an autopsy in the 1980s.ICD-10 J84.9 ICD-9 506.4, 508.1, 515, 516.3, 714.81, 770.7 Interstitial lung disease (ILD), also known as diffuse parenchymal lung disease (DPLD),[1] refers to a group of lung diseases affecting the interstitium (the tissue and space around the air sacs of the lungs). [2] It concerns alveolar epithelium, pulmonary capillary endothelium, basement membrane, perivascular and perilymphatic tissues.
The term ILD is used to distinguish these diseases from obstructive airways diseases.
Prolonged ILD may result in pulmonary fibrosis, but this is not always the case. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is one form of "interstitial lung disease".
Contents
Causes
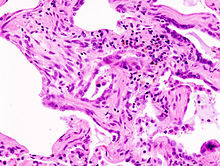
Micrograph of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). UIP is the most common pattern of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (a type of interstitial lung disease) and usually represents idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. H&E stain. Autopsy specimen.
ILD may be classified according to the cause.[3] One method of classification is as follows:
- Inhaled substances
- Inorganic
- Organic
- Drug induced
- Antibiotics
- Chemotherapeutic drugs
- Antiarrhythmic agents
- Statins
- Connective tissue disease
- Systemic sclerosis
- Polymyositis
- Dermatomyositis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Infection
- Atypical pneumonia
- Pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP)
- Tuberculosis
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- Respiratory Syncytial Virus
- Idiopathic
- Sarcoidosis
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Hamman-Rich syndrome
- Antisynthetase Syndrome
- Malignancy
- Lymphangitic carcinomatosis
Investigation
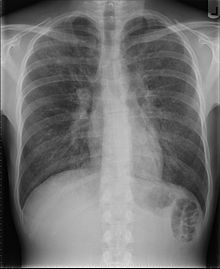
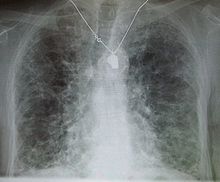
Patients with pneumocystis pneumonia can present with interstitial lung disease, as seen in the reticular markings on this AP chest x-ray A chest X-ray demonstrating pulmonary fibrosis due to amiodarone.
A chest X-ray demonstrating pulmonary fibrosis due to amiodarone.
Investigation is tailored towards the symptoms and signs. Most patients have blood testing, chest x-ray, pulmonary function testing, and high resolution CT thorax.
A lung biopsy is required if the clinical history and imaging are not clearly suggestive of a specific diagnosis or malignancy cannot otherwise be ruled out.
TLCO will be decreased in these patients.
Treatment
ILD is not a single disease, but encompasses many different pathological processes. Hence treatment is different for each disease.
If a specific occupational exposure cause is found, the person should avoid that environment. If a drug cause is suspected, that drug should be discontinued.
Many idiopathic and connective tissue-based causes of ILD are treated with corticosteroids,[4] such as prednisolone. Some patients respond to immunosuppressant treatment. Patients with hypoxemia may be given supplemental oxygen.
References
- ^ King TE (August 2005). "Clinical advances in the diagnosis and therapy of the interstitial lung diseases". Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 172 (3): 268–79. doi:10.1164/rccm.200503-483OE. PMID 15879420. http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=15879420.
- ^ "Frequently Asked Questions About Interstitial Lung Disease - University of Chicago Medical Center". http://www.uchospitals.edu/specialties/pulmonary/interstitial-lung/faq.html.
- ^ Bourke SJ (August 2006). "Interstitial lung disease: progress and problems". Postgrad Med J 82 (970): 494–9. doi:10.1136/pgmj.2006.046417. PMC 2585700. PMID 16891438. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2585700.
- ^ "Interstitial lung disease: Treatments and drugs - MayoClinic.com". http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/interstitial-lung-disease/DS00592/DSECTION=treatments%2Dand%2Ddrugs.
External links
For more information and resources on ILD, please visit the UCSF ILD Program website
- AIMIP Onlus - Italian Interstitial Lung Diseases No-Profit Organization
- 00736 at CHORUS
- 1476788304 at GPnotebook
- MeSH Pulmonary+Fibrosis
- MedlinePlus Overview pulmonaryfibrosis
- coalitionforpf.org - Coalition for Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pulmonary Fibrosis Patient Services, Education; Funding Research to Find a Cure for PF
- GeneReview/NCBI/NIH/UW entry on Pulmonary Fibrosis, Familial
- UCSF Interstitial Lung Disease Program at University of California San Francisco
- Interstitial Lung Disease Program at University of Chicago Medical Center
- Interstitial Lung Disease Center at University of Cincinnati
- PA-IPF - The Pennsylvania Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis State Registry at University of Pittsburgh
- WASOG - World Association for Sarcoidosis and Other Granulomatous Disorders
Categories:- Respiratory diseases principally affecting the interstitium
- Inhaled substances
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.