- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
-
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Classification and external resources
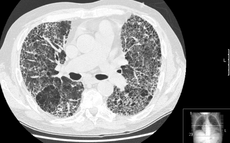
Extensive lung fibrosis from usual interstitial pneumonitisICD-10 J84.1 ICD-9 516.3 OMIM 178500 DiseasesDB 4815 MedlinePlus 000069 eMedicine radio/873 MeSH D011658 Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) (or cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis (CFA)[1]) is a chronic, progressive form of lung disease characterized by fibrosis of the supporting framework (interstitium) of the lungs. By definition, the term is used only when the cause of the pulmonary fibrosis is unknown ("idiopathic").
Microscopically, lung tissue from patients shows a characteristic set of histologic/pathologic features known as usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). UIP is therefore the pathologic counterpart of IPF.[2][3]
Contents
Etiology
Despite extensive investigation, the cause of IPF remains unknown. The condition involves abnormal and excessive deposition of collagen (fibrosis) in the pulmonary interstitium (mainly the walls of the alveoli) with minimal associated inflammation.[4] The fibrosis in IPF has been linked to cigarette smoking, gastroesophageal reflux disease and autoimmune disorders, but none of these are present in all patients with IPF, and therefore do not provide a completely satisfactory explanation for the disease.
Genetic associations include SFTPA1, SFTPA2, TERT, and TERC.[5]
Classification
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis is one specific presentation of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (IIP), which is in turn a type of interstitial lung disease.[6] Other forms of "idiopathic interstitial pneumonias" include non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP), desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP) and acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP). Examples of known causes of interstitial lung disease include sarcoidosis.[7][verification needed], hypersensitivity pneumonitis, pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis, asbestosis and collagen vascular diseases such as scleroderma and rheumatoid arthritis.
Clinical features
IPF affects both genders and is usually encountered in patients greater than 50 years of age. There are many different statements about average survival time following first diagnosis. Symptoms are gradual in onset. The most common are progressive dyspnea (difficulty breathing), but also include dry cough, clubbing (a disfigurement of the fingers), and rales (a crackling sound in the lungs during inhalation, heard with a stethoscope).[6] It should be noted that these features are not specific for IPF and can occur in a wide variety of other pulmonary disorders.
Differential diagnosis
The key issue facing clinicians is whether the presenting history, symptoms (or signs), radiology, and pulmonary function testing are collectively in keeping with the diagnosis of IPF (which carries the poor prognosis described above) or whether the findings are due to another process. It has long been recognized that patients with interstitial lung disease related to asbestos exposure, drugs (such as chemotherapeutic agents or nitrofurantoin), rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma/systemic sclerosis may be difficult to distinguish from IPF. Other differential diagnostic considerations include interstitial lung disease related to mixed connective tissue disease, advanced sarcoidosis, chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis, pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis and radiation-induced fibrosis.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis requires clinical findings compatible with interstitial lung disease in combination with either characteristic radiologic findings or a pathologic diagnosis of UIP on surgical lung biopsy. Generally, lung biopsy is only undertaken when its risks are outweighed by the potential benefits of identifying an alternative, treatable disease process. Establishing the diagnosis of IPF without a lung biopsy has been shown to be reliable when expert clinicians and radiologists concur that the presenting features are typical of IPF.[8] Based on this evidence, the 2002 ATS/ERS Multidisciplinary Consensus Statement on the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias proposed the following criteria for establishing the diagnosis of IPF without a lung biopsy:[6]
Major criteria (all 4 required):
- Exclusion of other known causes of interstitial lung disease (drugs, exposures, connective tissue diseases)
- Abnormal pulmonary function tests with evidence of restriction (reduced vital capacity) and impaired gas exchange (pO2, p(A-a)O2, DLCO)
- Bibasilar reticular abnormalities with minimal ground glass on high-resolution CT scans
- Transbronchial lung biopsy or bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) showing no features to support an alternative diagnosis
Minor criteria (3 of 4 required):
- Age > 50
- Insidious onset of otherwise unexplained exertional dyspnea
- Duration of illness > 3 months
- Bibasilar inspiratory crackles
Radiology
Plain chest x-rays reveal decreased lung volumes, typically with prominent reticular interstitial markings near the lung bases. Honeycombing, a pattern of lung fibrosis characterized by multiple cystic spaces located at the bases of the lungs, is frequently seen in advanced cases. In less severe cases, these changes may not be evident on a plain chest film.
