- Vitelline veins
-
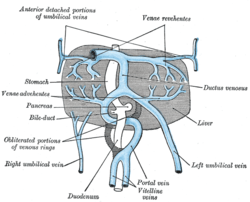
Vitelline veins The liver and the veins in connection with it, of a human embryo, twenty-four or twenty-five days old, as seen from the ventral surface. (Vitelline veins visible at center bottom.) Gray's subject #135 518 Carnegie stage 9 Days 28 The vitelline veins are veins which drain blood from the yolk sac.
Contents
Path
They run upward at first in front, and subsequently on either side of the intestinal canal.
They unite on the ventral aspect of the canal, and beyond this are connected to one another by two anastomotic branches, one on the dorsal, and the other on the ventral aspect of the duodenal portion of the intestine, which is thus encircled by two venous rings; into the middle or dorsal anastomosis the superior mesenteric vein opens.
The portions of the veins above the upper ring become interrupted by the developing liver and broken up by it into a plexus of small capillary-like vessels termed sinusoids.
Derivatives
The vitelline veins give rise to
- Hepatic veins
- Inferior portion of Inferior vena cava
- Portal vein
- Superior mesenteric vein[1]
The branches conveying the blood to the plexus are named the venae advehentes, and become the branches of the portal vein. The vessels draining the plexus into the sinus venosus are termed the venae revehentes, and form the future hepatic veins. Ultimately the left vena revehens no longer communicates directly with the sinus venosus, but opens into the right vena revehens. The persistent part of the upper venous ring, above the opening of the superior mesenteric vein, forms the trunk of the portal vein.
Additional images
References
- ^ "Vitelline veins: Derivatives". LifeHugger. http://mc.lifehugger.com/moc/1232/Vitelline_veins_Derivatives. Retrieved 2009-12-11.
External links
- Embryology at Temple Heart98/heart97a/sld020
- 127533117 at GPnotebook
- cardev-009 — Embryology at UNC
- cardev-016 — Embryology at UNC
Prenatal development/Mammalian development of circulatory system (GA 5, TE E5.11) Heart development Tubular heartSepta/ostiaAtrioventricular cushions/Septum intermedium · Primary interatrial foramen · Septum primum (Foramen secundum) · Septum secundum (Foramen ovale) · Aorticopulmonary septumOtherAtrioventricular canal · Primary interventricular foramenVasculogenesis,
angiogenesis,
and lymphangiogenesisBlood island of umbilical vesicle
Development of arteriesDevelopment of veinsDevelopment of lymph vesselsLymph sacsDevelopment of circulatory system about teeth near childrenanuli: Anulus sanguineus perienameleus · lacunae: Lacuna sanguinea supraenamelea (Ductus sanguineus mesialis · Ductus sanguineus distalis · Ductus sanguineus lingualis · Ductus sanguineus palatinus · Ductus sanguineus buccalis · Ductus sanguineus labialis), Lacuna sanguinea apicalis, Lacuna sanguinea periodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea parodontalis, Lacuna sanguinea gingivalisExtraembryonic
hemangiogenesisFetal circulation umbilical cord: Umbilical vein → Ductus venosus → Inferior vena cava → Heart → Pulmonary artery → Ductus arteriosus → Aorta → Umbilical artery
yolk sac: Vitelline veins · Vitelline arteriesCategories:- Embryology of cardiovascular system
- Cardiovascular system stubs
- Developmental biology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.