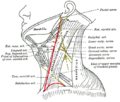
Transverse cervical nerve
- Transverse cervical nerve
-
| Nerve: Transverse cervical nerve |
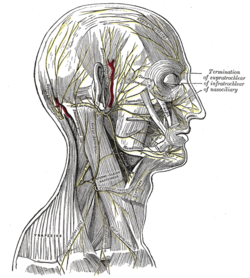 |
| The nerves of the scalp, face, and side of neck. ("Cervical cutaneous" identified at center.) |
 |
| Plan of the cervical plexus. ("Superficial cervical" labeled at center.) |
| Latin |
nervus transversus colli |
| Gray's |
subject #210 927 |
| Innervates |
Cutaneious innervation of the anterior and lateral parts of the neck |
| From |
cervical plexus (C2 and C3) |
The transverse cervical nerve (superficial cervical or cutaneous cervical) arises from the second and third cervical nerves, turns around the posterior border of the sternocleidomastoideus about its middle, and, passing obliquely forward beneath the external jugular vein to the anterior border of the muscle, it perforates the deep cervical fascia, and divides beneath the Platysma into ascending and descending branches, which are distributed to the antero-lateral parts of the neck.
During dissection, the SCM is the landmark. The transverse cervical nerves will pass horizontally directly over the SCM from Erb's point.
Additional images
-
Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve
-
Side of neck, showing chief surface markings.
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Categories:
- Neuroanatomy stubs
- Nerves of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation.
2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Transverse cervical artery — Artery: Transverse cervical artery Superficial dissection of the right side of the neck, showing the carotid and subclavian arteries. Transverse cervical artery is labeled, branching from the thyrocervical trunk … Wikipedia
Cervical plexus — Nerve: Cervical plexus Dermatome distribution of the trigeminal nerve (Superficial cervical plexus visible in purple, at center bottom.) Latin plexus cervicalis Gray s … Wikipedia
cervical nerve transverse — nervus transversus colli … Medical dictionary
Nerve — A bundle of fibers that uses electrical and chemical signals to transmit sensory and motor information from one body part to another. See nervous system. * * * A whitish cordlike structure composed of one or more bundles (fascicles) of myelinated … Medical dictionary
Cervical part of internal carotid artery — Artery: Cervical portion Latin pars cervicalis arteriae carotidis internae Gray s subject #146 567 The Cervical portion (or cervical segment) of the internal carotid begins at the bifurcation of the common carotid, opposite the upper border of… … Wikipedia
Phrenic nerve — Nerve: Phrenic nerve The phrenic nerve and its relations with the vagus nerve. (Phrenic labeled at upper left.) … Wikipedia
Cervical vertebrae — Bone: Cervical vertebrae Vertebral column … Wikipedia
Great auricular nerve — Nerve: Great auricular nerve The nerves of the scalp, face, and side of neck. (Great auricular visible below ear.) … Wikipedia
Cervical vertebra 6 — The cervical vertebra 6 (C6) is a vertebra of the spinal column. The cervical spinal nerve 6 (C6) passes out above it. The first cricoid ring is directly opposite C6. C6 is the vertebral level that the oesophagus becomes continuous with the… … Wikipedia
Cervical vertebra 5 — The cervical vertebra 5 (C5) is a vertebra of the spinal column. The cervical spinal nerve 5 (C5) passes out above it. C5 and C6 are the areas that see the highest amount of cervical spine trauma. References … Wikipedia