- Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9
-
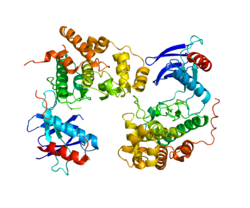
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAPK9 gene.[1]
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the MAP kinase family. MAP kinases act as an integration point for multiple biochemical signals, and are involved in a wide variety of cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, transcription regulation and development. This kinase targets specific transcription factors, and thus mediates immediate-early gene expression in response to various cell stimuli. It is most closely related to MAPK8, both of which are involved in UV radiation-induced apoptosis, thought to be related to the cytochrome c-mediated cell death pathway. This gene and MAPK8 are also known as c-Jun N-terminal kinases. This kinase blocks the ubiquitination of tumor suppressor p53, and thus it increases the stability of p53 in nonstressed cells. Studies of this gene's mouse counterpart suggest a key role in T-cell differentiation. Four alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.[2]
Contents
Interactions
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 9 has been shown to interact with TOB1,[3] Grb2,[4][5] MAPK8IP2,[6] P53,[7][8] MAPK8IP3[9][10] and MAPK8IP1.[6][11]
References
- ^ Kallunki T, Su B, Tsigelny I, Sluss HK, Derijard B, Moore G, Davis R, Karin M (Jan 1995). "JNK2 contains a specificity-determining region responsible for efficient c-Jun binding and phosphorylation". Genes Dev 8 (24): 2996–3007. doi:10.1101/gad.8.24.2996. PMID 8001819.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: MAPK9 mitogen-activated protein kinase 9". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=5601.
- ^ Maekawa, Momoko; Nishida Eisuke, Tanoue Takuji (Oct. 2002). "Identification of the Anti-proliferative protein Tob as a MAPK substrate". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (40): 37783–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M204506200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12151396.
- ^ Saleem, A; Datta R, Yuan Z M, Kharbanda S, Kufe D (Dec. 1995). "Involvement of stress-activated protein kinase in the cellular response to 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine and other DNA-damaging agents". Cell Growth Differ. (UNITED STATES) 6 (12): 1651–8. ISSN 1044-9523. PMID 9019171.
- ^ Kharbanda, S; Saleem A, Shafman T, Emoto Y, Taneja N, Rubin E, Weichselbaum R, Woodgett J, Avruch J, Kyriakis J (Aug. 1995). "Ionizing radiation stimulates a Grb2-mediated association of the stress-activated protein kinase with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 270 (32): 18871–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.32.18871. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 7642542.
- ^ a b Yasuda, J; Whitmarsh A J, Cavanagh J, Sharma M, Davis R J (Oct. 1999). "The JIP Group of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Scaffold Proteins". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 19 (10): 7245–54. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 84717. PMID 10490659. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=84717.
- ^ Hu, M C; Qiu W R, Wang Y P (Nov. 1997). "JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3 are p53 N-terminal serine 34 kinases". Oncogene (ENGLAND) 15 (19): 2277–87. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201401. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9393873.
- ^ Lin, Yenshou; Khokhlatchev Andrei, Figeys Daniel, Avruch Joseph (Dec. 2002). "Death-associated protein 4 binds MST1 and augments MST1-induced apoptosis". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (50): 47991–8001. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202630200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12384512.
- ^ Ito, M; Yoshioka K, Akechi M, Yamashita S, Takamatsu N, Sugiyama K, Hibi M, Nakabeppu Y, Shiba T, Yamamoto K I (Nov. 1999). "JSAP1, a Novel Jun N-Terminal Protein Kinase (JNK)-Binding Protein That Functions as a Scaffold Factor in the JNK Signaling Pathway". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 19 (11): 7539–48. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 84763. PMID 10523642. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=84763.
- ^ Kelkar, N; Gupta S, Dickens M, Davis R J (Feb. 2000). "Interaction of a Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Signaling Module with the Neuronal Protein JIP3". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 20 (3): 1030–43. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.3.1030-1043.2000. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 85220. PMID 10629060. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85220.
- ^ Whitmarsh, A J; Cavanagh J, Tournier C, Yasuda J, Davis R J (Sep. 1998). "A mammalian scaffold complex that selectively mediates MAP kinase activation". Science (UNITED STATES) 281 (5383): 1671–4. doi:10.1126/science.281.5383.1671. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9733513.
External Links
Further reading
- Davis RJ (2000). "Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases". Cell 103 (2): 239–52. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)00116-1. PMID 11057897.
- Freedman BD, Liu QH, Del Corno M, Collman RG (2004). "HIV-1 gp120 chemokine receptor-mediated signaling in human macrophages". Immunol. Res. 27 (2–3): 261–76. doi:10.1385/IR:27:2-3:261. PMID 12857973.
- Lee C, Liu QH, Tomkowicz B et al. (2004). "Macrophage activation through CCR5- and CXCR4-mediated gp120-elicited signaling pathways". J. Leukoc. Biol. 74 (5): 676–82. doi:10.1189/jlb.0503206. PMID 12960231.
- Denys H, Desmet R, Stragier M et al. (1978). "Cystitis emphysematosa". Acta urologica Belgica 45 (4): 327–31. PMID 602896.
- Dawson SJ, White LA (1992). "Treatment of Haemophilus aphrophilus endocarditis with ciprofloxacin". J. Infect. 24 (3): 317–20. doi:10.1016/S0163-4453(05)80037-4. PMID 1602151.
- Livingstone C, Patel G, Jones N (1995). "ATF-2 contains a phosphorylation-dependent transcriptional activation domain". EMBO J. 14 (8): 1785–97. PMC 398272. PMID 7737129. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=398272.
