- MAPK8
-
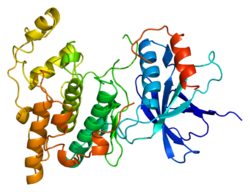
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK8 gene.[1][2]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase is activated by various cell stimuli, and targets specific transcription factors, and thus mediates immediate-early gene expression in response to cell stimuli. The activation of this kinase by tumor-necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha) is found to be required for TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis. This kinase is also involved in UV radiation-induced apoptosis, which is thought to be related to the cytochrome c-mediated cell death pathway. Studies of the mouse counterpart of this gene suggested that this kinase play a key role in T cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation. Four alternately spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.[3]
Contents
Interactions
MAPK8 has been shown to interact with SPIB,[4] DUSP1,[5] Activating transcription factor 2,[6][7][8][9] SH3BP5,[10] GSTP1,[11] MAPK8IP1,[12][13] MAP2K7,[9][14] CRK,[15] MAP2K4,[16][17][8][9][14] DUSP22,[18] Myc,[19] MAP3K2,[14] DUSP10,[20] REL,[21] MAPK8IP3,[22][23] IRS1,[24][25] MAP3K1[26] and C-jun.[27][28][1][29][30][21][31][9]
References
- ^ a b Derijard B, Hibi M, Wu IH, Barrett T, Su B, Deng T, Karin M, Davis RJ (Apr 1994). "JNK1: a protein kinase stimulated by UV light and Ha-Ras that binds and phosphorylates the c-Jun activation domain". Cell 76 (6): 1025–37. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(94)90380-8. PMID 8137421.
- ^ Gupta S, Barrett T, Whitmarsh AJ, Cavanagh J, Sluss HK, Derijard B, Davis RJ (Jul 1996). "Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors". EMBO J 15 (11): 2760–70. PMC 450211. PMID 8654373. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=450211.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: MAPK8 mitogen-activated protein kinase 8". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=5599.
- ^ Mao, C; Ray-Gallet D, Tavitian A, Moreau-Gachelin F (Feb. 1996). "Differential phosphorylations of Spi-B and Spi-1 transcription factors". Oncogene (ENGLAND) 12 (4): 863–73. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 8632909.
- ^ Slack, D N; Seternes O M, Gabrielsen M, Keyse S M (May. 2001). "Distinct binding determinants for ERK2/p38alpha and JNK map kinases mediate catalytic activation and substrate selectivity of map kinase phosphatase-1". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (19): 16491–500. doi:10.1074/jbc.M010966200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11278799.
- ^ Raingeaud, J; Gupta S, Rogers J S, Dickens M, Han J, Ulevitch R J, Davis R J (Mar. 1995). "Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 270 (13): 7420–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.13.7420. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 7535770.
- ^ Fuchs, S Y; Xie B, Adler V, Fried V A, Davis R J, Ronai Z (Dec. 1997). "c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases target the ubiquitination of their associated transcription factors". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 272 (51): 32163–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.51.32163. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9405416.
- ^ a b Chen, Z; Cobb M H (May. 2001). "Regulation of stress-responsive mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase pathways by TAO2". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (19): 16070–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100681200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11279118.
- ^ a b c d Tournier, C; Whitmarsh A J, Cavanagh J, Barrett T, Davis R J (Jul. 1997). "Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 7 is an activator of the c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (UNITED STATES) 94 (14): 7337–42. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.14.7337. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 23822. PMID 9207092. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=23822.
- ^ Wiltshire, Carolyn; Matsushita Masato, Tsukada Satoshi, Gillespie David A F, May Gerhard H W (Nov. 2002). "A new c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)-interacting protein, Sab (SH3BP5), associates with mitochondria". Biochem. J. (England) 367 (Pt 3): 577–85. doi:10.1042/BJ20020553. ISSN 0264-6021. PMC 1222945. PMID 12167088. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1222945.
- ^ Wang, T; Arifoglu P, Ronai Z, Tew K D (Jun. 2001). "Glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTP1-1) inhibits c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK1) signaling through interaction with the C terminus". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (24): 20999–1003. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101355200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11279197.
- ^ Whitmarsh, A J; Cavanagh J, Tournier C, Yasuda J, Davis R J (Sep. 1998). "A mammalian scaffold complex that selectively mediates MAP kinase activation". Science (UNITED STATES) 281 (5383): 1671–4. doi:10.1126/science.281.5383.1671. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9733513.
- ^ Cai, Yi; Lechner Mark S, Nihalani Deepak, Prindle Marc J, Holzman Lawrence B, Dressler Gregory R (Jan. 2002). "Phosphorylation of Pax2 by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase and enhanced Pax2-dependent transcription activation". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (2): 1217–22. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109663200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11700324.
- ^ a b c Cheng, J; Yang J, Xia Y, Karin M, Su B (Apr. 2000). "Synergistic Interaction of MEK Kinase 2, c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Kinase 2, and JNK1 Results in Efficient and Specific JNK1 Activation". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 20 (7): 2334–42. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.7.2334-2342.2000. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 85399. PMID 10713157. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85399.
