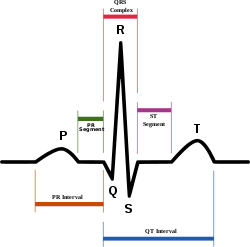- Osborn wave
-
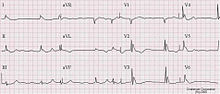 Atrial fibrillation and Osborne J wave in a person with hypothermia
Atrial fibrillation and Osborne J wave in a person with hypothermia
Osborn waves (also known as camel-hump sign, late delta wave, hathook junction, hypothermic wave, prominent J wave ,[1] K wave, H wave or current of injury) are a electrocardiogram finding.[2]
Osborn waves are positive deflections occurring at the junction between the QRS complex and the ST segment,[3][4] where the S point, also known as the J point, has a myocardial infarction-like elevation.
Causes
They are usually observed in people suffering from hypothermia with a temperature of less than 32 C,[5] though they may also occur in people with high blood levels of calcium (hypercalcemia), brain injury, vasospastic angina, or ventricular fibrillation.
Eponymm
These waves were definitively described in 1953 by JJ Osborn and were named in his honor.[6]
References
- ^ Aydin M, Gursurer M, Bayraktaroglu T, Kulah E, Onuk T (2005). "Prominent J wave (Osborn wave) with coincidental hypothermia in a 64-year-old woman". Tex Heart Inst J 32 (1): 105. PMC 555838. PMID 15902836. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=555838.
- ^ Maruyama M, Kobayashi Y, Kodani E, et al. (2004). "Osborn waves: history and significance". Indian Pacing Electrophysiol J 4 (1): 33–9. PMC 1501063. PMID 16943886. http://www.ipej.org/4/33.
- ^ "ecg_6lead018.html". http://library.med.utah.edu/kw/ecg/mml/ecg_6lead018.html. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ^ "THE MERCK MANUAL OF GERIATRICS, Ch. 67, Hyperthermia and Hypothermia, Fig. 67-1". http://www.merck.com/mkgr/mmg/figures/67f1.jsp. Retrieved 2008-12-20.
- ^ Marx, John (2010). Rosen's emergency medicine: concepts and clinical practice 7th edition. Philadelphia, PA: Mosby/Elsevier. p. 1869. ISBN 9780323054720.
- ^ Osborn JJ. Experimental hypothermia: Respiratory and blood pH changes in relation to cardiac function. Am J Physiol 1953; 175: 389-398.
Cardiovascular disease: heart disease · Circulatory system pathology (I00–I52, 390–429) Ischaemic Active ischemiaAngina pectoris (Prinzmetal's angina, Stable angina) · Acute coronary (Unstable angina, Myocardial infarction / heart attack)hours (Myocardial stunning, Hibernating myocardium) · days (Myocardial rupture) · weeks (Aneurysm of heart/Ventricular aneurysm, Dressler's syndrome)Layers Infective endocarditis (Subacute bacterial endocarditis) · noninfective endocarditis (Nonbacterial thrombotic endocarditis, Libman-Sacks endocarditis)Valvesmitral (regurgitation, prolapse, stenosis) · aortic (stenosis, insufficiency) · tricuspid (stenosis, insufficiency) · pulmonary (stenosis, insufficiency)Conduction/
arrhythmiaHeart block: Sinoatrial · AV (1°, 2°, 3°) · Intraventricular (Bundle branch/Right/Left, Left anterior fascicular/Left posterior fascicular, Bifascicular/Trifascicular) · Adams–Stokes syndromePremature contractionWolff-Parkinson-White · Lown-Ganong-LevineFlutter/fibrillationPacemakerWandering pacemaker · Ectopic pacemaker/Ectopic beat · Parasystole · Multifocal atrial tachycardia · Pacemaker syndromeOther/ungroupedhexaxial reference system (Right axis deviation, Left axis deviation) · QT (Short QT syndrome) · T (T wave alternans) · ST (Osborn wave, ST elevation, ST depression)Cardiomegaly Other Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.