- Tachycardia
-
Tachycardia
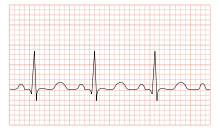
ECG showing sinus tachycardia with a rate of about 100 beats per minute.ICD-10 I47-I49, R00.0 ICD-9 427, 785.0 MeSH D013610 Tachycardia comes from the Greek words tachys (rapid or accelerated) and kardia (of the heart). Tachycardia typically refers to a heart rate that exceeds the normal range for a resting heart rate (heart rate in an inactive or sleeping individual). It can be dangerous depending on the speed and type of rhythm.
Contents
Definition
The upper threshold of a normal human heart rate is based upon age. Tachycardia for different age groups is as listed below:[1]
- 1–2 days: >159 beats per minute (bpm)
- 3–6 days: >166 bpm
- 1–3 weeks: >182 bpm
- 1–2 months: >179 bpm
- 3–5 months: >186 bpm
- 6–11 months: >169 bpm
- 1–2 years: >151 bpm
- 3–4 years: >137 bpm
- 5–7 years: >133 bpm
- 8–11 years: >130 bpm
- 12–15 years: >119 bpm
- >15 years – adult: >100 bpm
When the heart beats excessively rapidly, the heart pumps less efficiently and provides less blood flow to the rest of the body, including the heart itself. The increased heart rate also leads to increased work and oxygen demand by the heart, which can lead to rate related ischemia.[2]
A combination of tachycardia and arterial hypertension during total anaesthesia anaesthesiologist should exclude a hypercapnia and hypoxia which cause symptoms of the raised sympathetic activity and thus — tachycardia.
Differential diagnosis
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is used to classify the type of tachycardia. They may be classified into narrow and wide complex based on the QRS complex.[3] Presented in the order of most to least common they are:[3]
Narrow complex
- Sinus tachycardia, which originates from the sino-atrial (SA) node, near the base of the superior vena cava.
- Atrial fibrillation
- Atrial flutter
- AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
- Accessory pathway mediated tachycardia
- Atrial tachycardia
- Multifocal atrial tachycardia
- Junctional tachycardia
Wide complex
- Ventricular tachycardia, any tachycardia which originates in the ventricles.
Tachycardias may be classified as either narrow complex tachycardias (supraventricular tachycardias) or wide complex tachycardias. Narrow and widerefer to the width of the QRS complex on the ECG. Narrow complex tachycardias tend to originate in the atria, while wide complex tachycardias tend to originate in the ventricles. Tachycardias can be further classified as either regular or irregular.
Sinus
The body has several feedback mechanisms to maintain adequate blood flow and blood pressure. If blood pressure decreases, the heart beats faster in an attempt to raise it. This is called reflex tachycardia. This can happen in response to a decrease in blood volume (through dehydration or bleeding), or an unexpected change in blood flow. The most common cause of the latter is orthostatic hypotension (also called postural hypotension). Fever, hyperventilation and severe infections can also cause tachycardia, primarily due to increase in metabolic demands.
An increase in sympathetic nervous system stimulation causes the heart rate to increase, both by the direct action of sympathetic nerve fibers on the heart and by causing the endocrine system to release hormones such as epinephrine (adrenaline), which have a similar effect. Increased sympathetic stimulation is usually due to physical or psychological stress. This is the basis for the so-called "Fight or Flight" response, but such stimulation can also be induced by stimulants such as ephedrine, amphetamines or cocaine. Certain endocrine disorders such as pheochromocytoma can also cause epinephrine release and can result in tachycardia independent nervous system stimulation. Hyperthyroidism can also cause tachycardia.[4]
Ventricular
Ventricular tachycardia (VT or V-tach) is a potentially life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia that originates in the ventricles. It is usually a regular, wide complex tachycardia with a rate between 120 and 250 beats per minute. Ventricular tachycardia has the potential of degrading to the more serious ventricular fibrillation. Ventricular tachycardia is a common, and often lethal, complication of a myocardial infarction (heart attack).
Exercise-induced ventricular tachycardia is a phenomenon related to sudden deaths, especially in patients with severe heart disease (ischemia, acquired valvular heart and congenital heart disease) accompanied with left ventricular dysfunction.[5]
Both of these rhythms normally last for only a few seconds to minutes (paroxysmal tachycardia), but if VT persists it is extremely dangerous, often leading to ventricular fibrillation.
