- Lymphadenopathy
-
Lymphadenopathy
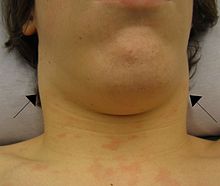
Cervical lymphadenopathy in someone with mononucleosisICD-10 I88, L04, R59.1 ICD-9 289.1-289.3, 683, 785.6 DiseasesDB 22225 eMedicine ped/1333 MeSH D008206 Lymphadenopathy is a term meaning "disease of the lymph nodes."[1] It is, however, almost synonymously used with "swollen/enlarged lymph nodes". It could be due to infection, auto-immune disease, or malignancy.
Inflammation of a lymph node is called lymphadenitis.[2] In practice, the distinction between lymphadenopathy and lymphadenitis is rarely made. (Inflammation of lymph channels is called lymphangitis.[3])
Contents
Types
- Localized lymphadenopathy : due to localized spot of infection e.g. an infected spot on the scalp will cause lymph nodes in the neck on that same side to swell up
- Generalized lymphadenopathy : due to generalized infection all over the body e.g. influenza
- persistent generalized lymphadenopathy (PGL) : persisting for a long time, possibly without an apparent cause
- Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy : lymphadenopathy associated with skin disease.
Tangier disease (ABCA1 deficiency) may also cause this
Cause
Enlarged lymph nodes are a common symptom in a number of infectious and malignant diseases. It is a recognized symptom of very many diseases, of which some are as follows:
- Reactive: acute infection (e.g. bacterial, or viral), or chronic infections (tuberculous lymphadenitis, cat-scratch disease).
- The most distinctive symptom of bubonic plague is extreme swelling of one or more lymph nodes that bulge out of the skin as "buboes." The buboes often become necrotic and may even rupture.
- Infectious mononucleosis is an acute viral infection, the hallmark of which is marked enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes.
- It is also a symptom of cutaneous anthrax, measles and Human African trypanosomiasis, the latter two giving lymphadenopathy in lymph nodes in the neck.
- Toxoplasmosis, a parasitic disease, gives a generalized lymphadenopathy (Piringer-Kuchinka lymphadenopathy).[4]
- Plasma cell variant of Castleman's disease - associated with HHV-8 infection and HIV infection.
- Mesenteric lymphadenitis after viral systemic infection (particularly in the GALT in the appendix) can commonly present like appendicitis.
- Tumoral:
- Primary: Hodgkin lymphoma and non-Hodgkin lymphoma give lymphadenopathy in all or a few lymph nodes. [4]
- Secondary: metastasis, Virchow's Node, Neuroblastoma, and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
- Autoimmune etiology: systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis all giving a generalized lymphadenopathy.[4]
- Immunocompromised etiology: AIDS. Generalized lymphadenopathy is an early sign of infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the virus that causes acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). "Lymphadenopathy syndrome" has been used to describe the first symptomatic stage of HIV progression, preceding a diagnosis of AIDS.[5]
- Bites from certain venomous snakes, most notably the black mamba, kraits, Australian brown snakes, coral snakes, tiger snakes, taipans, death adders, and some of the more toxic species of cobra.
- Unknown etiology: Kikuchi disease, progressive transformation of germinal centres, sarcoidosis, hyaline-vascular variant of Castleman's disease, Rosai-Dorfman disease, Kawasaki disease
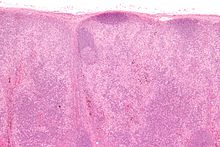
Benign (reactive) lymphadenopathy
There are three distinct patterns of benign lymphadenopathy:
- Follicular hyperplasia - Seen in infections, autoimmune disorders, and nonspecific reactions.
- Paracortical hyperplasia - Seen in viral infections, skin diseases, and nonspecific reactions.
- Sinus histiocytosis - Seen in lymph nodes draining limbs, inflammatory lesions, and malignancies.
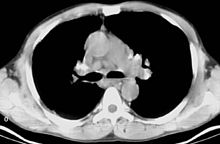
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy (BHL) is a radiographic term that describes the enlargement of mediastinal lymph nodes. It is easily and most commonly identified by a chest x-ray.
