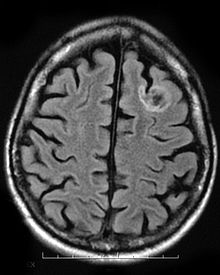
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour
-
Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour Classification and external resources 
DNETICD-O: 9413/0 Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour, commonly abbreviated DNT or DNET, is a type of brain tumour.
It appears similar to oligodendroglioma, but with visible neurons.[1]
It falls into Grade I of the WHO classification of brain tumours and, generally, has a good prognosis.[2][3]
Contents
Treatment
Treatment of DNTs is usually surgical resection.[5]
References
- ^ O'Brien DF; Farrell M; Delanty N et al. (December 2007). "The Children's Cancer and Leukaemia Group guidelines for the diagnosis and management of dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumours". Br J Neurosurg 21 (6): 539–49. doi:10.1080/02688690701594817. PMID 18071981. http://www.informaworld.com/openurl?genre=article&doi=10.1080/02688690701594817&magic=pubmed%7C%7C1B69BA326FFE69C3F0A8F227DF8201D0.
- ^ Daumas-Duport C, Scheithauer B, Chodkiewicz J, Laws E, Vedrenne C (1988). "Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor: a surgically curable tumor of young patients with intractable partial seizures. Report of thirty-nine cases". Neurosurgery 23 (5): 545–56. doi:10.1227/00006123-198811000-00002. PMID 3143922.
- ^ Salah Uddin ABM, Jarmi T. Oligodendroglioma. eMedicine.com. URL: http://www.emedicine.com/neuro/topic281.htm. Accessed on: April 9, 2007.
- ^ Campos AR; Clusmann H; von Lehe M et al. (February 2009). "Simple and complex dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumors (DNT) variants: clinical profile, MRI, and histopathology". Neuroradiology 51 (7): 433–43. doi:10.1007/s00234-009-0511-1. PMID 19242688.
- ^ Ray WZ; Blackburn SL; Casavilca-Zambrano S et al. (March 2009). "Clinicopathologic features of recurrent dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumor and rare malignant transformation: a report of 5 cases and review of the literature". J. Neurooncol. 94 (2): 283–92. doi:10.1007/s11060-009-9849-9. PMID 19267228.
See also
External links
- Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour - www.childrenshospital.org
Nervous tissue tumors/NS neoplasm/Neuroectodermal tumor (ICD-O 9350–9589) (C70–C72, D32–D33, 191–192/225) Endocrine/
sellar (9350–9379)other: PinealomaCNS
(9380–9539)Astrocytoma (Pilocytic astrocytoma, Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma, Fibrillary (also diffuse or lowgrade) astrocytomas, Anaplastic astrocytoma, Glioblastoma multiforme)Ependymoma · SubependymomaMultiple/unknownMature
neuronGanglioneuroma: Ganglioglioma · Retinoblastoma · Neurocytoma · Dysembryoplastic neuroepithelial tumour · Lhermitte-Duclos diseaseNeuroblastoma (Esthesioneuroblastoma, Ganglioneuroblastoma) · Medulloblastoma · Atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumorPrimitiveMeningiomas
(meninges)HematopoieticPNS: NST
(9540–9579)cranial and paraspinal nerves: Neurofibroma (Neurofibrosarcoma, Neurofibromatosis) · Neurilemmoma/Schwannoma (Acoustic neuroma) · Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumornote: not all brain tumors are of nervous tissue, and not all nervous tissue tumors are in the brain (see brain metastases)
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.