- Chorioamnionitis
-
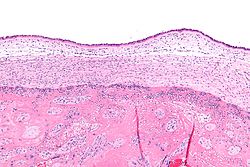
Chorioamnionitis Classification and external resources 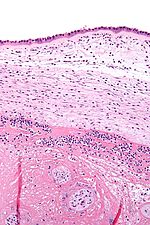
Micrograph showing chorioamnionitis. The clusters of blue dots are inflammatory cells (neutrophils, eosinophils and lymphocytes). H&E stain.ICD-10 O41.1, P02.7 ICD-9 658.4, 762.7 eMedicine ped/89 MeSH D002821 Chorioamnionitis is an inflammation of the fetal membranes (amnion and chorion) due to a bacterial infection. It typically results from bacteria ascending into the uterus from the vagina and is most often associated with prolonged labour. Risk of developing chorioamnionitis increases with each vaginal exam during final month of pregnancy and during labor.[3]
Contents
Background
The fetal membranes consist of two parts:
- The outer membrane is the chorion. It is closest to the mother and physically supports the much thinner amnion.
- The inner membrane is the amnion. It is in direct contact with the amniotic fluid, which surrounds the fetus.
Diagnosis
Clinical
Chorioamnionitis is diagnosed clinically in the setting of:[1]
- maternal fever.
- uterine tenderness in the presence of confirmed premature rupture of membranes (PROM).
Exclusions:
- maternal upper respiratory infection.
- maternal urinary tract infection.
Pathologic
Chorioamnionitis can be diagnosed from a histologic examination of the fetal membranes.
Infiltration of the chorionic plate by neutrophils is diagnostic of (mild) chorioamnionitis. More severe chorioamnionitis involves subamniotic tissue and may have fetal membrane necrosis and/or abscess formation.
Severe chorioamnionitis may be accompanied by vasculitis of the umbilical vessels (due to the fetus' inflammatory cells) and, if very severe, funisitis (inflammation of the umbilical cord's connective tissue).
Treatment
Treatment consists of:
- antibiotics (amoxicillin + gentamicin + metronidazole) for the mother, and
- quickly delivering the baby.
Associations
Chorioamnionitis is a risk factor for periventricular leukomalacia and cerebral palsy.[2]
See also
References
- ^ Elmar Peter Sakala, MD, MA, MPH, FACOG. Professor of GYNOB, Loma Linda University of medicine, California. Codirector of Student Clerkship. Dept of GYNOB
- ^ Wu YW, Colford JM (2000). "Chorioamnionitis as a risk factor for cerebral palsy: A meta-analysis". JAMA 284 (11): 1417–24. doi:10.1001/jama.284.11.1417. PMID 10989405.
3. Excess Digital Exams Raise Risk of Chorioamnionitis, Ob.Gyn. News, August 15, 1997
External links
- Overview at Cleveland Clinic.
- Cerebral palsy inflammation link (29 November 2003) at BBC.
Certain conditions originating in the perinatal period / fetal disease (P, 760–779) Maternal factors and
complications of pregnancy,
labour and deliveryLength of gestation
and fetal growthSmall for gestational age/Large for gestational age · Preterm birth/Postmature birth · Intrauterine growth restrictionBirth trauma By system Vitamin K deficiency (Haemorrhagic disease of the newborn)HDN (ABO • Anti-Kell • Rh c • Rh D • Rh E) · Hydrops fetalis · Hyperbilirubinemia (Kernicterus, Neonatal jaundice)Integument and
temperature regulationErythema toxicum · Sclerema neonatorumInfectious Other Inflammation Acute preformed: Lysosome granules · vasoactive amines (Histamine, Serotonin)
synthesized on demand: cytokines (IFN-γ, IL-8, TNF-α, IL-1) · eicosanoids (Leukotriene B4, Prostaglandins) · Nitric oxide · KininsChronic Processes Traditional: Rubor · Calor · Tumor · Dolor (pain) · Functio laesa
Modern: Acute-phase reaction/Fever · Vasodilation · Increased vascular permeability · Exudate · Leukocyte extravasation · ChemotaxisSpecific locations CNS (Encephalitis, Myelitis) · Meningitis (Arachnoiditis) · PNS (Neuritis) · eye (Dacryoadenitis, Scleritis, Keratitis, Choroiditis, Retinitis, Chorioretinitis, Blepharitis, Conjunctivitis, Iritis, Uveitis) · ear (Otitis, Labyrinthitis, Mastoiditis)CardiovascularCarditis (Endocarditis, Myocarditis, Pericarditis) · Vasculitis (Arteritis, Phlebitis, Capillaritis)upper (Sinusitis, Rhinitis, Pharyngitis, Laryngitis) · lower (Tracheitis, Bronchitis, Bronchiolitis, Pneumonitis, Pleuritis) · MediastinitisDigestivemouth (Stomatitis, Gingivitis, Gingivostomatitis, Glossitis, Tonsillitis, Sialadenitis/Parotitis, Cheilitis, Pulpitis, Gnathitis) · tract (Esophagitis, Gastritis, Gastroenteritis, Enteritis, Colitis, Enterocolitis, Duodenitis, Ileitis, Caecitis, Appendicitis, Proctitis) · accessory (Hepatitis, Cholangitis, Cholecystitis, Pancreatitis) · PeritonitisArthritis · Dermatomyositis · soft tissue (Myositis, Synovitis/Tenosynovitis, Bursitis, Enthesitis, Fasciitis, Capsulitis, Epicondylitis, Tendinitis, Panniculitis)
Osteochondritis: Osteitis (Spondylitis, Periostitis) · Chondritisfemale: Oophoritis · Salpingitis · Endometritis · Parametritis · Cervicitis · Vaginitis · Vulvitis · Mastitis
male: Orchitis · Epididymitis · Prostatitis · Balanitis · Balanoposthitis
pregnancy/newborn: Chorioamnionitis · OmphalitisCategories:- Inflammations
- Pathology of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium
- Disease stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.