- Dorsal striatum
-
Brain: Dorsal striatum 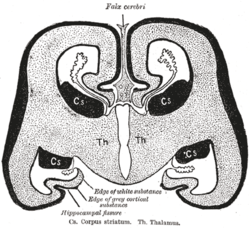
Diagrammatic coronal section of brain to show relations of neopallium. Cs. dorsal striatum. Th. Thalamus. 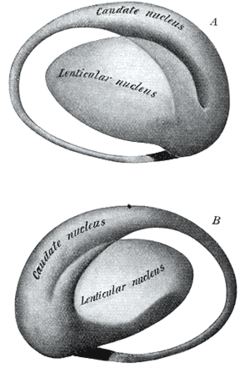
Two views of a model of the striatum: A, lateral aspect; B, mesal aspect. Gray's subject #189 833 NeuroNames ancil-255 MeSH Dorsal+Striatum The dorsal striatum, corpus striatum or striated body is a compound structure consisting of the caudate nucleus, and the lentiform nucleus (which consists of the putamen and the globus pallidus).[1] It is a pair of nuclear masses which form the basal ganglia, along with the subthalamic nucleus and the substantia nigra.
Contents
Definition
The term has been defined in a few different ways:
- According to the 1917 version of Gray's Anatomy, it is the combination of the lentiform nucleus and the caudate nucleus
- According to BrainInfo it is a part of the basal ganglia comprising the globus pallidus and striatum.[2]
- It may also refer to both the basal ganglia and the internal capsule collectively.[3]
Anatomy
A part of the dorsal striatum is imbedded in the white substance of the hemisphere, and is therefore external to the ventricle; it is termed the extraventricular portion, or the lentiform nucleus.
The remainder, however, projects into the ventricle, and is named the intraventricular portion, or the caudate nucleus.
The dorsal striatum has received its name from the striped appearance which a section of its anterior part presents, in consequence of diverging white fibers being mixed with the gray substance which forms its chief mass. From lateral to medial, there lies the external capsule (white matter), the lentiform nucleus (gray matter), the internal capsule (white matter), and the caudate nucleus (gray matter).
References
- ^ "Basal Ganglia and Cerebellum". http://thalamus.wustl.edu/course/cerebell.html.
- ^ "BrainInfo". http://braininfo.rprc.washington.edu/Scripts/ancilcentraldirectory.aspx?ID=255.
- ^ "General Description of the Central Nervous System". http://www.csuchico.edu/~pmccaffrey/syllabi/CMSD%20320/362unit2.html.
External links
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
See also
- striatum
- ventral striatum
- caudate nucleus
- lentiform nucleus
Human brain, cerebrum, Interior of the cerebral hemispheres—Rostral Basal ganglia and associated structures (TA A14.1.09.321–552, GA 9.832–837) Basal ganglia Ventral striatumOtherInternal capsule (Anterior limb · Genu · Posterior limb, Optic radiation)
Corona radiata · External capsule · Extreme capsule
Pallidothalamic tracts: Thalamic fasciculus (Ansa lenticularis, Lenticular fasciculus) · Subthalamic fasciculusRhinencephalon Other basal forebrain Diagonal band of Broca · Stria terminalisArchicortex:
Hippocampal formation/
Hippocampus anatomyCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