High-resolution CT scans of the chest demonstrate fibrotic changes in both lungs, with a predilection for the bases and the periphery. The most charactersitic radiologic feature of IPF is honeycombing, often described as traction bronchiectasis. There may be ground glass opacities of the lungs but these changes are relatively minor in comparison with the fibrotic changes.[9]
Pulmonary function tests
Spirometry classically reveals a reduction in the vital capacity with either a proportionate reduction in airflows, or increased airflows for the observed vital capacity. The latter finding reflects the increased lung stiffness (reduced lung compliance) associated with pulmonary fibrosis, which leads to increased lung elastic recoil.[10]
Measurement of static lung volumes using body plethysmography or other techniques typically reveals reduced lung volumes (restriction). This reflects the difficulty encountered in inflating the fibrotic lungs.
The diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) is invariably reduced in IPF and may be the only abnormality in mild or early disease. Its impairment underlies the propensity of patients with IPF to exhibit oxygen desaturation with exercise.
Histology/Pathology
Main article: Usual interstitial pneumoniaMicrograph of usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). UIP most often represents idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. H&E stain. Autopsy specimen.
Histologic specimens for the diagnosis of IPF must be large enough that the pathologist can comment on the underlying lung architecture. Small biopsies, such as those obtained via transbronchial lung biopsy (performed during bronchoscopy) are usually not sufficient for this purpose. Hence, larger biopsies obtained surgically via a thoracotomy or thoracoscopy are usually necessary.[6]
The histological appearance associated with IPF is referred to as usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). Although a pathologic diagnosis of UIP often corresponds to a clinical diagnosis of IPF, it can be seen in other diseases as well.[11] Key features of UIP include interstitial fibrosis in a "patchwork pattern", interstitial scarring, honeycomb changes and fibroblast foci. There is usually only a relatively mild or minor component of interstitial chronic inflammation.[6]
Treatment
Although there is no consensus on the optimal management of IPF, it is recognized that no satisfactory treatment exists at present. None of what follows should be taken as specific advice regarding therapy, as the latter is a decision that must be made on a case-by-case basis in individual patients.[12]
There is a lack of large, randomized placebo-controlled trials of therapy for IPF. Moreover, many of the earlier studies were based on the hypothesis that IPF is an inflammatory disorder, and hence studied anti-inflammatory agents such as corticosteroids. Another problem has been that studies conducted prior to the more recent classification of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias failed to distinguish IPF/UIP from NSIP in particular. Hence, many patients with arguably more steroid-responsive diseases were included in earlier studies, confounding the interpretation of their results.[4]
Small early studies demonstrated that the combination of prednisone with either cyclophosphamide or azathioprine over many months had very modest, if any, beneficial effect in IPF, and were associated with substantial adverse effects (predominantly myelotoxicity). Other treatments studied have included interferon gamma-1b, the antifibrotic agent pirfenidone and bosentan. Pirfenidone and bosentan are currently being studied in patients with IPF while interferon gamma-1b is no longer considered a viable treatment option. Finally, the addition of the antioxidant N-acetylcysteine to prednisone and azathioprine produced a slight benefit in terms of FVC and DLCO over 12 months of follow up. However, the major benefit appeared to be prevention of the myelotoxicity associated with azathioprine.[13]
Prognosis
Many patients end up on supplementary oxygen and some will need a lung transplant.[14]
Half of IPF sufferers in the UK die within three years of diagnosis.[14]
Incidence
In the UK IPF kills about 5,000 pa[15] (more than leukemia or ovarian cancer).[14]
Clinical trials
Intedanib (BIBF 1120) is in two phase III trials for IPF.
As of 2011[update] another 40 or so trials for IPF were recruiting.[16] including a phase II trial of QAX576[17].
External links
References
- ^ Fellrath JM, du Bois RM (September 2003). "Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis/cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis". Clin. Exp. Med. 3 (2): 65–83. doi:10.1007/s10238-003-0010-3. PMID 14598183.
