- ASK1
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) also known as mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5 (MAP3K5) is a member of MAP kinase kinase kinase family and as such a part of mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. It activates c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases in a Raf-independent fashion in response to an array of stresses such as oxidative stress, endoplasmic reticulum stress and calcium influx. ASK1 has been found to be involved in cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular and neurodegenerative diseases.[1]
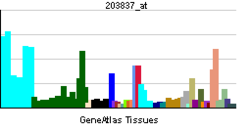
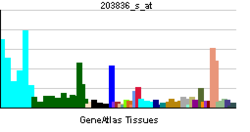
MAP3K5 gene coding for the protein is located on chromosome 6 at locus 6q22.33.[2] and the transcribed protein contains 1,374 amino acids with 11 kinase subdomains.[citation needed] Northern blot analysis shows that MAP3K5 transcript is abundant in human heart and pancreas.[3]
Contents
Mechanism of activation
Under nonstress conditions ASK1 is oligomerized (a requirement for its activation) through its C-terminal coiled-coil domain (CCC), but remains in an inactive form by the suppressive effect of reduced thioredoxin (Trx) and calcium and integrin binding protein 1 (CIB1).[4] Trx inhibits ASK1 kinase activity by direct binding to its N-terminal coiled-coil domain (NCC). Trx and CIB1 regulate ASK1 activation in a redox- or calcium- sensitive manner, respectively. Both appear to compete with TNF-α receptor-associated factor 2 (TRAF2), an ASK1 activator. TRAF2 and TRAF6 are then recruited to ASK1 to form a larger molecular mass complex.[5] Subsequently, ASK1 forms homo-oligomeric interactions not only through the CCC, but also the NCC, which leads to full activation of ASK1 through autophosphorylation at threonine 845.[6]
Interactions
ASK1 has been shown to interact with PP5[7] GADD45B,[8] Protein kinase R,[9] CDC25A,[10] Death associated protein 6,[11] RB1CC1,[12] HSPA1A,[13] C-Raf,[14] PDCD6,[15] TRAF2,[16][12] PPP5C,[7] MAPK8IP3,[17] TRAF6,[16][18][19] MAP2K6,[20][7] TRAF5,[16][18] MAP3K7[19] and DUSP19.[21]
References
- ^ Hattori K, Naguro I, Runchel C, Ichijo H (2009). "The roles of ASK family proteins in stress responses and diseases". Cell Commun. Signal 7: 9. doi:10.1186/1478-811X-7-9. PMC 2685135. PMID 19389260. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2685135.
- ^ Rampoldi L, Zimbello R, Bortoluzzi S, Tiso N, Valle G, Lanfranchi G, Danieli GA (1997). "Chromosomal localization of four MAPK signaling cascade genes: MEK1, MEK3, MEK4 and MEKK5". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 78 (3–4): 301–3. doi:10.1159/000134677. PMID 9465908.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: MAP3K5 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=4217.
- ^ Yoon KW, Cho JH, Lee JK, et al. (October 2009). "CIB1 functions as a Ca2+-sensitive modulator of stress-induced signaling by targeting ASK1". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 106 (41): 17389–94. doi:10.1073/pnas.0812259106. PMC 2762684. PMID 19805025. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2762684.
- ^ Noguchi T, Takeda K, Matsuzawa A, et al. (November 2005). "Recruitment of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor family proteins to apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 signalosome is essential for oxidative stress-induced cell death". J. Biol. Chem. 280 (44): 37033–40. doi:10.1074/jbc.M506771200. PMID 16129676.
- ^ Fujino G, Noguchi T, Matsuzawa A, et al. (December 2007). "Thioredoxin and TRAF Family Proteins Regulate Reactive Oxygen Species-Dependent Activation of ASK1 through Reciprocal Modulation of the N-Terminal Homophilic Interaction of ASK1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 27 (23): 8152–63. doi:10.1128/MCB.00227-07. PMC 2169188. PMID 17724081. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2169188.
