- CHEK1
-
Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CHEK1 gene.[1][2]
Chk1 is a kinase that phosphorylates cdc25, an important phosphatase in cell cycle control, particularly for entry into mitosis. Cdc25, when phosphorylated on serine 216 by chk1 becomes bound by an adaptor protein in the cytoplasm. Therefore it is inhibited from removing the inhibiting phosphate from MPF (mitotic/maturation promoting factor) added by Wee1. Consequently, a cell is prevented from entering mitosis.
References
- ^ Sanchez Y, Wong C, Thoma RS, Richman R, Wu Z, Piwnica-Worms H, Elledge SJ (Sep 1997). "Conservation of the Chk1 checkpoint pathway in mammals: linkage of DNA damage to Cdk regulation through Cdc25". Science 277 (5331): 1497–501. doi:10.1126/science.277.5331.1497. PMID 9278511.
- ^ Flaggs G, Plug AW, Dunks KM, Mundt KE, Ford JC, Quiggle MR, Taylor EM, Westphal CH, Ashley T, Hoekstra MF, Carr AM (Feb 1998). "Atm-dependent interactions of a mammalian chk1 homolog with meiotic chromosomes". Curr Biol 7 (12): 977–86. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(06)00417-9. PMID 9382850.
Further reading
- Giaccia AJ, Kastan MB (1998). "The complexity of p53 modulation: emerging patterns from divergent signals.". Genes Dev. 12 (19): 2973–83. doi:10.1101/gad.12.19.2973. PMID 9765199.
- Kastan MB, Lim DS (2001). "The many substrates and functions of ATM.". Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1 (3): 179–86. doi:10.1038/35043058. PMID 11252893.
- Chini CC, Chen J (2005). "Claspin, a regulator of Chk1 in DNA replication stress pathway.". DNA Repair (Amst.) 3 (8-9): 1033–7. doi:10.1016/j.dnarep.2004.03.001. PMID 15279790.
- Peng CY, Graves PR, Thoma RS, et al. (1997). "Mitotic and G2 checkpoint control: regulation of 14-3-3 protein binding by phosphorylation of Cdc25C on serine-216.". Science 277 (5331): 1501–5. doi:10.1126/science.277.5331.1501. PMID 9278512.
- Ouyang B, Li W, Pan H, et al. (1999). "The physical association and phosphorylation of Cdc25C protein phosphatase by Prk.". Oncogene 18 (44): 6029–36. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202983. PMID 10557092.
- Kim ST, Lim DS, Canman CE, Kastan MB (2000). "Substrate specificities and identification of putative substrates of ATM kinase family members.". J. Biol. Chem. 274 (53): 37538–43. doi:10.1074/jbc.274.53.37538. PMID 10608806.
- Shieh SY, Ahn J, Tamai K, et al. (2000). "The human homologs of checkpoint kinases Chk1 and Cds1 (Chk2) phosphorylate p53 at multiple DNA damage-inducible sites.". Genes Dev. 14 (3): 289–300. PMC 316358. PMID 10673501. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=316358.
- Graves PR, Yu L, Schwarz JK, et al. (2000). "The Chk1 protein kinase and the Cdc25C regulatory pathways are targets of the anticancer agent UCN-01.". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (8): 5600–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.8.5600. PMID 10681541.
- Semba S, Ouyang H, Han SY, et al. (2000). "Analysis of the candidate target genes for mutation in microsatellite instability-positive cancers of the colorectum, stomach, and endometrium.". Int. J. Oncol. 16 (4): 731–7. PMID 10717241.