- Sluss HK, Barrett T, Dérijard B, Davis RJ (1994). "Signal transduction by tumor necrosis factor mediated by JNK protein kinases". Mol. Cell. Biol. 14 (12): 8376–84. PMC 359376. PMID 7969172. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=359376.
- Gille H, Strahl T, Shaw PE (1996). "Activation of ternary complex factor Elk-1 by stress-activated protein kinases". Curr. Biol. 5 (10): 1191–200. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(95)00235-1. PMID 8548291.
- Chu Y, Solski PA, Khosravi-Far R et al. (1996). "The mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatases PAC1, MKP-1, and MKP-2 have unique substrate specificities and reduced activity in vivo toward the ERK2 sevenmaker mutation". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (11): 6497–501. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.11.6497. PMID 8626452.
- Bocco JL, Bahr A, Goetz J et al. (1996). "In vivo association of ATFa with JNK/SAP kinase activities". Oncogene 12 (9): 1971–80. PMID 8649858.
- Gupta S, Barrett T, Whitmarsh AJ et al. (1996). "Selective interaction of JNK protein kinase isoforms with transcription factors". EMBO J. 15 (11): 2760–70. PMC 450211. PMID 8654373. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=450211.
- Kallunki T, Deng T, Hibi M, Karin M (1997). "c-Jun can recruit JNK to phosphorylate dimerization partners via specific docking interactions". Cell 87 (5): 929–39. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(00)81999-6. PMID 8945519.
- Jabado N, Pallier A, Jauliac S et al. (1997). "gp160 of HIV or anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody ligation of CD4 induces inhibition of JNK and ERK-2 activities in human peripheral CD4+ T lymphocytes". Eur. J. Immunol. 27 (2): 397–404. doi:10.1002/eji.1830270209. PMID 9045910.
- Janknecht R, Hunter T (1997). "Convergence of MAP kinase pathways on the ternary complex factor Sap-1a". EMBO J. 16 (7): 1620–7. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.7.1620. PMC 1169766. PMID 9130707. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1169766.
- Fukunaga R, Hunter T (1997). "MNK1, a new MAP kinase-activated protein kinase, isolated by a novel expression screening method for identifying protein kinase substrates". EMBO J. 16 (8): 1921–33. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.8.1921. PMC 1169795. PMID 9155018. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1169795.
- Chow CW, Rincón M, Cavanagh J et al. (1997). "Nuclear accumulation of NFAT4 opposed by the JNK signal transduction pathway". Science 278 (5343): 1638–41. doi:10.1126/science.278.5343.1638. PMID 9374467.
- Hu MC, Qiu WR, Wang YP (1997). "JNK1, JNK2 and JNK3 are p53 N-terminal serine 34 kinases". Oncogene 15 (19): 2277–87. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201401. PMID 9393873.
- Lannuzel A, Barnier JV, Hery C et al. (1998). "Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and its coat protein gp120 induce apoptosis and activate JNK and ERK mitogen-activated protein kinases in human neurons". Ann. Neurol. 42 (6): 847–56. doi:10.1002/ana.410420605. PMID 9403476.
- Fuchs SY, Xie B, Adler V et al. (1998). "c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases target the ubiquitination of their associated transcription factors". J. Biol. Chem. 272 (51): 32163–8. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.51.32163. PMID 9405416.
This article incorporates text from the United States National Library of Medicine, which is in the public domain.
Kinases: Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11-12) Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1-EC 2.7.11.20) Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1)Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (EC 2.7.11.2)Dephospho-(reductase kinase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.3)(isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)) kinase (EC 2.7.11.5)(tyrosine 3-monooxygenase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.6)Myosin-heavy-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.7)Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.8)Goodpasture-antigen-binding protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.9)-IκB kinase (EC 2.7.11.10)cAMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.11)cGMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.12)Protein kinase C (EC 2.7.11.13)Rhodopsin kinase (EC 2.7.11.14)Beta adrenergic receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.15)G-protein coupled receptor kinases (EC 2.7.11.16)Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent (EC 2.7.11.17)BRSK2, CAMK1, CAMK2A, CAMK2B, CAMK2D, CAMK2G, CAMK4, MLCK, CASK, CHEK1, CHEK2, DAPK1, DAPK2, DAPK3, STK11, MAPKAPK2, MAPKAPK3, MAPKAPK5, MARK1, MARK2, MARK3, MARK4, MELK, MKNK1, MKNK2, NUAK1, NUAK2, OBSCN, PASK, PHKG1, PHKG2, PIM1, PIM2, PKD1, PRKD2, PRKD3, PSKH1, SNF1LK2, KIAA0999, STK40, SNF1LK, SNRK, SPEG, TSSK2, Kalirin, TRIB1, TRIB2, TRIB3, TRIO, Titin, DCLK1Myosin light-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.18)MYLK, MYLK2, MYLK3, MYLK4Phosphorylase kinase (EC 2.7.11.19)Elongation factor 2 kinase (EC 2.7.11.20)Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.21-EC 2.7.11.30) Polo kinase (EC 2.7.11.21)Cyclin-dependent kinase (EC 2.7.11.22)(RNA-polymerase)-subunit kinase (EC 2.7.11.23)Mitogen-activated protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.24)Extracellular signal-regulated (MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK4, MAPK6, MAPK7, MAPK12, MAPK15), C-Jun N-terminal (MAPK8, MAPK9, MAPK10), P38 mitogen-activated protein (MAPK11, MAPK13, MAPK14)MAP3K (EC 2.7.11.25)Tau-protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.26)(acetyl-CoA carboxylase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.27)-Tropomyosin kinase (EC 2.7.11.28)-Low-density-lipoprotein receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.29)-Receptor protein serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.30)Dual-specificity kinases (EC 2.7.12) B enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 This transferase article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.