- Diastasis symphysis pubis
-
Diastasis symphysis pubis Classification and external resources
Post traumatic diastasis of symphysis pubisMeSH D046548 Diastasis symphysis pubis is the separation of normally joined pubic bones, as in the dislocation of the bones, without a fracture.
Contents
Diagnosis
This abnormally wide gap can be diagnosed by radiologic studies such as x-ray, MRI, CT scan or bone scan. Manual testing by a Healthcare Professional can also be used. The patient is placed in various positions and pressure is applied in such a way that it provokes pain and maybe movement in the pubis.
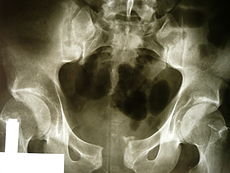
X-ray
An X-ray film will show a marked gap between the pubic bones, normally there is a 4–5 mm gap but in pregnancy, hormonal influences cause relaxation of the connecting ligaments and the bones separate up to 9 mm. To demonstrate instability of the joint the patient is required to stand in the "flamingo" position, (standing with weight on one leg and the other bent).[1] A vertical displacement of more than 1 cm is an indicator of symphysis pubis instability.[2] A displacement of more than 2 cm usually indicates involvement of the sacroiliac joints.
CT scan and MRI
Both diagnostic machines can produce detailed cross sections of the pelvic area. Images will show degrees soft tissue injury, inflammation of the subchondral region and the bone marrow [3] and any abnormal posturing of the pelvic joints.
Bone Scan
A bone scan is able to determine areas of bone inflammation.
External forces
External forces such as falling from a horse or a car accident can result in this type of injury to the symphysis pubis.
In former times obstructed childbirth was sometimes treated by cutting the pubic symphysis (symphysiotomy), letting the pelvis halves hinge outwards at the sacroiliac joints.
Other conditions
- In extroversion of the bladder[4] there is a gap between the pubes, which are joined by a strong interpubic ligament.
References
- ^ An Analysis of Pubis Symphysis Misalignment Using Plain Film Radiography Ruch WJ, Ruch BM. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2005;28(5):330-335
- ^ Vertically Unstable Pelvic Fractures Fixed with Percutaneous Iliosacral Screws: Does Posterior Injury Predict Fixation Failure? Damian R. Griffin, MA, FRCS (Orth); Adam J. Starr, MD; Charles M. Reinert , MD; Alan L. Jones, MD; Shelly Whitlock, CCRA; University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX
- ^ Magnetic resonance imaging changes of sacroiliac joints in patients with recent-onset inflammatory back pain: inter-reader reliability and prevalence of abnormalities. Arthritis Research & Therapy 2006, 8:R11 doi:10.1186/ar1859. Liesbeth Heuft-Dorenbosch1, René Weijers, Robert Landewé1, Sjef van der Linden1, Désirée van der Heijde1
- ^ http://www.bartleby.com/107/255.html (end of page)
External links
Injury: Dislocations/subluxations, sprains and strains (Sx3 where x=0 to 9, 830–848) Joints and
ligamentsHead and neckShoulder and upper armMuscles and
tendonsShoulder and upper armM: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Pelvis
- Skeletal disorders
- Health issues in pregnancy
- Pathology of pregnancy, childbirth and the puerperium
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.