- ^ a b c Morita, K; Saitoh M, Tobiume K, Matsuura H, Enomoto S, Nishitoh H, Ichijo H (Nov. 2001). "Negative feedback regulation of ASK1 by protein phosphatase 5 (PP5) in response to oxidative stress". EMBO J. (England) 20 (21): 6028–36. doi:10.1093/emboj/20.21.6028. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 125685. PMID 11689443. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=125685.
- ^ Papa, Salvatore; Zazzeroni Francesca, Bubici Concetta, Jayawardena Shanthi, Alvarez Kellean, Matsuda Shuji, Nguyen Dung U, Pham Can G, Nelsbach Andreas H, Melis Tiziana, De Smaele Enrico, Tang Wei-Jen, D'Adamio Luciano, Franzoso Guido (Feb. 2004). "Gadd45 beta mediates the NF-kappa B suppression of JNK signalling by targeting MKK7/JNKK2". Nat. Cell Biol. (England) 6 (2): 146–53. doi:10.1038/ncb1093. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 14743220.
- ^ Takizawa, Takenori; Tatematsu Chizuru, Nakanishi Yoshinobu (Dec. 2002). "Double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase interacts with apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1. Implications for apoptosis signaling pathways". Eur. J. Biochem. (Germany) 269 (24): 6126–32. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1033.2002.03325.x. ISSN 0014-2956. PMID 12473108.
- ^ Zou, X; Tsutsui T, Ray D, Blomquist J F, Ichijo H, Ucker D S, Kiyokawa H (Jul. 2001). "The Cell Cycle-Regulatory CDC25A Phosphatase Inhibits Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1". Mol. Cell. Biol. (United States) 21 (14): 4818–28. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.14.4818-4828.2001. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 87174. PMID 11416155. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=87174.
- ^ Chang, H Y; Nishitoh H, Yang X, Ichijo H, Baltimore D (Sep. 1998). "Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by the adapter protein Daxx". Science (UNITED STATES) 281 (5384): 1860–3. doi:10.1126/science.281.5384.1860. ISSN 0036-8075. PMID 9743501.
- ^ a b Gan, Boyi; Peng Xu, Nagy Tamas, Alcaraz Ana, Gu Hua, Guan Jun-Lin (Oct. 2006). "Role of FIP200 in cardiac and liver development and its regulation of TNFα and TSC–mTOR signaling pathways". J. Cell Biol. (United States) 175 (1): 121–33. doi:10.1083/jcb.200604129. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 2064504. PMID 17015619. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2064504.
- ^ Park, Hee-Sae; Cho Ssang-Goo, Kim Chang Kyun, Hwang Hyun Sub, Noh Kyung Tae, Kim Mi-Sung, Huh Sung-Ho, Kim Myung Jin, Ryoo Kanghyun, Kim Eun Kyung, Kang Woo Jin, Lee Jae-Seon, Seo Jeong-Sun, Ko Young-Gyu, Kim Sunghoon, Choi Eui-Ju (Nov. 2002). "Heat Shock Protein Hsp72 Is a Negative Regulator of Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1". Mol. Cell. Biol. (United States) 22 (22): 7721–30. doi:10.1128/MCB.22.22.7721-7730.2002. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 134722. PMID 12391142. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=134722.
- ^ Chen, J; Fujii K, Zhang L, Roberts T, Fu H (Jul. 2001). "Raf-1 promotes cell survival by antagonizing apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 through a MEK–ERK independent mechanism". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (United States) 98 (14): 7783–8. doi:10.1073/pnas.141224398. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 35419. PMID 11427728. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=35419.
- ^ Hwang, In-Sik; Jung Yong-Sam, Kim Eunhee (Oct. 2002). "Interaction of ALG-2 with ASK1 influences ASK1 localization and subsequent JNK activation". FEBS Lett. (Netherlands) 529 (2–3): 183–7. doi:10.1016/S0014-5793(02)03329-X. ISSN 0014-5793. PMID 12372597.