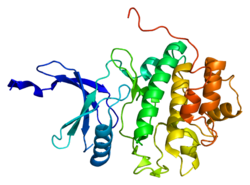
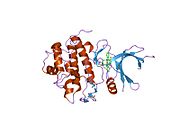
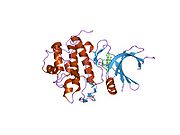
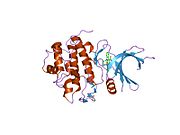
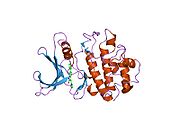
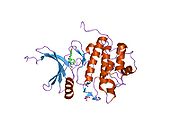
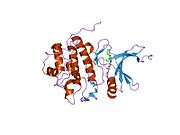
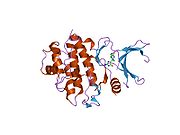
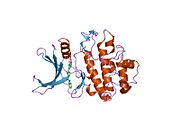
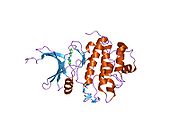
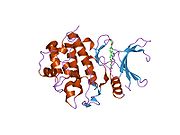
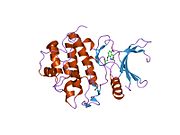
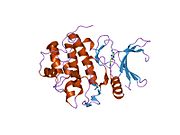
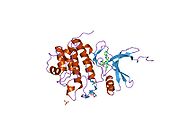
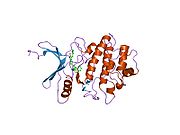
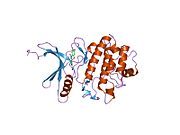
- Chen P, Luo C, Deng Y, et al. (2000). "The 1.7 A crystal structure of human cell cycle checkpoint kinase Chk1: implications for Chk1 regulation.". Cell 100 (6): 681–92. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80704-7. PMID 10761933.
- Liu Q, Guntuku S, Cui XS, et al. (2000). "Chk1 is an essential kinase that is regulated by Atr and required for the G(2)/M DNA damage checkpoint.". Genes Dev. 14 (12): 1448–59. doi:10.1101/gad.840500. PMC 316686. PMID 10859164. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=316686.
- Bulavin DV, Higashimoto Y, Popoff IJ, et al. (2001). "Initiation of a G2/M checkpoint after ultraviolet radiation requires p38 kinase.". Nature 411 (6833): 102–7. doi:10.1038/35075107. PMID 11333986.
- Zhao H, Piwnica-Worms H (2001). "ATR-mediated checkpoint pathways regulate phosphorylation and activation of human Chk1.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 21 (13): 4129–39. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.13.4129-4139.2001. PMC 87074. PMID 11390642. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=87074.
- Feijoo C, Hall-Jackson C, Wu R, et al. (2001). "Activation of mammalian Chk1 during DNA replication arrest: a role for Chk1 in the intra-S phase checkpoint monitoring replication origin firing.". J. Cell Biol. 154 (5): 913–23. doi:10.1083/jcb.200104099. PMC 1255922. PMID 11535615. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1255922.
- Xie S, Wu H, Wang Q, et al. (2001). "Plk3 functionally links DNA damage to cell cycle arrest and apoptosis at least in part via the p53 pathway.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (46): 43305–12. doi:10.1074/jbc.M106050200. PMID 11551930.
- Latonen L, Taya Y, Laiho M (2001). "UV-radiation induces dose-dependent regulation of p53 response and modulates p53-HDM2 interaction in human fibroblasts.". Oncogene 20 (46): 6784–93. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204883. PMID 11709713.
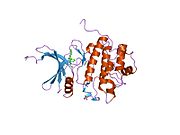
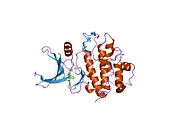
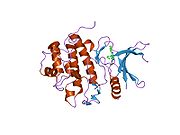
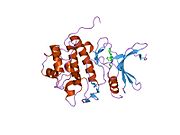
PDB gallery 1ia8: THE 1.7 A CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF HUMAN CELL CYCLE CHECKPOINT KINASE CHK11nvq: The Complex Structure Of Checkpoint Kinase Chk1/UCN-011nvr: The Complex Structure Of Checkpoint Kinase Chk1/Staurosporine1nvs: The Complex Structure Of Checkpoint Kinase Chk1/SB2180781zlt: Crystal Structure of Chk1 Complexed with a Hymenaldisine Analog1zys: Co-crystal structure of Checkpoint Kinase Chk1 with a pyrrolo-pyridine inhibitor2ayp: Crystal Structure of CHK1 with an Indol Inhibitor2br1: STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN OF NOVEL CHK1 INHIBITORS: INSIGHTS INTO HYDROGEN BONDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND AFFINITY2brb: STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN OF NOVEL CHK1 INHIBITORS: INSIGHTS INTO HYDROGEN BONDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND AFFINITY2brg: STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN OF NOVEL CHK1 INHIBITORS: INSIGHTS INTO HYDROGEN BONDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND AFFINITY2brh: STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN OF NOVEL CHK1 INHIBITORS: INSIGHTS INTO HYDROGEN BONDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND AFFINITY2brm: STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN