- Discitis
-
Discitis Classification and external resources 
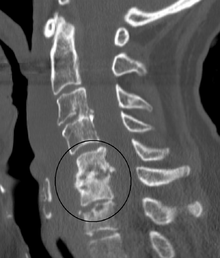
Discitis in a 2 year old child.ICD-10 M46.4 ICD-9 722.90 DiseasesDB 3847 MedlinePlus 000993 eMedicine article/1263845 MeSH D015299 Discitis or diskitis is an infection in the intervertebral disc space that affects different age groups, but usually spontaneously affects children under 8 years of age. Nonetheless, discitis occurs post surgically in approximately 1-2 percent of patients status post spine surgery.
Contents
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms include severe back pain, leading to lack of mobility. Some very young children may refuse to walk and arching of the back is possible. In post-operative situations, the symptoms occur within a week and result in severe low back pain or neck pain (depending on the surgical location). If untreated, the discitis may resolve on its own, cause a chronic low grade infection, or progress to osteomyelitis and possibly even an epidural abscess. In case of concomitant inflammation of one or more vertebrae (in such cases usually a the areas adjacent to the intervertebral disc spaces)[1] the condition is called spondylodiscitis.
Causes
There is debate as to the cause, although hematogenous seeding of the offending organism is favored as well as direct spread, e.g. following instrumentation. It is important to differentiate between spontaneous discitis which is usually from hematologic spread from a urinary or respiratory infection versus that from a post-operative complication which usually involves skin flora such as staph aureus.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is usually apparent on MRI although plain X-rays and CT examinations can be suggestive. The MRI will reveal air changes in the disc and possibly even external involvement involving the bone or epidural regions. A biopsy may be performed and helps with diagnosis in some cases but often an organism is not obtained. C-reactive protein levels and ESR levels will be elevated and are useful for treatment. Often, the white blood cell count will be normal and the patient will be apyrexic.
Treatment
Treatment usually includes antibiotics, and reducing the mobility of the affected region, either with a back brace or a plaster cast. Without treatment, the patient may form an abscess which may need to be surgically corrected. Due to the poor vascularity of the disc, drugs required for treatment often include potent agents such as Ciprofloxacin along with Vancomycin. Occasionally, oral drugs can be used to treat the infection but it may fail and IV drugs may be required.
If the patient is an adult many surgeons and doctors now recommend moving little and often and within the pain limits of the medication. Discs respond to osmotic pressure therefore movement is beneficial to increase their blood flow and fluid dynamics. This is why disc patients are no longer told to bed rest. In children whether to bed rest or move a little is decided on an individual basis, depending on the site and severity of the discitis.
References
- ^ Page 147 in:Hinchcliffe, Ronald; Fritz Hefti; Jundt, Gernot; Freuler, F. (2007). Pediatric Orthopedics in Practice. Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3-540-69963-5.
- ^ Langlois, S.; Cedoz, J. P.; Lohse, A.; Toussirot, E.; Wendling, D. (2005). "Aseptic discitis in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: a retrospective study of 14 cases". Joint, bone, spine : revue du rhumatisme 72 (3): 248–253. doi:10.1016/j.jbspin.2004.05.015. PMID 15850997.
External links
- Learning Radiology: Damage appears on an X-ray image
Discitis in young children: From The Hospital for Children, London, EnglandDorsopathies / spinal disease (M40–M54, 720–724, 737) Deforming dorsopathies OtherSpondylopathy inflammatory: Spondylitis (Ankylosing spondylitis) · Sacroiliitis · Discitis · Spondylodiscitis · Pott diseaseBack pain Intervertebral disc disorder M: JNT
anat(h/c, u, t, l)/phys
noco(arth/defr/back/soft)/cong, sysi/epon, injr
proc, drug(M01C, M4)
Categories:- Infectious diseases
- Vertebral column disorders
- Medicine stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.