- Dorsal interossei of the hand
-
For the muscles of the foot, see Dorsal interossei muscles (foot).
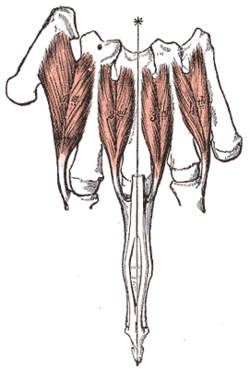
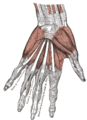
Dorsal interossei of the hand The Interossei dorsales of left hand. Latin musculi interossei dorsales manus Gray's subject #126 464 Origin metacarpals Insertion proximal phalanges Artery Dorsal metacarpal artery and palmar metacarpal artery Nerve deep branch of ulnar nerve Actions abduct finger Antagonist Palmar interossei muscles The dorsal interossei of the hand are muscles that occupy the space between the metacarpals.
Contents
Structure
There are four dorsal interossei in each hand. They are specified as 'dorsal' to contrast them with the palmar interossei, which are located on the anterior side of the metacarpals.
The dorsal interosseous muscles are bipennate, with each muscle arising by two heads from the adjacent sides of the metacarpal bones, but more extensively from the metacarpal bone of the finger into which the muscle is inserted. They are inserted into the bases of the proximal phalanges and into the extensor expansion of the corresponding extensor digitorum tendon. The middle digit has two dorsal interossei insert onto it while the first digit (thumb) and the fifth digit (little finger) have none.
# Origin Insertion first on the radial side of the second metacarpal and the proximal half of the ulnar side of the first metacarpal on the radial side of the base of the second proximal phalanx (index finger) and the extensor expansion second on the radial side of the third metacarpal and the ulnar side of the second metacarpal on the radial side of the third proximal phalanx (the middle finger) and the extensor expansion third on the radial side of the fourth metacarpal and the ulnar side of the third metacarpal on the ulnar side of the third proximal phalanx (the middle finger) and the extensor expansion fourth on the radial side of the fifth metacarpal and the ulnar side of the fourth metacarpal on the ulnar side of the fourth proximal phalanx (the ring finger) and the extensor expansion The first dorsal interosseous muscle is larger than the others. Between its two heads, the radial artery passes from the back of the hand into the palm.
Between the heads of dorsal interossei two, three, and four, a perforating branch from the deep palmar arch is transmitted.
Innervation
All interosseous muscles of the hand are innervated by the deep branch of the ulnar nerve.
Actions
The primary action of the dorsal interossei is to: flex the metacarpophalangeal joint (MCP) and to extend the interphalangeal joints and thus assist the lumbricals. In addition, a secondary function is to abduct the fingers away from the middle finger. This is in contrast to the palmar interossei, which adduct the fingers. This is often remembered by the mnemonic DAB PAD, short for "Dorsal ABducts, Palmar ADducts".[1]
Additional images
References
- ^ "Interossei of hand: actions". lifehugger. 2008-11-01. http://mc.lifehugger.com/moc/352/interossei-hand-actions. Retrieved 2009-04-26.
External links
- LUC dih
- UWASH interossei
- SUNY Labs 09:08-0101
- dorsal+interossei+%28interosseous+muscles%29+of+hand at eMedicine Dictionary
- Mnemonic at medicalmnemonics.com 293 96
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
List of muscles of upper limbs (TA A04.6, GA 4.432) Shoulder deltoid · rotator cuff (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis) · teres major
fascia: Deltoid fascia · Supraspinous fascia · Infraspinous fasciaArm
(compartments)OtherForearm OtherHand Lateral volarMedial volarhypothenar (opponens digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi brevis, abductor digiti minimi) · palmaris brevisIntermediateposterior: Extensor retinaculum · Extensor expansion
anterior: Flexor retinaculum · Palmar aponeurosisCategories:- Muscles of the upper limb
- Hand
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.