- ^ a b c Nishitoh, H; Saitoh M, Mochida Y, Takeda K, Nakano H, Rothe M, Miyazono K, Ichijo H (Sep. 1998). "ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2". Mol. Cell (UNITED STATES) 2 (3): 389–95. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80283-X. ISSN 1097-2765. PMID 9774977.
- ^ Matsuura, Hiroshi; Nishitoh Hideki, Takeda Kohsuke, Matsuzawa Atsushi, Amagasa Teruo, Ito Michihiko, Yoshioka Katsuji, Ichijo Hidenori (Oct. 2002). "Phosphorylation-dependent scaffolding role of JSAP1/JIP3 in the ASK1-JNK signaling pathway. A new mode of regulation of the MAP kinase cascade". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (43): 40703–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M202004200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 12189133.
- ^ a b Hoeflich, K P; Yeh W C, Yao Z, Mak T W, Woodgett J R (Oct. 1999). "Mediation of TNF receptor-associated factor effector functions by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1)". Oncogene (ENGLAND) 18 (42): 5814–20. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202975. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 10523862.
- ^ a b Mochida, Y; Takeda K, Saitoh M, Nishitoh H, Amagasa T, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Matsumoto K, Ichijo H (Oct. 2000). "ASK1 inhibits interleukin-1-induced NF-kappa B activity through disruption of TRAF6-TAK1 interaction". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 275 (42): 32747–52. doi:10.1074/jbc.M003042200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 10921914.
- ^ Huang, Shile; Shu Lili, Dilling Michael B, Easton John, Harwood Franklin C, Ichijo Hidenori, Houghton Peter J (Jun. 2003). "Sustained activation of the JNK cascade and rapamycin-induced apoptosis are suppressed by p53/p21(Cip1)". Mol. Cell (United States) 11 (6): 1491–501. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00180-1. ISSN 1097-2765. PMID 12820963.
- ^ Zama, Takeru; Aoki Ryoko, Kamimoto Takahiro, Inoue Koichi, Ikeda Yasuo, Hagiwara Masatoshi (Jun. 2002). "Scaffold role of a mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase, SKRP1, for the JNK signaling pathway". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 277 (26): 23919–26. doi:10.1074/jbc.M200838200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 11959862.
Further reading
- Hayakawa T, Matsuzawa A, Noguchi T, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2006). "The ASK1-MAP kinase pathways in immune and stress responses". Microbes Infect. 8 (4): 1098–107. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2005.12.001. PMID 16517200.
- Nagai H, Noguchi T, Takeda K, Ichijo H (2007). "Pathophysiological roles of ASK1-MAP kinase signaling pathways". J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 40 (1): 1–6. doi:10.5483/BMBRep.2007.40.1.001. PMID 17244475.
- Wang XS, Diener K, Jannuzzi D, et al. (1997). "Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel protein kinase with a catalytic domain homologous to mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (49): 31607–11. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.49.31607. PMID 8940179.
- Ichijo H, Nishida E, Irie K, et al. (1997). "Induction of apoptosis by ASK1, a mammalian MAPKKK that activates SAPK/JNK and p38 signaling pathways". Science 275 (5296): 90–4. doi:10.1126/science.275.5296.90. PMID 8974401.
- Saitoh M, Nishitoh H, Fujii M, et al. (1998). "Mammalian thioredoxin is a direct inhibitor of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK) 1". EMBO J. 17 (9): 2596–606. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.9.2596. PMC 1170601. PMID 9564042. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1170601.
- Chang HY, Nishitoh H, Yang X, et al. (1998). "Activation of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) by the adapter protein Daxx". Science 281 (5384): 1860–3. doi:10.1126/science.281.5384.1860. PMID 9743501.
