- Umbilical artery
-
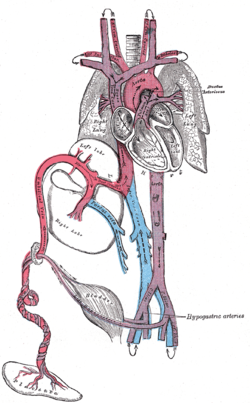
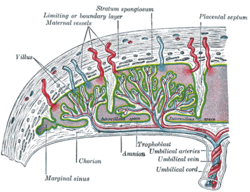
Artery: Umbilical artery Fetal circulation; the umbilical vein is the large, red vessel at the far left. The umbilical arteries are purple and wrap around the umbilical vein. Scheme of placental circulation. Latin a. umbilicalis Gray's subject #139 540 Source internal iliac artery Branches superior vesical artery
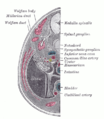
artery of the ductus deferensVein umbilical vein MeSH Umbilical+Arteries The umbilical artery is a paired artery (with one for each half of the body) that is found in the abdominal and pelvic regions. In the fetus, it extends into the umbilical cord.
Contents
Umbilical arteries in the fetus
Umbilical arteries supply deoxygenated blood from the fetus to the placenta in the umbilical cord. There are usually two umbilical arteries present together with one umbilical vein in the cord. The umbilical arteries are actually the latter of the internal iliac arteries that supply the hind limbs with blood and nutrients in the fetus. The umbilical arteries surround the urinary bladder and then carry all the deoxygenated blood out of the fetus through the umbilical cord.
The umbilical arteries are the only arteries in the human body, aside from the pulmonary arteries, that carry deoxygenated blood.
The pressure inside the umbilical artery is approximately 50 mmHg.[1]
Inside the placenta, the umbilical arteries connect with each other at a distance of approximately 5 mm from the cord insertion in what is called the Hyrtl anastomosis.[2] Subsequently, they branch into chorionic arteries or intraplacental fetal arteries.[3]
Umbilical artery in the adult
The umbilical artery is a branch of the anterior division of the internal iliac artery and represents the patent (open) part of the embryonic umbilical artery. (The non-patent obliterated part of the artery is the medial umbilical ligament.) The umbilical artery is found in the pelvis, and gives rise to the superior vesical arteries. In males, it also gives rise to the artery to the ductus deferens.
Additional images
See also
- Single umbilical artery
References
- ^ Fetal and maternal blood circulation systems From Online course in embryology for medicine students. Universities of Fribourg, Lausanne and Bern (Switzerland). Retrieved on 6 April 2009
- ^ Gordon, Z.; Elad, D.; Almog, R.; Hazan, Y.; Jaffa, A. J.; Eytan, O. (2007). "Anthropometry of fetal vasculature in the chorionic plate". Journal of Anatomy 211 (6): 698–706. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7580.2007.00819.x. PMC 2375851. PMID 17973911. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2375851.
- ^ Hsieh, FJ; Kuo, PL; Ko, TM; Chang, FM; Chen, HY (1991). "Doppler velocimetry of intraplacental fetal arteries". Obstetrics and gynecology 77 (3): 478–82. PMID 1992421.
External links
- 1349189694 at GPnotebook
- SUNY Labs 43:13-0203 - "The Female Pelvis: Branches of Internal Iliac Artery"
List of arteries of torso – abdomen (TA A12.2.12–15, GA 6.598) AA ParietalAnteriorPosteriorvisceralAnteriorumbilicalvaginal branch ♀V/IVPosteriorsee arteries of lower limbsEmbryonic adnexa Trophoblast (Cytotrophoblast, Syncytiotrophoblast, Intermediate trophoblast)
Chorionic villi/Intervillous space · Amnion/Amniotic sac/Amniotic cavity
rostral embryonic ligament · caudal embryonic ligamentFetal membranes Circulatory Ungrouped Prenatal development/Mammalian development of circulatory system (GA 5, TE E5.11) Heart development Tubular heartSepta/ostiaAtrioventricular cushions/Septum intermedium · Primary interatrial foramen · Septum primum (Foramen secundum) · Septum secundum (Foramen ovale) · Aorticopulmonary septumOtherAtrioventricular canal · Primary interventricular foramenVasculogenesis,
angiogenesis,
and lymphangiogenesisBlood island of umbilical vesicle
Development of arteriesDevelopment of veinsDevelopment of lymph vesselsLymph sacsDevelopment of circulatory system about teeth near childrenanuli: Anulus sanguineus perienameleus · lacunae: Lacuna sanguinea supraenamelea (Ductus sanguineus mesialis · Ductus sanguineus distalis · Ductus sanguineus lingualis · Ductus sanguineus palatinus · Ductus sanguineus buccalis · Ductus sanguineus labialis), Lacuna sanguinea apicalis, Lacuna sanguinea periodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea parodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea gingivalisExtraembryonic
hemangiogenesisFetal circulation umbilical cord: Umbilical vein → Ductus venosus → Inferior vena cava → Heart → Pulmonary artery → Ductus arteriosus → Aorta → Umbilical artery
yolk sac: Vitelline veins · Vitelline arteriesCategories:- Arteries of the abdomen
- Embryology of cardiovascular system
- Cardiovascular system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.