Causes of BHL
The following are causes of BHL:[6]
- Sarcoidosis
- Infection
- Tuberculosis
- Mycoplasma
- Intestinal Lipodystrophy (Whipple's Disease)[7]
- Malignancy
- Organic dust disease
- Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
- Such as bird fancier's lung
- Less common causes also exist:[citation needed]
- Churg-Strauss syndrome
- Human immunodeficiency virus
- Extrinsic allergic alveolitis
- Pneumoconiosis
- Adult-onset Still's disease
References
- ^ "lymphadenopathy" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ "lymphadenitis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ "lymphangitis" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ^ a b c Status and anamnesis, Anders Albinsson. Page 12
- ^ Mindel & Tenant-Flowers (2001) ABC of AIDS; natural history and management of early HIV infection, BMJ, 322 p1290 – 1293
- ^ M. Longmore, I. Wilkinson, T. Turmezei, CK. Cheug (2007). Oxford Handbook of Clinical Medicine 7th Edition. United States, New York: Oxford University Press. p. 179. ISBN 0-19356887-1.
- ^ Beers, Mark (2006). The Merck Manual.
Infectious skin disease: Bacterial skin disease (L00–L08, 680–686) Gram + Gram - α: Endemic typhus · Epidemic typhus · Scrub typhus · North Asian tick typhus · Queensland tick typhus · Flying squirrel typhus · Trench fever · Bacillary angiomatosis · African tick bite fever · American tick bite fever · Rickettsia aeschlimannii infection · Rickettsialpox · Rocky Mountain spotted fever · Human granulocytotropic anaplasmosis · Human monocytotropic ehrlichiosis · Flea-borne spotted fever · Japanese spotted fever · Mediterranean spotted fever · Flinders Island spotted fever · Verruga peruana · Brill–Zinsser disease · Brucellosis · Cat scratch disease · Oroya fever · Ehrlichiosis ewingii infectionβ: Gonococcemia/Gonorrhea/Primary gonococcal dermatitis · Melioidosis · Cutaneous Pasteurella hemolytica infection · Meningococcemia · Glanders · Chromobacteriosis infectionγ: Pasteurellosis · Tularemia · Vibrio vulnificus infection · Rhinoscleroma · Haemophilus influenzae cellulitis · Pseudomonal pyoderma/Pseudomonas hot-foot syndrome/Hot tub folliculitis/Ecthyma gangrenosum/Green nail syndrome · Q fever · Salmonellosis · Shigellosis · Plague · Granuloma inguinale · Chancroid · Aeromonas infectionε: Helicobacter cellulitisOtherSyphilid · Syphilis · Chancre · Yaws · Pinta · Bejel · Chlamydial infection · Leptospirosis · Rat-bite fever · Lyme disease · Lymphogranuloma venereum ·Unspecified
pathogenAbscess (Periapical abscess) · Boil/furuncle (Hospital furunculosis) · Carbuncle · Cellulitis (Paronychia/Pyogenic paronychia, Perianal cellulitis) · Acute lymphadenitis · Pilonidal cyst · PyodermaFolliculitis (Superficial pustular folliculitis, Sycosis vulgaris) · Pimple · Ecthyma · Pitted keratolysis · Trichomycosis axillaris · Necrotizing fascitis · Gangrene (Chronic undermining burrowing ulcers, Fournier gangrene) · Elephantiasis nostras · Blistering distal dactylitis · Botryomycosis · Malakoplakia · Gram-negative folliculitis · Gram-negative toe web infection · Pyomyositis · Blastomycosis-like pyoderma · Bullous impetigo · Chronic lymphangitis · Recurrent toxin-mediated perineal erythema · Tick-borne lymphadenopathy · Tropical ulcer ·Symptoms and signs: circulatory (R00–R03, 785) Cardiovascular Tachycardia/Bradycardia · Palpitation
Heart sounds: Heart murmur (Systolic, Diastolic, Continuous) · Gallop rhythm (Third heart sound, Fourth heart sound) · Pericardial friction rub · Split S2 · Heart clickVascular manifestations of heart disease (pulse): Pulsus tardus et parvus · Pulsus paradoxus · doubled (Pulsus bisferiens, Dicrotic pulse, Pulsus bigeminus) · Pulsus alternans · Carotid bruit · Cannon A wavesMyeloid/blood Lymphatic disease: Lymphatic organ disease (D73/E32/I88–I89, 254/289.4–289.5/457) Thymus Spleen Acquired asplenia/hyposplenism · Wandering spleen · Splenomegaly (Banti's syndrome) · Splenic infarctionTonsil see Template:Respiratory pathologyLymph node Lymphadenopathy/lymphadenitis · Generalized lymphadenopathy · Castleman's disease · Intranodal palisaded myofibroblastoma · Kikuchi diseaseM: LMO
anat(h, u, t, a, l)/phys/depv
noco/cong/tumr
proc
Categories:- Inflammations
- Diseases of veins, lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.