- Nishitoh H, Saitoh M, Mochida Y, et al. (1998). "ASK1 is essential for JNK/SAPK activation by TRAF2". Mol. Cell 2 (3): 389–95. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80283-X. PMID 9774977.
- Wang XS, Diener K, Tan TH, Yao Z (1999). "MAPKKK6, a novel mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, that associates with MAPKKK5". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 253 (1): 33–7. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1998.9749. PMID 9875215.
- Zhang L, Chen J, Fu H (1999). "Suppression of apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1-induced cell death by 14-3-3 proteins". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (15): 8511–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.15.8511. PMC 17547. PMID 10411906. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=17547.
- Hoeflich KP, Yeh WC, Yao Z, et al. (1999). "Mediation of TNF receptor-associated factor effector functions by apoptosis signal-regulating kinase-1 (ASK1)". Oncogene 18 (42): 5814–20. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202975. PMID 10523862.
- Takeda K, Hatai T, Hamazaki TS, et al. (2000). "Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 (ASK1) induces neuronal differentiation and survival of PC12 cells". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (13): 9805–13. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.13.9805. PMID 10734135.
- Charette SJ, Lavoie JN, Lambert H, Landry J (2000). "Inhibition of Daxx-Mediated Apoptosis by Heat Shock Protein 27". Mol. Cell. Biol. 20 (20): 7602–12. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.20.7602-7612.2000. PMC 86317. PMID 11003656. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=86317.
- Ko YG, Kim EY, Kim T, et al. (2001). "Glutamine-dependent antiapoptotic interaction of human glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase with apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (8): 6030–6. doi:10.1074/jbc.M006189200. PMID 11096076.
- Kim AH, Khursigara G, Sun X, et al. (2001). "Akt Phosphorylates and Negatively Regulates Apoptosis Signal-Regulating Kinase 1". Mol. Cell. Biol. 21 (3): 893–901. doi:10.1128/MCB.21.3.893-901.2001. PMC 86680. PMID 11154276. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=86680.
- Cho SG, Lee YH, Park HS, et al. (2001). "Glutathione S-transferase mu modulates the stress-activated signals by suppressing apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1". J. Biol. Chem. 276 (16): 12749–55. doi:10.1074/jbc.M005561200. PMID 11278289.
- Geleziunas R, Xu W, Takeda K, et al. (2001). "HIV-1 Nef inhibits ASK1-dependent death signalling providing a potential mechanism for protecting the infected host cell". Nature 410 (6830): 834–8. doi:10.1038/35071111. PMID 11298454.
PDB gallery Kinases: Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11-12) Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.1-EC 2.7.11.20) -G-protein coupled receptor kinases (EC 2.7.11.16)BRSK2, CAMK1, CAMK2A, CAMK2B, CAMK2D, CAMK2G, CAMK4, MLCK, CASK, CHEK1, CHEK2, DAPK1, DAPK2, DAPK3, STK11, MAPKAPK2, MAPKAPK3, MAPKAPK5, MARK1, MARK2, MARK3, MARK4, MELK, MKNK1, MKNK2, NUAK1, NUAK2, OBSCN, PASK, PHKG1, PHKG2, PIM1, PIM2, PKD1, PRKD2, PRKD3, PSKH1, SNF1LK2, KIAA0999, STK40, SNF1LK, SNRK, SPEG, TSSK2, Kalirin, TRIB1, TRIB2, TRIB3, TRIO, Titin, DCLK1Serine/threonine-specific protein kinases (EC 2.7.11.21-EC 2.7.11.30) Extracellular signal-regulated (MAPK1, MAPK3, MAPK4, MAPK6, MAPK7, MAPK12, MAPK15), C-Jun N-terminal (MAPK8, MAPK9, MAPK10), P38 mitogen-activated protein (MAPK11, MAPK13, MAPK14)---Dual-specificity kinases (EC 2.7.12) Categories:- Human proteins
- Cell signaling
- Signal transduction
- Programmed cell death
- EC 2.7.11
- Apoptosis
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.