OF NOVEL CHK1 INHIBITORS: INSIGHTS INTO HYDROGEN BONDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND AFFINITY2brn: STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN OF NOVEL CHK1 INHIBITORS: INSIGHTS INTO HYDROGEN BONDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND AFFINITY2bro: STRUCTURE-BASED DESIGN OF NOVEL CHK1 INHIBITORS: INSIGHTS INTO HYDROGEN BONDING AND PROTEIN-LIGAND AFFINITY2c3j: IDENTIFICATION OF A BURIED POCKET FOR POTENT AND SELECTIVE INHIBITION OF CHK1: PREDICTION AND VERIFICATION2c3k: IDENTIFICATION OF A BURIED POCKET FOR POTENT AND SELECTIVE INHIBITION OF CHK1: PREDICTION AND VERIFICATION2c3l: IDENTIFICATION OF A BURIED POCKET FOR POTENT AND SELECTIVE INHIBITION OF CHK1: PREDICTION AND VERIFICATION2cgu: IDENTIFICATION OF CHEMICALLY DIVERSE CHK1 INHIBITORS BY RECEPTOR-BASED VIRTUAL SCREENING2cgv: IDENTIFICATION OF CHEMICALLY DIVERSE CHK1 INHIBITORS BY RECEPTOR-BASED VIRTUAL SCREENING2cgw: IDENTIFICATION OF CHEMICALLY DIVERSE CHK1 INHIBITORS BY RECEPTOR-BASED VIRTUAL SCREENING2cgx: IDENTIFICATION OF CHEMICALLY DIVERSE CHK1 INHIBITORS BY RECEPTOR-BASED VIRTUAL SCREENING2gdo: 4-(Aminoalkylamino)-3-Benzimidazole-Quinolinones As Potent CHK1 Inhibitors2ghg: h-CHK1 complexed with A4319942hog: crystal structure of Chek1 in complex with inhibitor 202ywp: Crystal Structure of CHK1 with a Urea InhibitorKinases: Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11-12) Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1-EC 2.7.11.20) Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1)Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (EC 2.7.11.2)Dephospho-(reductase kinase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.3)(isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)) kinase (EC 2.7.11.5)(tyrosine 3-monooxygenase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.6)Myosin-heavy-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.7)Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.8)Goodpasture-antigen-binding protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.9)-IκB kinase (EC 2.7.11.10)cAMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.11)cGMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.12)Protein kinase C (EC 2.7.11.13)Rhodopsin kinase (EC 2.7.11.14)Beta adrenergic receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.15)G-protein coupled receptor kinases (EC 2.7.11.16)Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent (EC 2.7.11.17)BRSK2, CAMK1, CAMK2A, CAMK2B, CAMK2D, CAMK2G, CAMK4, MLCK, CASK, CHEK1, CHEK2, DAPK1, DAPK2, DAPK3, STK11, MAPKAPK2, MAPKAPK3, MAPKAPK5, MARK1, MARK2, MARK3, MARK4, MELK, MKNK1, MKNK2, NUAK1, NUAK2, OBSCN, PASK, PHKG1, PHKG2, PIM1, PIM2, PKD1, PRKD2, PRKD3, PSKH1, SNF1LK2, KIAA0999, STK40, SNF1LK, SNRK, SPEG, TSSK2, Kalirin, TRIB1, TRIB2, TRIB3, TRIO, Titin, DCLK1Myosin light-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.18)MYLK, MYLK2, MYLK3, MYLK4Phosphorylase kinase (EC 2.7.11.19)Elongation factor 2 kinase (EC 2.7.11.20)Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.21-EC 2.7.11.30) Polo kinase (EC 2.7.11.21)Cyclin-dependent kinase (EC 2.7.11.22)(RNA-polymerase)-subunit kinase (EC 2.7.11.23)Mitogen-activated protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.24)Extracellular signal-regulated (MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK4, MAPK6, MAPK7, MAPK12, MAPK15), C-Jun N-terminal (MAPK8, MAPK9, MAPK10), P38 mitogen-activated protein (MAPK11, MAPK13, MAPK14)MAP3K (EC 2.7.11.25)Tau-protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.26)(acetyl-CoA carboxylase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.27)-Tropomyosin kinase (EC 2.7.11.28)-Low-density-lipoprotein receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.29)-Receptor protein serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.30)Dual-specificity kinases (EC 2.7.12) B enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 Categories:- Human proteins
- Cell signaling
- Signal transduction
- Chromosome 11 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.