- ^ Meltzer EB, Noble PW (2008). "Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis". Orphanet J Rare Dis 3 (1): 8. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-3-8. PMC 2330030. PMID 18366757. http://www.ojrd.com/content/3//8.
- ^ "Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Diagnosis and Treatment". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 161 (2): 646–664. 1 February 2000. PMID 10673212. http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/content/full/161/2/646.
- ^ a b Selman, Moisés; Talmadge E. King, Jr.; and Annie Pardo (16 January 2001). "Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: prevailing and evolving hypotheses about its pathogenesis and implications for therapy". Annals of Internal Medicine 134 (2): 136–51. PMID 11177318. http://www.annals.org/cgi/content/abstract/134/2/136.
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 178500
- ^ a b c d e American Thoracic, Society; European Respiratory, Society (15 January 2002). "American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 165 (2): 277–304. PMID 11790668. http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/content/full/165/2/277.
- ^ Cooper, Daniel H.; Andrew J. Krainik, Sam J. Lubner, Hilary E. L. Reno (eds.) (2007). The Washington Manual of Medical Therapeutics (32nd ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 276. ISBN 978-0781781251.
- ^ Flaherty, Kevin R.; Talmadge E. King, Jr., Ganesh Raghu, Joseph P. Lynch, III, Thomas V. Colby, William D. Travis, Barry H. Gross, Ella A. Kazerooni, Galen B. Toews, Qi Long, Susan Murray, Vibha N. Lama, Steven E. Gay, and Fernando J. Martinez (2004). "Idiopathic interstitial pneumonia: what is the effect of a multidisciplinary approach to diagnosis?". American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 170 (8): 904–10. doi:10.1164/rccm.200402-147OC. PMID 15256390. http://ajrccm.atsjournals.org/cgi/content/full/170/8/904.
- ^ Webb, W. Richard; Nestor L. Müller and David P. Naidich (2001). High-resolution CT of the lung. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 196. ISBN 978-0781722780.
- ^ Pellegrino, R., Viegi G., Brusasco V. et al. (November 2005). "Interpretative strategies for lung function tests". European Respiratory Journal (European Respiratory Society) 26 (5): 948–68. doi:10.1183/09031936.05.00035205. PMID 16264058. http://erj.ersjournals.com/cgi/content/full/26/5/948?maxtoshow=&HITS=10&hits=10&RESULTFORMAT=1&andorexacttitle=and&andorexacttitleabs=and&andorexactfulltext=and&searchid=1&FIRSTINDEX=0&sortspec=relevance&volume=26&firstpage=948&resourcetype=HWCIT.
- ^ Kumar, Vinay; Nelso Fausto and Abul Abbas (2005). Robbins and Cotran's Pathological Basis of Disease (7th ed.). Saunders. p. 729. ISBN 978-0721601878.
- ^ Walter, N; Collard HR, Talmadge E. King, Jr. (June 2006). "Current perspectives on the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis". Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society (American Thoracic Society) 3 (4): 330–338. doi:10.1513/pats.200602-016TK. PMID 16738197. http://pats.atsjournals.org/cgi/content/full/3/4/330. Retrieved 2008-03-05.
- ^ Demedts, Maurits; Juergen Behr; Roland Buhl et al. (2005). "High-dose acetylcysteine in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The IFIGENIA Study". New England Journal of Medicine 353 (21): 2229–2242. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa042976. PMID 16306520. http://content.nejm.org/cgi/content/full/353/21/2229.
- ^ a b c Elkins, Lucy (10 May 2011). "It's a new killer baffling doctors. And the only warning sign is feeling out of breath...". Daily Mail. http://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-1385311/New-killer-baffling-doctors-And-warning-sign-feeling-breath-.html.
- ^ Navaratnam, V.; Fleming, K. M.; West, J.; Smith, C. J. P.; Jenkins, R. G.; Fogarty, A.; Hubbard, R. B. (2011). "The rising incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the UK". Thorax 66 (6): 462–467. doi:10.1136/thx.2010.148031. PMID 21525528.
- ^ http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=IPF&recr=Open
- ^ http://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01266135 Phase II Safety and Efficacy of QAX576 in Patients With Progressive Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)
Categories:- Respiratory diseases principally affecting the interstitium
- Idiopathic diseases
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.