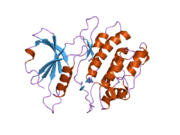- DAPK1
-
Death-associated protein kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DAPK1 gene.[1]
Death-associated protein kinase 1 is a positive mediator of gamma-interferon induced programmed cell death. DAPK1 encodes a structurally unique 160-kD calmodulin dependent serine-threonine kinase that carries 8 ankyrin repeats and 2 putative P-loop consensus sites. It is a tumor suppressor candidate.[2]
In melanocytic cells DAPK1 gene expression may be regulated by MITF.[3]
References
- ^ Feinstein E, Druck T, Kastury K, Berissi H, Goodart SA, Overhauser J, Kimchi A, Huebner K (Feb 1996). "Assignment of DAP1 and DAPK--genes that positively mediate programmed cell death triggered by IFN-gamma--to chromosome regions 5p12.2 and 9q34.1, respectively". Genomics 29 (1): 305–7. doi:10.1006/geno.1995.1255. PMID 8530096.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: DAPK1 death-associated protein kinase 1". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1612.
- ^ Hoek KS, Schlegel NC, Eichhoff OM, et al. (2008). "Novel MITF targets identified using a two-step DNA microarray strategy". Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 21 (6): 665–76. doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2008.00505.x. PMID 19067971.
Further reading
- Deiss LP, Feinstein E, Berissi H, et al. (1995). "Identification of a novel serine/threonine kinase and a novel 15-kD protein as potential mediators of the gamma interferon-induced cell death.". Genes Dev. 9 (1): 15–30. doi:10.1101/gad.9.1.15. PMID 7828849.
- Inbal B, Shani G, Cohen O, et al. (2000). "Death-associated protein kinase-related protein 1, a novel serine/threonine kinase involved in apoptosis.". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (3): 1044–54. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.3.1044-1054.2000. PMC 85221. PMID 10629061. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=85221.
- Jin Y, Blue EK, Dixon S, et al. (2001). "Identification of a new form of death-associated protein kinase that promotes cell survival.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (43): 39667–78. doi:10.1074/jbc.M101886200. PMC 2823794. PMID 11485996. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2823794.
- Shohat G, Spivak-Kroizman T, Cohen O, et al. (2002). "The pro-apoptotic function of death-associated protein kinase is controlled by a unique inhibitory autophosphorylation-based mechanism.". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (50): 47460–7. doi:10.1074/jbc.M105133200. PMID 11579085.
- Soria JC, Rodriguez M, Liu DD, et al. (2002). "Aberrant promoter methylation of multiple genes in bronchial brush samples from former cigarette smokers.". Cancer Res. 62 (2): 351–5. PMID 11809677.
- Larramendy ML, Niini T, Elonen E, et al. (2003). "Overexpression of translocation-associated fusion genes of FGFRI, MYC, NPMI, and DEK, but absence of the translocations in acute myeloid leukemia. A microarray analysis.". Haematologica 87 (6): 569–77. PMID 12031912.
- Hasegawa M, Nelson HH, Peters E, et al. (2002). "Patterns of gene promoter methylation in squamous cell cancer of the head and neck.". Oncogene 21 (27): 4231–6. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1205528. PMID 12082610.
- Jin Y, Blue EK, Dixon S, et al. (2003). "A death-associated protein kinase (DAPK)-interacting protein, DIP-1, is an E3 ubiquitin ligase that promotes tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis and regulates the cellular levels of DAPK.". J. Biol. Chem. 277 (49): 46980–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208585200. PMC 2824503. PMID 12351649. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2824503.
- Wang WJ, Kuo JC, Yao CC, Chen RH (2002). "DAP-kinase induces apoptosis by suppressing integrin activity and disrupting matrix survival signals.". J. Cell Biol. 159 (1): 169–79. doi:10.1083/jcb.200204050. PMC 2173490. PMID 12370243. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2173490.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences.". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=139241.
- Nakatsuka S, Takakuwa T, Tomita Y, et al. (2003). "Hypermethylation of death-associated protein (DAP) kinase CpG island is frequent not only in B-cell but also in T- and natural killer (NK)/T-cell malignancies.". Cancer Sci. 94 (1): 87–91. doi:10.1111/j.1349-7006.2003.tb01357.x. PMID 12708480.
- Tian JH, Das S, Sheng ZH (2003). "Ca2+-dependent phosphorylation of syntaxin-1A by the death-associated protein (DAP) kinase regulates its interaction with Munc18.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (28): 26265–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M300492200. PMID 12730201.
- Gonzalez-Gomez P, Bello MJ, Alonso ME, et al. (2004). "Frequent death-associated protein-kinase promoter hypermethylation in brain metastases of solid tumors.". Oncol. Rep. 10 (4): 1031–3. PMID 12792765.
- Matsumoto H, Nagao M, Ogawa S, et al. (2003). "Prognostic significance of death-associated protein-kinase expression in hepatocellular carcinomas.". Anticancer Res. 23 (2B): 1333–41. PMID 12820391.
- Henshall DC, Araki T, Schindler CK, et al. (2003). "Expression of death-associated protein kinase and recruitment to the tumor necrosis factor signaling pathway following brief seizures.". J. Neurochem. 86 (5): 1260–70. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01934.x. PMID 12911633.
