- Sulindac
-
Sulindac 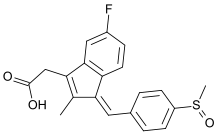
Systematic (IUPAC) name {(1Z)-5-fluoro-2-methyl-1-[4-(methylsulfinyl)benzylidene]-1H-indene-3-yl}acetic acid Clinical data Trade names Clinoril AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a681037 Pregnancy cat. C(AU) C(US) Legal status POM (UK) ℞-only (US) Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability Approximately 90% (Oral) Metabolism ? Half-life 7.8 hours, metabolites up to 16.4 hours Excretion Renal (50%) and fecal (25%) Identifiers CAS number 38194-50-2 
ATC code M01AB02 PubChem CID 1548887 DrugBank APRD01243 ChemSpider 1265915 
UNII 184SNS8VUH 
KEGG D00120 
ChEBI CHEBI:9352 
ChEMBL CHEMBL15770 
Chemical data Formula C20H17FO3S Mol. mass 356.412 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Sulindac is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug of the arylalkanoic acid class that is marketed in the UK & U.S. by Merck as Clinoril.
Contents
Uses
Like other NSAIDs, it is useful in the treatment of acute or chronic inflammatory conditions. Sulindac is a prodrug, derived from sulfinylindene, that is converted in the body to the active NSAID. More specifically, the agent is converted by liver enzymes to a sulfide that is excreted in the bile and then reabsorbed from the intestine. This is thought to help maintain constant blood levels with reduced gastrointestinal side effects. Some studies have shown sulindac to be relatively less irritating to the stomach than other NSAIDs except for drugs of the COX-2 inhibitor class[citation needed]. The exact mechanism of its NSAID properties is unknown, but it is thought to act on enzymes COX-1 and COX-2, inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis.
Its usual dosage is 150-200 milligrams twice per day, with food. It should not be used by persons with a history of major allergic reactions (urticaria or anaphylaxis) to aspirin or other NSAIDs, and should be used with caution by persons having pre-existing peptic ulcer disease. Sulindac is much more likely than other NSAIDs to cause damage to the liver or pancreas.
Sulindac seems to have a property, independent of COX-inhibition, of reducing the growth of polyps and precancerous lesions in the colon, especially in association with familial adenomatous polyposis, and may have other anti-cancer properties.[1][2]
Sulindac is an effective tocolytic and may be used in the treatment of preterm labor. In common with other NSAIDs, sulindac is currently being investigated for its role in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Since it was found that the sulfoxide functional group can be reduced by methionine sulfoxide reductase A (MsrA), a possible anti-oxidative capability is being discussed.
Sulindac inhibits canonical Wnt signaling by blocking the PDZ Domain of the protein dishevelled.[3]
Litigation
In September 2010 a federal jury in New Hampshire awarded $21 million to a woman blinded and scarred by a generic brand of Sulindac (Clinoril) that she took for shoulder pain. Karen Bartlett said she suffered extreme burns to her skin, mucus membranes and eyes after taking sulindac.
References
- ^ Scheper MA, Nikitakis NG, Chaisuparat R, Montaner S, Sauk JJ (March 2007). "Sulindac induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in vivo in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma". Neoplasia 9 (3): 192–9. doi:10.1593/neo.06781. PMC 1838577. PMID 17401459. http://www.neoplasia.com/abstract.php?msid=1062.
- ^ Shiff SJ, Qiao L, Tsai LL, Rigas B (July 1995). "Sulindac sulfide, an aspirin-like compound, inhibits proliferation, causes cell cycle quiescence, and induces apoptosis in HT-29 colon adenocarcinoma cells". J. Clin. Invest. 96 (1): 491–503. doi:10.1172/JCI118060. PMC 185223. PMID 7615821. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=185223.
- ^ Lee HJ, Wang NX, Shi DL, Zheng JJ. Sulindac Inhibits Canonical Wnt Signaling by Blocking the PDZ Domain of the Protein Dishevelled.
External links
Anti-inflammatory products (M01A) Pyrazolidine/Butylpyrazolidines Ampyrone • Clofezone • Kebuzone • Metamizole • Mofebutazone • Oxyphenbutazone • Phenazone • Phenylbutazone • Sulfinpyrazone • Feprazone •Acetic acid derivatives
and related substancesAceclofenac • Acemetacin • Alclofenac • Bromfenac • Bumadizone • Bufexamac • Diclofenac • Difenpiramide • Etodolac • Fentiazac • Indometacin • Ketorolac • Lonazolac • Oxametacin • Proglumetacin • Sulindac • Tolmetin • Zomepirac • AmfenacOxicams Propionic acid derivatives Alminoprofen • Benoxaprofen • Dexibuprofen • Dexketoprofen • Fenbufen • Fenoprofen • Flunoxaprofen • Flurbiprofen • Ibuprofen • Ibuproxam • Indoprofen • Ketoprofen • Naproxen • Oxaprozin • Pirprofen • Suprofen • Tiaprofenic acidFenamates Coxibs Other 
This drug article relating to the musculoskeletal system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
