- Chorion
-
- For the chorion in invertebrate eggs, see Chorion (egg).
Chorion 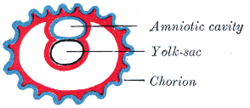
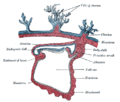
Diagram showing earliest observed stage of human embryo. 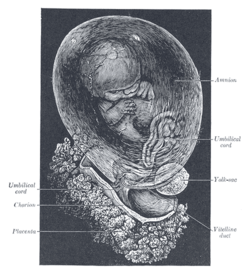
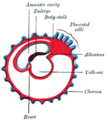
Human fetus, enclosed in the amnion. Gray's subject #12 60 MeSH Chorion Code TE E5.11.3.1.1.0.3 - For the entertainment company see Chorion (company).
The chorion is one of the membranes that exist during pregnancy between the developing fetus and mother. It is formed by extraembryonic mesoderm and the two layers of trophoblast and surrounds the embryo and other membranes. The chorionic villi emerge from the chorion, invade the endometrium, and allow transfer of nutrients from maternal blood to fetal blood.
Contents
Layers
The chorion consists of two layers: an outer formed by the trophoblast, and an inner formed by the somatic mesoderm; the amnion is in contact with the latter.
The trophoblast is made up of an internal layer of cubical or prismatic cells, the cytotrophoblast or layer of Langhans, and an external layer of richly nucleated protoplasm devoid of cell boundaries, the syncytiotrophoblast.
Growth
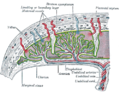
The chorion undergoes rapid proliferation and forms numerous processes, the chorionic villi, which invade and destroy the uterine decidua and at the same time absorb from it nutritive materials for the growth of the embryo.
The chorionic villi are at first small and non-vascular, and consist of the trophoblast only, but they increase in size and ramify, whereas the mesoderm, carrying branches of the umbilical vessels, grows into them, and, in this way, are vascularized.
Blood is carried to the villi by the paired umbilical arteries, which branch into chorionic arteries and enter the chorionic villi as cotyledon arteries. After circulating through the capillaries of the villi, the blood is returned to the embryo by the umbilical veins. Until about the end of the second month of pregnancy, the villi cover the entire chorion, and are almost uniform in size; but, after this, they develop unequally.
Parts
The part of the chorion that is in contact with the decidua capsularis undergoes atrophy, so that by the fourth month scarcely a trace of the villi is left. This part of the chorion becomes smooth, and is named the chorion laeve (from the Latin word levis, meaning smooth). As it takes no share in the formation of the placenta, this is also named the non-placental part of the chorion. As the chorion grows, the chorion laeve comes in contact with the decidua parietalis and these layers fuse.
On the other hand, the villi at the embryonic pole, which is in contact with the decidua basalis, increase greatly in size and complexity, and hence this part is named the chorion frondosum.
Thus the placenta develops from the chorion frondosum and the decidua basalis.
Monochorionic twins
Main article: Monochorionic twinsMonochorionic twins are twins that share the same placenta. It occurs in 0.3% of all pregnancies,[1] and in 75% of monozygotic (identical) twins, when the split takes place after the third day after fertilization.[2] The remaining 25% of monozygous twins become dichorionic diamniotic.[2] The condition may affect any type of multiple birth, resulting in monochorionic multiples.
Additional images
See also
- Amniotic sac
- Choriogenesis
- Chorioamnionitis, an inflammation of the chorion and amnion, usually due to bacterial infection.
- Gestational trophoblastic disease, any abnormal proliferation of the trophoblasts, including choriocarcinoma, a highly invasive cancer.
References
- ^ Cordero L, Franco A, Joy SD, O'shaughnessy RW (December 2005). "Monochorionic diamniotic infants without twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome". Journal of Perinatology 25 (12): 753–8. doi:10.1038/sj.jp.7211405. PMID 16281049.
- ^ a b Shulman, Lee S.; van Vugt, John M. G. (2006). Prenatal medicine. Washington, DC: Taylor & Francis. p. 447. ISBN 0-8247-2844-0.
External links
- Histology at BU 19903loa - "Female Reproductive System: placenta, chorionic plate"
- McGill
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Embryonic adnexa Trophoblast (Cytotrophoblast, Syncytiotrophoblast, Intermediate trophoblast)
Chorionic villi/Intervillous space · Amnion/Amniotic sac/Amniotic cavity
rostral embryonic ligament · caudal embryonic ligamentFetal membranes Circulatory Placenta · ChorionUngrouped Prenatal development/Mammalian development of circulatory system (GA 5, TE E5.11) Heart development Tubular heartSepta/ostiaAtrioventricular cushions/Septum intermedium · Primary interatrial foramen · Septum primum (Foramen secundum) · Septum secundum (Foramen ovale) · Aorticopulmonary septumOtherAtrioventricular canal · Primary interventricular foramenVasculogenesis,
angiogenesis,
and lymphangiogenesisBlood island of umbilical vesicle
Development of arteriesDevelopment of veinsDevelopment of lymph vesselsLymph sacsDevelopment of circulatory system about teeth near childrenanuli: Anulus sanguineus perienameleus · lacunae: Lacuna sanguinea supraenamelea (Ductus sanguineus mesialis · Ductus sanguineus distalis · Ductus sanguineus lingualis · Ductus sanguineus palatinus · Ductus sanguineus buccalis · Ductus sanguineus labialis), Lacuna sanguinea apicalis, Lacuna sanguinea periodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea parodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea gingivalisExtraembryonic
hemangiogenesisFetal circulation Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.