- Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
-
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor Classification and external resources 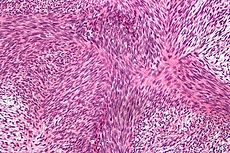
Micrograph of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour with the typical herringbone pattern. H&E stain.ICD-O: M9540/3 MeSH D018317 A malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (also known as "Malignant schwannoma,"[1] "Neurofibrosarcoma,"[1] and "Neurosarcoma"[1]) is a form of cancer of the connective tissue surrounding nerves. Given its origin and behavior it is classified as a sarcoma. About half the cases are diagnosed in people with neurofibromatosis; the lifetime risk for an MPNST in patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 is 8-13%.[2] MPNST with rhabdomyoblastomatous component are called Malignant triton tumors.
The first-line treatment is surgical resection with wide margins. Chemotherapy (e.g. high-dose doxorubicin) and often radiotherapy are done as adjuvant and/or neoadjuvant treatment.
Contents
Causes
Soft tissue sarcomas have been linked within families, so it is hypothesized that neurofibrosarcoma may be genetic, although researchers still do not know the exact cause of the disease. Evidence supporting this hypothesis includes loss of heterozygosity on the 17p chromosome. The p53 (a tumor suppressor gene in the normal population) genome on 17p in neurofibrosarcoma patients is mutated, increasing the probability of cancer. The normal p53 gene will regulate cell growth and inhibit any uncontrollable cell growth in the healthy population; since p53 is inactivated in neurofibrosarcoma patients, they are much more susceptible to developing tumors.
Symptoms
Symptoms may include:
- Swelling in the extremities (arms or legs), also called peripheral edema; the swelling often is painless.
- Difficulty in moving the extremity that has the tumor, including a limp.
- Soreness localized to the area of the tumor or in the extremity.
Diagnosis
The most conclusive test for a patient with a potential neurofibrosarcoma is a tumor biopsy (taking a sample of cells directly from the tumor itself). MRIs, X-rays, CT scans, and bone scans can aid in locating a tumor and/or possible metastasis.
Treatment
Treatment for neurofibrosarcoma is similar to that of other cancers. Surgery is an option; the removal of the tumor along with surrounding tissue may be vital for the patient’s survival. For discrete, localized tumors, surgery is often followed by radiation therapy of the excised area to reduce the chance of recurrence. For patients suffering from neurofibrosarcomas in an extremity, if the tumor is vascularized (has its own blood supply) and has many nerves going through it and/or around it, amputation of the extremity may be necessary. Some surgeons argue that amputation should be the procedure of choice when possible, due to the increased chance of a better quality of life. Otherwise, surgeons may opt for a limb-saving treatment, by removing less of the surrounding tissue or part of the bone, which is replaced by a metal rod or grafts. Radiation will also be used in conjunction with surgery, especially if the limb was not amputated. Radiation is rarely used as a sole treatment. In some instances, the oncologist may choose chemotherapy drugs when treating a patient with neurofibrosarcoma, usually in conjunction with surgery. Patients taking chemotherapy must be prepared for the side effects that come with any other chemotherapy treatment, such as; hair loss, lethargy, weakness, etc.
Prognosis
Patient response to treatment will vary based on age, health, and the tolerance to medications and therapies. Also, the extent of the disease i.e. metastasis and size/location of the tumor, have an effect on the patient’s recovery
It is a rare tumor type, with a relatively poor prognosis.[3]
See also
- Keratinizing metaplasia
- List of cutaneous conditions
References
- ^ a b c Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 1-4160-2999-0.
- ^ Evans DG, Baser ME, McGaughran J, Sharif S, Howard E, Moran A (May 2002). "Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumours in neurofibromatosis 1". J. Med. Genet. 39 (5): 311–4. doi:10.1136/jmg.39.5.311. PMC 1735122. PMID 12011145. http://jmg.bmj.com/cgi/content/full/39/5/311.
- ^ Neville H, Corpron C, Blakely ML, Andrassy R (2003). "Pediatric neurofibrosarcoma". J. Pediatr. Surg. 38 (3): 343–6; discussion 343–6. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2003.50105. PMID 12632346.
External links
- Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNST) by David S. Geller, MD and Mark Gebhardt, MD
Nervous tissue tumors/NS neoplasm/Neuroectodermal tumor (ICD-O 9350–9589) (C70–C72, D32–D33, 191–192/225) Endocrine/
sellar (9350–9379)other: PinealomaCNS
(9380–9539)Astrocytoma (Pilocytic astrocytoma, Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, Fibrillary (also diffuse or lowgrade) astrocytomas, Anaplastic astrocytoma, Glioblastoma multiforme)Multiple/unknownNeuroblastoma (Esthesioneuroblastoma, Ganglioneuroblastoma) · Medulloblastoma · Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumorPrimitiveHematopoieticPNS: NST
(9540–9579)cranial and paraspinal nerves: Neurofibroma (Neurofibrosarcoma, Neurofibromatosis) · Neurilemmoma/Schwannoma (Acoustic neuroma) · Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumornote: not all brain tumors are of nervous tissue, and not all nervous tissue tumors are in the brain (see brain metastases)
Categories:- PNS neoplasia
- Dermal and subcutaneous growths
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
