- Ulnar nerve
Infobox Nerve
Name = Ulnar nerve
Latin = nervus ulnaris
GraySubject = 210
GrayPage = 943 |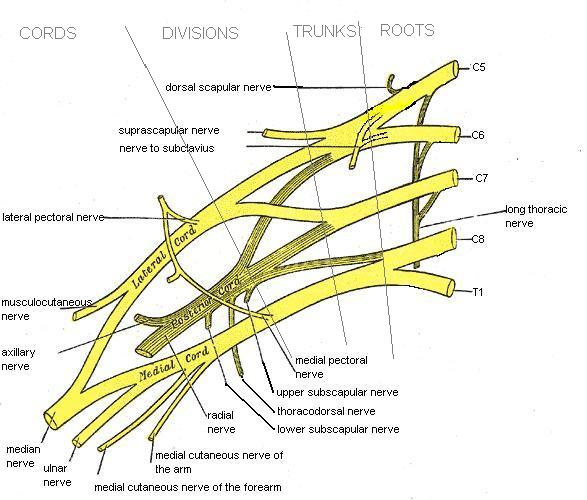
Caption = Click image to enlarge - ulnar nerve is visible in lower left

Caption2 = Nerves of the left upper extremity. (Ulnar labeled at center left.)
Innervates =flexor carpi ulnaris flexor digitorum profundis lumbrical muscle sopponens digiti minimi
flexor digiti minimi
abductor digiti minimiinterossei adductor pollicis
BranchFrom =Medial cord
BranchTo =
MeshName = Ulnar+nerve
MeshNumber = A08.800.800.720.050.850
DorlandsPre = n_05
DorlandsSuf = 12566994
Inhuman anatomy , the ulnar nerve is a nerve which runs near theulna bone. Aggravation of this nerve is commonly referred to as hitting one's "funny bone." The ulnar nerve is the largest unprotected nerve in the human body (meaning, unprotected by muscle or bone), and the only unprotected nerve that does not serve a purely sensory function (those nerves specifically meant to perceive changes in the environment, such as nerves in the skin). This nerve is directly connected to the little finger.Course
Arm
The ulnar nerve comes from the medial cord of the
brachial plexus , and runs inferior on the posterior and medial (posteromedial) aspects of thehumerus down the arm, going behind themedial epicondyle , through thecubital tunnel , at the elbow (where it is exposed for a few centimeters, just above the joint). Because of the mild pain and tingling throughout the forearm associated with an inadvertent impact of the nerve at this point, it is usually called the funny bone. (It may also have to do with its location relative to the humerus, as the name "humerus" is ahomophone to the word "humor ous").Forearm
It enters the anterior (flexor/front) compartment of the forearm through the two heads of flexor carpi ulnaris and runs alongside the
ulna . There it supplies one and a half muscles (flexor carpi ulnaris & medial half of flexor digitorum profundus). It soon joins with theulnar artery , and the two travel inferiorly together, deep to theflexor carpi ulnaris muscle.Here it gives off the following branches: cite book |author=Ellis, Harold; Susan Standring; Gray, Henry David |title=Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice |publisher=Elsevier Churchill Livingstone |location=St. Louis, Mo |year=2005 |pages=700 |isbn=0-443-07168-3 |oclc= |doi=]
*muscular branches of ulnar nerve
*palmar branch of ulnar nerve
*dorsal branch of ulnar nerve Hand
After it travels down the ulna, the ulnar nerve enters the palm of the hand. Unlike the
median nerve which travels below theflexor retinaculum of the hand and through thecarpal tunnel , the ulnar nerve and artery pass superficial to the flexor retinaculum via theulnar canal .Here it gives off the following branches: cite book |author=Ellis, Harold; Susan Standring; Gray, Henry David |title=Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice |publisher=Elsevier Churchill Livingstone |location=St. Louis, Mo |year=2005 |pages=726 |isbn=0-443-07168-3 |oclc= |doi=]
*Superficial branch of ulnar nerve
*Deep branch of ulnar nerve Branches and innervation
Muscular
The ulnar nerve and its branches innervate the following muscles in the forearm and hand:
An Articular branch that passes to the elbow joint while the ulnar nerve is passing between the olecranon and medial epicondyle of the humerus.
*In the
forearm , via themuscular branches of ulnar nerve :
**Flexor carpi ulnaris
**Flexor digitorum profundus (medial half)*In the
hand , via thedeep branch of ulnar nerve :
**hypothenar muscles
***Opponens digiti minimi
***Abductor digiti minimi
***Flexor digiti minimi brevis
**Adductor pollicis
**The third and fourth lumbrical muscles
**Dorsal interossei
**Palmar interossei *In the hand, via the
superficial branch of ulnar nerve :
**Palmaris brevis Cutaneous
The ulnar nerve also provides
sensory innervation to the part of the hand corresponding to the fourth and fifth digits:
*Palmar branch of ulnar nerve - anterior
*Dorsal branch of ulnar nerve - posteriorUlnar nerve entrapment
The Ulnar nerve can be trapped or pinched in various ways as it proceeds down the arm from the Brachial plexus to the ring and middle fingers. One common cause is
cubital tunnel syndrome, where the tunnel runs the inner outside side of the elbow. Pinching of the nerve often causes tingling symptoms in the little and ring fingers. In some cases moderate to severe pain is experienced from pinching this nerve. Often such pins and needles sensations can be caused by sleeping wrongly on your arm, but sometimes the problems last for days. In severe cases, surgery is performed to move the nerve.ee also
*
Radial nerve
*Axillary nerve
*Median nerve
*Musculocutaneous nerve
=AdditionalReferences
External links
*
* [http://www.cubital-tunnel.com Cubital Tunnel Support Forums]
* - "The major subdivisions and terminal nerves of thebrachial plexus ."
* - "Anterior view of the nerves, vessels, and superficial tendons that cross the leftwrist ."
* - "Transverse section through thecarpal tunnel and distal row of thecarpal bones."
*
*
*
* - "Axilla, dissection, anterior view"
* [http://www.neuro.wustl.edu/neuromuscular/nanatomy/ulnar.htm Overview at neuro.wustl.edu]
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
