- Foramen ovale (heart)
-
Foramen ovale (heart) 
Sketch showing foramen ovale in a fetal heart. Red arrow shows blood from the inferior caval vein. HF: right atrium, VF: left atrium. HH og VH: right and left ventricle. The heart still has a common pulmonary vein (LV), instead of four. 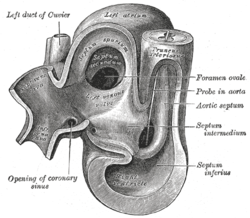
Heart of human embryo of about thirty-five days, opened on right side. Gray's subject #135 512 MeSH Foramen+Ovale In the fetal heart, the foramen ovale (also ostium secundum of Born or falx septi) allows blood to enter the left atrium from the right atrium. It is one of two fetal cardiac shunts, the other being the ductus arteriosus (which allows blood that still escapes to the right ventricle to bypass the pulmonary circulation). Another similar adaptation in the fetus is the ductus venosus. In most individuals, the foramen ovale (pronounced /fɒˈreɪmɨn oʊˈvæliː/) closes at birth. It later forms the fossa ovalis.
Contents
Development
The foramen ovale forms in the late fourth week of gestation. Initially the atria are separated from one another by the septum primum except for a small opening in the septum, the ostium primum. As the septum primum grows, the ostium primum narrows and eventually closes. Before it does so, bloodflow from the inferior vena cava wears down a portion of the septum primum, forming the ostium secundum. Some embryologists postulate that the ostium secundum may be formed through programmed cell death.[1]
The ostium secundum provides communication between the atria after the ostium primum closes completely. Subsequently, a second wall of tissue, the septum secundum, grows over the ostium secundum in the right atrium. Bloodflow then only passes from the right to left atrium by way of a small passageway in the septum secundum and then through the ostium secundum. This passageway is called the foramen ovale.
Closure
Normally this opening closes in the first three months following birth. When the lungs become functional at birth, the pulmonary pressure decreases and the left atrial pressure exceeds that of the right. This forces the septum primum against the septum secundum, functionally closing the foramen ovale. In time the septa eventually fuse, leaving a remnant of the foramen ovale, the fossa ovalis.
Clinical relevance
In about 30% of adults the foramen ovale does not close completely, but remains as a small patent foramen ovale.
PFO has long been studied because of its demonstrated role in some cases of paradoxical embolism. After exclusion of more common causes of stroke and TIA, transesophageal echocardiography should be considered in order to exclude cardiogenic foci of embolism. The presence of a patent foramen ovale should be considered as a possible cause of the cerebrovascular event, even though it may simply be an occasional finding in patients with cryptogenic stroke.
References
- ^ Sadler, Thomas W. (2004). Langman's Essential Medical Embryology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 0781755719.
- Carlson, Bruce (2004). Human Embryology And Developmental Biology (3rd edition). Elsevier Mosby. ISBN 0-323-03649-X.
External links
Prenatal development/Mammalian development of circulatory system (GA 5, TE E5.11) Heart development Tubular heartSepta/ostiaAtrioventricular cushions/Septum intermedium · Primary interatrial foramen · Septum primum (Foramen secundum) · Septum secundum (Foramen ovale) · Aorticopulmonary septumOtherAtrioventricular canal · Primary interventricular foramenVasculogenesis,
angiogenesis,
and lymphangiogenesisBlood island of umbilical vesicle
Development of arteriesDevelopment of veinsDevelopment of lymph vesselsLymph sacsDevelopment of circulatory system about teeth near childrenanuli: Anulus sanguineus perienameleus · lacunae: Lacuna sanguinea supraenamelea (Ductus sanguineus mesialis · Ductus sanguineus distalis · Ductus sanguineus lingualis · Ductus sanguineus palatinus · Ductus sanguineus buccalis · Ductus sanguineus labialis), Lacuna sanguinea apicalis, Lacuna sanguinea periodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea parodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea gingivalisExtraembryonic
hemangiogenesisFetal circulation Categories:- Cardiology
- Embryology of cardiovascular system
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