- Voso MT, Scardocci A, Guidi F, et al. (2004). "Aberrant methylation of DAP-kinase in therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes.". Blood 103 (2): 698–700. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-07-2249. PMID 14504087.
- Jin Y, Gallagher PJ (2004). "Antisense depletion of death-associated protein kinase promotes apoptosis.". J. Biol. Chem. 278 (51): 51587–93. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309165200. PMC 2823796. PMID 14530257. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2823796.
- Kim WS, Son HJ, Park JO, et al. (2004). "Promoter methylation and down-regulation of DAPK is associated with gastric atrophy.". Int. J. Mol. Med. 12 (6): 827–30. PMID 14612952.
- Bai T, Tanaka T, Yukawa K, et al. (2004). "Reduced expression of death-associated protein kinase in human uterine and ovarian carcinoma cells.". Oncol. Rep. 11 (3): 661–5. PMID 14767518.
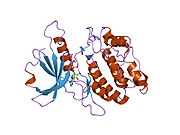
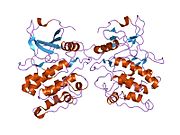
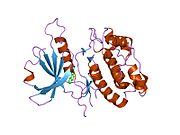
PDB gallery 1ig1: 1.8A X-Ray structure of ternary complex of a catalytic domain of death-associated protein kinase with ATP analogue and Mn.1jkk: 2.4A X-RAY STRUCTURE OF TERNARY COMPLEX OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE WITH ATP ANALOGUE AND MG.1jkl: 1.6A X-RAY STRUCTURE OF BINARY COMPLEX OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE WITH ATP ANALOGUE1jks: 1.5A X-RAY STRUCTURE OF APO FORM OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE1jkt: TETRAGONAL CRYSTAL FORM OF A CATALYTIC DOMAIN OF DEATH-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE1p4f: DEATH ASSOCIATED PROTEIN KINASE CATALYTIC DOMAIN WITH BOUND INHIBITOR FRAGMENT1wvw: Crystal structures of kinase domain of DAP kinase in complex with small molecular inhibitors1wvx: Crystal structures of kinase domain of DAP kinase in complex with small molecular inhibitors1wvy: Crystal structures of kinase domain of DAP kinase in complex with small molecular inhibitorsKinases: Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11-12) Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1-EC 2.7.11.20) Non-specific serine/threonine protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1)Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (EC 2.7.11.2)Dephospho-(reductase kinase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.3)(isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP+)) kinase (EC 2.7.11.5)(tyrosine 3-monooxygenase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.6)Myosin-heavy-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.7)Fas-activated serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.8)Goodpasture-antigen-binding protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.9)-IκB kinase (EC 2.7.11.10)cAMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.11)cGMP-dependent protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.12)Protein kinase C (EC 2.7.11.13)Rhodopsin kinase (EC 2.7.11.14)Beta adrenergic receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.15)G-protein coupled receptor kinases (EC 2.7.11.16)Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent (EC 2.7.11.17)BRSK2, CAMK1, CAMK2A, CAMK2B, CAMK2D, CAMK2G, CAMK4, MLCK, CASK, CHEK1, CHEK2, DAPK1, DAPK2, DAPK3, STK11, MAPKAPK2, MAPKAPK3, MAPKAPK5, MARK1, MARK2, MARK3, MARK4, MELK, MKNK1, MKNK2, NUAK1, NUAK2, OBSCN, PASK, PHKG1, PHKG2, PIM1, PIM2, PKD1, PRKD2, PRKD3, PSKH1, SNF1LK2, KIAA0999, STK40, SNF1LK, SNRK, SPEG, TSSK2, Kalirin, TRIB1, TRIB2, TRIB3, TRIO, Titin, DCLK1Myosin light-chain kinase (EC 2.7.11.18)MYLK, MYLK2, MYLK3, MYLK4Phosphorylase kinase (EC 2.7.11.19)Elongation factor 2 kinase (EC 2.7.11.20)Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.21-EC 2.7.11.30) Polo kinase (EC 2.7.11.21)Cyclin-dependent kinase (EC 2.7.11.22)(RNA-polymerase)-subunit kinase (EC 2.7.11.23)Mitogen-activated protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.24)Extracellular signal-regulated (MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK4, MAPK6, MAPK7, MAPK12, MAPK15), C-Jun N-terminal (MAPK8, MAPK9, MAPK10), P38 mitogen-activated protein (MAPK11, MAPK13, MAPK14)MAP3K (EC 2.7.11.25)Tau-protein kinase (EC 2.7.11.26)(acetyl-CoA carboxylase) kinase (EC 2.7.11.27)-Tropomyosin kinase (EC 2.7.11.28)-Low-density-lipoprotein receptor kinase (EC 2.7.11.29)-Receptor protein serine/threonine kinase (EC 2.7.11.30)Dual-specificity kinases (EC 2.7.12) B enzm: 1.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8/10/11/13/14/15-18, 2.1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8, 2.7.10, 2.7.11-12, 3.1/2/3/4/5/6/7, 3.1.3.48, 3.4.21/22/23/24, 4.1/2/3/4/5/6, 5.1/2/3/4/99, 6.1-3/4/5-6 Categories:- Human proteins
- Cell signaling
- Signal transduction
- Chromosome 9 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.