- Globus pallidus
-
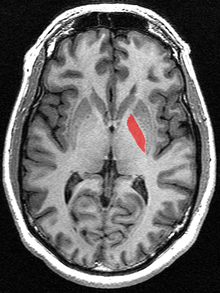
Brain: Globus pallidus 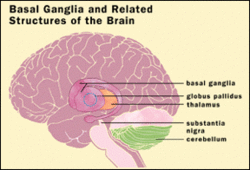
Globus pallidus labeled at bottom right. 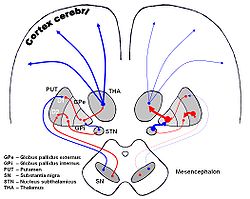
DA-loops in PD NeuroNames hier-213 MeSH Globus+Pallidus NeuroLex ID birnlex_1234 The globus pallidus (Latin for "pale globe") also known as paleostriatum, is a sub-cortical structure of the brain. Topographically, it is part of the telencephalon, but retains close functional ties with the subthalamus - both of which are part of the extrapyramidal motor system.[1] The globus pallidus is a major component of the basal ganglia core along with the striatum and its direct target, the substantia nigra. The latter are made up of similar neuronal elements, have similar afferents from the dorsal striatum and have a similar synaptology; neither receive cortical afferents.
Contents
History of name
The origin of the name is not established. It was known by Dejerine (1906) but not by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1909–1911). As the elements in no way have the shape of a globe, Foix and Nicolesco (1925), the Vogts (1941), Crosby et al. (1962) followed by the Terminologia anatomica proposed the simpler term (neuter adjective) of pallidum ("pale"). For a long time the globus pallidus was linked to the putamen and termed the lentiform nucleus (nucleus lenticularis or lentiformis), a heterogeneous anatomical entity that is part of the striatum rather than the pallidum. The link with the substantia nigra pars reticulata was stressed very early on due to the similarities in dendritic arborisation (and they are sometimes known as the pallidonigral set) but, in spite of strong evidence, this association remains controversial.
Parts
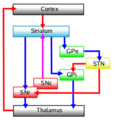
In primates, the dorsal pallidum, or globus pallidus, is divided into two parts by the medial medullary lamina. These are often termed "internal" and "external" (the internal globus pallidus [GPi] and the external globus pallidus [GPe]); both are composed of closed nuclei surrounded by myelinic walls.
The ventral pallidum lies within the substantia innominata (Latin for un-named substance) and receives efferent connections from the ventral striatum (the nucleus accumbens and the olfactory tubercle). It projects to the dorsomedial nucleus of the dorsal thalamus which, in turn, projects to the prefrontal cortex; it also projects to the pedunculopontine nucleus and tegmental motor areas. Its function is to serve as a limbic-somatic motor interface and it is involved in the planning and inhibition of movements from the dorsal striatopallidal complex.
Structure
Pallidal nuclei are made up of the same neuronal components. In primates, almost all pallidal neurons are very large, parvalbumin positive, with very large dendritic arborizations. These have the peculiarity of having the three-dimensional shape of flat discs, parallel to one another, parallel to the border of the pallidum[2] and perpendicular to the afferent striatopallidal axons.[3] There are only a few small local circuitry neurons.
The globus pallidus is traversed by the numerous myelinated axons of the striato-pallidonigral bundle that give it the pale appearance from which it is named.
The ultrastructure is very peculiar, as the long dendrites are everywhere, without discontinuity, covered by synapses.[4][5]
Pallidonigral pacemaker
The two pallidal nuclei and the two nigral (pars compacta and pars reticulata) parts constitute a high-frequency autonomous pacemaker[6] (see primate basal ganglia system#Pallido-nigral_set_and_pacemaker)
Common afferents
The two parts receive successively a large quantity of GABAergic axonal terminal arborisations from the striatum through the dense striato-pallidonigral bundle. The synaptology is very peculiar (see primate basal ganglia system).[4][5] The striatal afference contribute for more than 90% of synapses.[citation needed] The two pallidal nuclei receives dopaminergic axons from the pars compacta of the substantia nigra.