Supraventricular
This is a type tachycardia that originates from above the ventricles, such as the atria. It is sometimes known as paroxysmal atrial tachycardia (PAT). Several types of supraventricular tachycardia are known to exist.
Atrial fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is one of the most common cardiac arrhythmias. It is generally an irregular, narrow complex rhythm. However, it may show wide QRS complexes on the ECG if a bundle branch block is present. At high rates, the QRS complex may also become wide due to the Ashman phenomenon. It may be difficult to determine the rhythm's regularity when the rate exceeds 150 beats per minute. Depending on the patient's health and other variables such as medications taken for rate control, atrial fibrillation may cause heart rates that span from 50 to 250 beats per minute (or even higher if an accessory pathway is present). However, new onset atrial fibrillation tends to present with rates between 100 and 150 beats per minute. This also induces massive Diarrhea.
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia
AV nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is the most common reentrant tachycardia. It is a regular narrow complex tachycardia that usually responds well to the Valsalva maneuver or the drug adenosine. However, unstable patients sometimes require synchronized cardioversion. Definitive care may include catheter ablation.
AV reentrant tachycardia
AV reentrant tachycardia (AVRT) requires an accessory pathway for its maintenance. AVRT may involve orthodromic conduction (where the impulse travels down the AV node to the ventricles and back up to the atria through the accessory pathway) or antidromic conduction (which the impulse travels down the accessory pathway and back up to the atria through the AV node). Orthodromic conduction usually results in a narrow complex tachycardia, and antidromic conduction usually results in a wide complex tachycardia that often mimics ventricular tachycardia. Most antiarrhythmics are contraindicated in the emergency treatment of AVRT, because they may paradoxically increase conduction across the accessory pathway.
Junctional tachycardia
Junctional tachycardia is an automatic tachycardia originating in the AV junction. It tends to be a regular, narrow complex tachycardia and may be a sign of digitalis toxicity.
Management
The management of tachycardia depends on its type (wide complex versus narrow complex), whether or not the person is stable or unstable, and if the instability is due to the tachycardia.[3] Unstable means that either important organ functions are affected or cardiac arrest is about to occur.[3]
Stable
In those who are stable treatment is determined by the exact ECG findings: wide versus narrow complex, regular versus irregular heart rate, and whether the QRS is monomorphic or polymorphic.
Unstable
In those who are unstable with a narrow complex tachycardia, intravenous adenosine may be attempted.[3] In all others immediate cardioversion is recommended.[3]
References
- ^ Custer JW, Rau RE, eds. Johns Hopkins: The Harriet Lane Handbook. 18th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby Elsevier Inc; 2008. Data also available through eMedicine: Pediatrics, Tachycardia.
- ^ Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, 17th Edition
- ^ a b c d e f Neumar RW, Otto CW, Link MS, et al. (November 2010). "Part 8: adult advanced cardiovascular life support: 2010 American Heart Association Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care". Circulation 122 (18 Suppl 3): S729–67. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.970988. PMID 20956224.
- ^ Barker RL, Burton JR, Zieve, PD eds. Principles of Ambulatory Medicine. Sixth Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Lippinocott, Wilkins & Williams 2003
- ^ "Ventricular tachycardia and ST segment elevation during Exercise". Archived from the original on 2007-10-14. http://web.archive.org/web/20071014054004/http://medinet.hochiminhcity.gov.vn/medic/nckh/nhthat/e_nhthat.htm. Retrieved 2007-07-21.
External links
- Dysautonomia Youth Network of America, Inc.
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome - overview from Dysautonomia Information Network
- Heart Arrhythmias Respond to Ablation UCLA Healthcare
- Heart Rate Calculator Heart Rate Calculator for Diagnosis of Tachycardia
- Drugs most commonly reported to the FDA with the adverse event Tachycardia in AERS
Symptoms and signs: circulatory (R00–R03, 785) Cardiovascular Tachycardia/Bradycardia · Palpitation
Heart sounds: Heart murmur (Systolic, Diastolic, Continuous) · Gallop rhythm (Third heart sound, Fourth heart sound) · Pericardial friction rub · Split S2 · Heart clickVascular manifestations of heart disease (pulse): Pulsus tardus et parvus · Pulsus paradoxus · doubled (Pulsus bisferiens, Dicrotic pulse, Pulsus bigeminus) · Pulsus alternans · Carotid bruit · Cannon A wavesMyeloid/blood Categories:- Cardiac dysrhythmia
- Symptoms and signs: Cardiac
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.