- Primary interatrial foramen
-
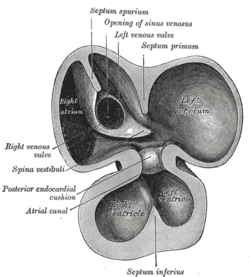
Primary interatrial foramen Interior of dorsal half of heart from a human embryo of about thirty days. (Ostium primum visible below septum primum, but not labeled.) Latin foramen primum Gray's subject #135 512 Code TE E5.11.1.5.2.1.1 In the developing heart, the atria initially communicate with each other by an opening between the free edge of the septum primum and the AV cushions, known as the primary interatrial foramen or ostium primum (interatrial foramen primum), below the free margin of the septum.
Contents
Closing of ostium primum
This opening is closed by the union of the septum primum with the septum intermedium, and as the ostium primum closes, the communication between the atria is preserved with the formation of an opening in the upper part of the septum primum; this opening is known as the ostium secundum as it is chronologically the second opening that occurs in the septum prium.
A second entity, the septum secundum, develops to the right of the septum primum and the opening between the upper and lower limbs of the septum secundum is known as the foramen ovale of the heart. The part of the septum primum that remains to the left of the septum secundum acts as a one way flow valve due to the greater pressures in the right atrium compared to the left atrium. At birth the neonate begins breathing and the associated decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance leads to a reversal of the pressure differential between the atria. The left atrium now has a greater pressure compared to the right, effectively closing the one way flow valve formed by the two septae. The two septae fuse later in life, to complete the formation of the atrial septum.
Persistence of the ostium secundum is the most common atrial septal defect.[1] Additionally, in a subset of the population, the foramen ovale is not overtly patent, however the two septae have not fused. In normal physiologic circumstances the septum primum acts as a one way valve preventing blood flow as described above, however if pathologic conditions cause right atrial pressure to exceed left atrial pressure, blood may flow through the foramen ovale from right to left.
Clinical significance
Failure of the septum primum to fuse with the atrio-ventricular cushion can lead to an ostium primum atrial septal defect.[2] This is the second most common type of atrial septal defect[1] and is commonly seen in Down's syndrome. Typically this defect will cause a shunt to occur from the left atrium to the right atrium. Children born with this defect may be asymptomatic, however, over time pulmonary hypertension and the resulting hypertrophy of the right side of the heart will lead to a reversal of this shunt. This reversal is called Eisenmenger syndrome.
References
External links
- Embryology at Temple Heart98/heart97a/sld036
- Overview and diagram at um.edu.mt
- MedEd at Loyola GrossAnatomy/thorax0/Heart_Development/Atria.html
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Prenatal development/Mammalian development of circulatory system (GA 5, TE E5.11) Heart development Tubular heartSepta/ostiaAtrioventricular cushions/Septum intermedium · Primary interatrial foramen · Septum primum (Foramen secundum) · Septum secundum (Foramen ovale) · Aorticopulmonary septumOtherAtrioventricular canal · Primary interventricular foramenVasculogenesis,
angiogenesis,
and lymphangiogenesisBlood island of umbilical vesicle
Development of arteriesDevelopment of veinsDevelopment of lymph vesselsLymph sacsDevelopment of circulatory system about teeth near childrenanuli: Anulus sanguineus perienameleus · lacunae: Lacuna sanguinea supraenamelea (Ductus sanguineus mesialis · Ductus sanguineus distalis · Ductus sanguineus lingualis · Ductus sanguineus palatinus · Ductus sanguineus buccalis · Ductus sanguineus labialis), Lacuna sanguinea apicalis, Lacuna sanguinea periodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea parodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea gingivalisExtraembryonic
hemangiogenesisFetal circulation Categories:- Embryology of cardiovascular system
- Developmental biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.