- ^ Girardin, S E; Yaniv M (Jul. 2001). "A direct interaction between JNK1 and CrkII is critical for Rac1-induced JNK activation". EMBO J. (England) 20 (13): 3437–46. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.13.3437. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 125507. PMID 11432831. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=125507.
- ^ Lee, Clement M; Onésime Djamila, Reddy C Damodara, Dhanasekaran N, Reddy E Premkumar (Oct. 2002). "JLP: A scaffolding protein that tethers JNK/p38MAPK signaling modules and transcription factors". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (United States) 99 (22): 14189–94. doi:10.1073/pnas.232310199. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 137859. PMID 12391307. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=137859.
- ^ Park, Hee-Sae; Kim Mi-Sung, Huh Sung-Ho, Park Jihyun, Chung Jongkyeong, Kang Sang Sun, Choi Eui-Ju (Jan. 2002). "Akt (protein kinase B) negatively regulates SEK1 by means of protein phosphorylation". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (4): 2573–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110299200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11707464.
- ^ Aoyama, K; Nagata M, Oshima K, Matsuda T, Aoki N (Jul. 2001). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dual specificity phosphatase, LMW-DSP2, that lacks the cdc25 homology domain". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (29): 27575–83. doi:10.1074/jbc.M100408200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11346645.
- ^ Noguchi, K; Kitanaka C, Yamana H, Kokubu A, Mochizuki T, Kuchino Y (Nov. 1999). "Regulation of c-Myc through phosphorylation at Ser-62 and Ser-71 by c-Jun N-terminal kinase". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 274 (46): 32580–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.46.32580. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10551811.
- ^ Tanoue, T; Moriguchi T, Nishida E (Jul. 1999). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dual specificity phosphatase, MKP-5". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 274 (28): 19949–56. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.28.19949. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10391943.
- ^ a b Meyer, C F; Wang X, Chang C, Templeton D, Tan T H (Apr. 1996). "Interaction between c-Rel and the mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 1 signaling cascade in mediating kappaB enhancer activation". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (15): 8971–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.15.8971. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8621542.
- ^ Ito, M; Yoshioka K, Akechi M, Yamashita S, Takamatsu N, Sugiyama K, Hibi M, Nakabeppu Y, Shiba T, Yamamoto K I (Nov. 1999). "JSAP1, a Novel Jun N-Terminal Protein Kinase (JNK)-Binding Protein That Functions as a Scaffold Factor in the JNK Signaling Pathway". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 19 (11): 7539–48. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 84763. PMID 10523642. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=84763.
- ^ Kelkar, N; Gupta S, Dickens M, Davis R J (Feb. 2000). "Interaction of a Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Module with the Neuronal Protein JIP3". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 20 (3): 1030–43. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.3.1030-1043.2000. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 85220. PMID 10629060. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85220.
- ^ Aguirre, Vincent; Werner Eric D, Giraud Jodel, Lee Yong Hee, Shoelson Steve E, White Morris F (Jan. 2002). "Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (2): 1531–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101521200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11606564.
- ^ Aguirre, V; Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White M F (Mar. 2000). "The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307)". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (12): 9047–54. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.12.9047. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10722755.
- ^ Xu, S; Cobb M H (Dec. 1997). "MEKK1 binds directly to the c-Jun N-terminal kinases/stress-activated protein kinases". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 272 (51): 32056–60. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.51.32056. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9405400.
- ^ Ishitani, Tohru; Takaesu Giichi, Ninomiya-Tsuji Jun, Shibuya Hiroshi, Gaynor Richard B, Matsumoto Kunihiro (Dec. 2003). "Role of the TAB2-related protein TAB3 in IL-1 and TNF signaling". EMBO J. (England) 22 (23): 6277–88. doi:10.1093/emboj/cdg605. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 291846. PMID 14633987. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=291846.
- ^ Nishitoh, H; Saitoh M, Mochida Y, Takeda K, Nakano H, Rothe M, Miyazono K, Ichijo H (Sep. 1998). "ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2". Mol. Cell (UNITED STATES) 2 (3): 389–95. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80283-X. ISSN 1097-2765. PMID 9774977.
- ^ Yazgan, Oya; Pfarr Curt M (Aug. 2002). "Regulation of two JunD isoforms by Jun N-terminal kinases". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (33): 29710–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204552200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12052834.
- ^ Tada, K; Okazaki T, Sakon S, Kobarai T, Kurosawa K, Yamaoka S, Hashimoto H, Mak T W, Yagita H, Okumura K, Yeh W C, Nakano H (Sep. 2001). "Critical roles of TRAF2 and TRAF5 in tumor necrosis factor-induced NF-kappa B activation and protection from cell death". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 276 (39): 36530–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.M104837200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11479302.