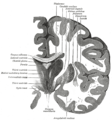
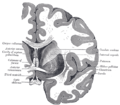
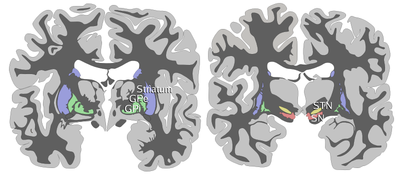 Coronal slices of human brain showing the basal ganglia.
Coronal slices of human brain showing the basal ganglia.
ROSTRAL: striatum, globus pallidus (GPe and GPi)
CAUDAL: subthalamic nucleus (STN), substantia nigra (SN)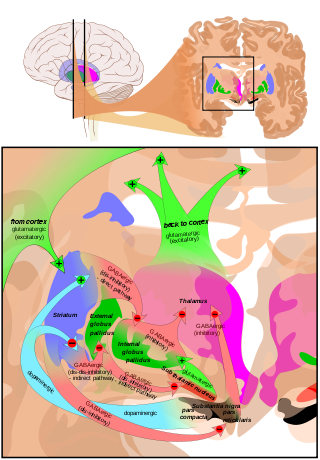 Overview of the main circuits of the basal ganglia. Globus pallidus externa and interna are shown in green. Picture shows 2 coronal slices that have been superimposed to include the involved basal ganglia structures. + and - signs at the point of the arrows indicate respectively whether the pathway is excitatory or inhibitory in effect. Green arrows refer to excitatory glutamatergic pathways, red arrows refer to inhibitory GABAergic pathways and turquoise arrows refer to dopaminergic pathways that are excitatory on the direct pathway and inhibitory on the indirect pathway.
Overview of the main circuits of the basal ganglia. Globus pallidus externa and interna are shown in green. Picture shows 2 coronal slices that have been superimposed to include the involved basal ganglia structures. + and - signs at the point of the arrows indicate respectively whether the pathway is excitatory or inhibitory in effect. Green arrows refer to excitatory glutamatergic pathways, red arrows refer to inhibitory GABAergic pathways and turquoise arrows refer to dopaminergic pathways that are excitatory on the direct pathway and inhibitory on the indirect pathway.
See also
References
- ^ Theme atlas of anatomy: head and neuroanathomy. http://books.google.si/books?id=wlGDPwz_7KoC&lpg=PA211&ots=UDAn_MHYjU&dq=%2Bsubthalamus%20part%20%22globus%20pallidus%22&pg=PA211#v=onepage&q=+subthalamus%20part%20%22globus%20pallidus%22&f=false.
- ^ Yelnik, J., Percheron, G., and François, C. (1984) A Golgi analysis of the primate globus pallidus. II- Quantitative morphology and spatial orientation of dendritic arborisations. J. Comp. Neurol. 227:200-213
- ^ Percheron, G.,Yelnik, J. and François. C. (1984) A Golgi analysis of the primate globus pallidus. III-Spatial organization of the striato-pallidal complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 227: 214-227
- ^ a b Fox, C.A., Andrade, A.N. Du Qui, I.J., Rafols, J.A. (1974) The primate globus pallidus. A Golgi and electron microscopic study. J. Hirnforsch. 15: 75-93
- ^ a b di Figlia, M., Pasik, P., Pasik, T. (1982) A Golgi and ultrastructural study of the monkey globus pallidus. J. Comp. Neurol. 212: 53-75
- ^ Surmeier, D.J., Mercer, J.N. and Savio Chan, C. (2005) Autonomous pacemakers in the basal ganglia: who needs excitatory synapses anyway? Cur. Opin.Neurobiol. 15:312-318.
Additional images
External links
- Globus+pallidus at eMedicine Dictionary
- Paleostriatum at eMedicine Dictionary
- Diagram at uni-tuebingen.de
- NIF Search - Globus Pallidus via the Neuroscience Information Framework
Human brain, cerebrum, Interior of the cerebral hemispheres—Rostral Basal ganglia and associated structures (TA A14.1.09.321–552, GA 9.832–837) Basal ganglia Ventral striatumOtherInternal capsule (Anterior limb · Genu · Posterior limb, Optic radiation)
Corona radiata · External capsule · Extreme capsule
Pallidothalamic tracts: Thalamic fasciculus (Ansa lenticularis, Lenticular fasciculus) · Subthalamic fasciculusRhinencephalon Other basal forebrain Archicortex:
Hippocampal formation/
Hippocampus anatomyCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.