- ^ Cano, E; Hazzalin C A, Kardalinou E, Buckle R S, Mahadevan L C (Nov. 1995). "Neither ERK nor JNK/SAPK MAP kinase subtypes are essential for histone H3/HMG-14 phosphorylation or c-fos and c-jun induction". J. Cell. Sci. (ENGLAND) 108 ( Pt 11): 3599–609. ISSN 0021-9533. PMID 8586671.
External Links
Further reading
- Davis RJ (2000). "Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases". Cell 103 (2): 239–52. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00116-1. PMID 11057897.
- Liu J, Lin A (2007). "Wiring the cell signaling circuitry by the NF-kappa B and JNK1 crosstalk and its applications in human diseases". Oncogene 26 (22): 3267–78. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1210417. PMID 17496921.
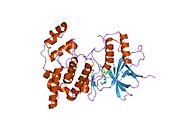
PDB gallery 1jnk: THE C-JUN N-TERMINAL KINASE (JNK3S) COMPLEXED WITH MGAMP-PNP1pmn: Crystal structure of JNK3 in complex with an imidazole-pyrimidine inhibitor1pmq: The structure of JNK3 in complex with an imidazole-pyrimidine inhibitor1pmu: The crystal structure of JNK3 in complex with a phenantroline inhibitor1pmv: The structure of JNK3 in complex with a dihydroanthrapyrazole inhibitor1ukh: Structural basis for the selective inhibition of JNK1 by the scaffolding protein JIP1 and SP6001251uki: Structural basis for the selective inhibition of JNK1 by the scaffolding protein JIP1 and SP6001252b1p: inhibitor complex of JNK32exc: Inhibitor complex of JNK32g01: Pyrazoloquinolones as Novel, Selective JNK1 inhibitors2gmx: Selective Aminopyridine-Based C-Jun N-terminal Kinase inhibitors with cellular activity2h96: Discovery of Potent, Highly Selective, and Orally Bioavailable Pyridine Carboxamide C-jun NH2-terminal Kinase Inhibitors2no3: Novel 4-anilinopyrimidines as potent JNK1 Inhibitors2o0u: Crystal structure of human JNK3 complexed with N-{3-cyano-6-[3-(1-piperidinyl)propanoyl]-4,5,6,7-tetrahydrothieno[2,3-c]pyridin-2-yl}-1-naphthalenecarboxamide2o2u: Crystal structure of human JNK3 complexed with N-(3-cyano-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1-benzothien-2-yl)-2-fluorobenzamide2ok1: Crystal structure of JNK3 bound to N-benzyl-4-(4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1H-pyrazol-3-yl)-1H-pyrrole-2-carboxamideThis article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Kinases: Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11-12) Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1-EC 2.7.11.20) Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1)Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (EC 2.7.11.2)Dephospho-(reductase kinase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.3)(isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)) kinase (EC 2.7.11.5)(tyrosine 3-monooxygenase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.6)Myosin-heavy-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.7)Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.8)Goodpasture-antigen-binding protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.9)-IκB kinase (EC 2.7.11.10)cAMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.11)cGMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.12)Protein kinase C (EC 2.7.11.13)Rhodopsin kinase (EC 2.7.11.14)Beta adrenergic receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.15)G-protein coupled receptor kinases (EC 2.7.11.16)Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent (EC 2.7.11.17)BRSK2, CAMK1, CAMK2A, CAMK2B, CAMK2D, CAMK2G, CAMK4, MLCK, CASK, CHEK1, CHEK2, DAPK1, DAPK2, DAPK3, STK11, MAPKAPK2, MAPKAPK3, MAPKAPK5, MARK1, MARK2, MARK3, MARK4, MELK, MKNK1, MKNK2, NUAK1, NUAK2, OBSCN, PASK, PHKG1, PHKG2, PIM1, PIM2, PKD1, PRKD2, PRKD3, PSKH1, SNF1LK2, KIAA0999, STK40, SNF1LK, SNRK, SPEG, TSSK2, Kalirin, TRIB1, TRIB2, TRIB3, TRIO, Titin, DCLK1Myosin light-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.18)MYLK, MYLK2, MYLK3, MYLK4Phosphorylase kinase (EC 2.7.11.19)Elongation factor 2 kinase (EC 2.7.11.20)Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.21-EC 2.7.11.30) Polo kinase (EC 2.7.11.21)Cyclin-dependent kinase (EC 2.7.11.22)(RNA-polymerase)-subunit kinase (EC 2.7.11.23)Mitogen-activated protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.24)Extracellular signal-regulated (MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK4, MAPK6, MAPK7, MAPK12, MAPK15), C-Jun N-terminal (MAPK8, MAPK9, MAPK10), P38 mitogen-activated protein (MAPK11, MAPK13, MAPK14)MAP3K (EC 2.7.11.25)Tau-protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.26)(acetyl-CoA carboxylase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.27)-Tropomyosin kinase (EC 2.7.11.28)-Low-density-lipoprotein receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.29)-Receptor protein serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.30)Dual-specificity kinases (EC 2.7.12) This transferase article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.