- Cyclin-dependent kinase 4
-
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 is part of the cyclin-dependent kinase family.
The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28 and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of this kinase is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). This kinase was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product (Rb). Mutations in this gene as well as in its related proteins including D-type cyclins, p16(INK4a) and Rb were all found to be associated with tumorigenesis of a variety of cancers. Multiple polyadenylation sites of this gene have been reported.[1]
It is regulated by Cyclin D.
Contents
Interactions
Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 has been shown to interact with SERTAD1,[2][3] CDC37,[4][5][6][7] CEBPA,[8] PCNA,[9][10] Cyclin D3,[11][12][13][14] Cyclin D1,[3][9][13][15][16][17] CDKN2C,[4][18] MyoD,[19][20] P16,[2][3][4][9][17][21] CDKN2B,[11][22] Drebrin-like[4] and CDKN1B.[13][16]
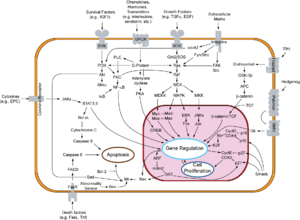 Overview of signal transduction pathways involved in apoptosis.
Overview of signal transduction pathways involved in apoptosis.
References
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CDK4 cyclin-dependent kinase 4". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=1019.
- ^ a b Li, Junan, , Tsai Ming-Daw, Muscarella Peter, Tsai, Ming-Daw, Muscarella, Peter (Apr. 2004). "The nuclear protein p34SEI-1 regulates the kinase activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 in a concentration-dependent manner". Biochemistry (United States) 43 (14): 4394–9. doi:10.1021/bi035601s. ISSN 0006-2960. PMID 15065884.
- ^ a b c Sugimoto, M, Ohtani N, Hampson L, Hampson I N, Shimamoto A, Furuichi Y, Okumura K, Niwa S et al. (Nov. 1999). "Regulation of CDK4 activity by a novel CDK4-binding protein, p34SEI-1". Genes Dev. (UNITED STATES) 13 (22): 3027–33. doi:10.1101/gad.13.22.3027. ISSN 0890-9369. PMC 317153. PMID 10580009. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=317153.
- ^ a b c d Ewing, Rob M, Elisma Fred, Li Hongyan, Taylor Paul, Climie Shane, McBroom-Cerajewski Linda, Robinson Mark D, Connor Liam et al. (2007). "Large-scale mapping of human protein–protein interactions by mass spectrometry". Mol. Syst. Biol. (England) 3 (1): 89. doi:10.1038/msb4100134. PMC 1847948. PMID 17353931. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1847948.
- ^ Dai, K, , Beach D, Beach, D (Sep. 1996). "Physical interaction of mammalian CDC37 with CDK4". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 271 (36): 22030–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.36.22030. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 8703009.
- ^ Lamphere, L, Xu X, Brizuela L, Keezer S, Sardet C, Draetta G F, , Gyuris J, Gyuris, Jeno (Apr. 1997). "Interaction between Cdc37 and Cdk4 in human cells". Oncogene (ENGLAND) 14 (16): 1999–2004. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201036. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 9150368.
- ^ Stepanova, L, Parker S B, , Harper J W, Harper, J W (Jun. 1996). "Mammalian p50Cdc37 is a protein kinase-targeting subunit of Hsp90 that binds and stabilizes Cdk4". Genes Dev. (UNITED STATES) 10 (12): 1491–502. doi:10.1101/gad.10.12.1491. ISSN 0890-9369. PMID 8666233.
- ^ Wang, H, Wilde M, Welm A, Goode T, Roesler W J, , Timchenko N A, Timchenko, Nikolai A (Oct. 2001). "C/EBPalpha arrests cell proliferation through direct inhibition of Cdk2 and Cdk4". Mol. Cell (United States) 8 (4): 817–28. doi:10.1016/S1097-2765(01)00366-5. ISSN 1097-2765. PMID 11684017.
- ^ a b c Serrano, M, , Beach D, Beach, David (Dec. 1993). "A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4". Nature (ENGLAND) 366 (6456): 704–7. doi:10.1038/366704a0. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 8259215.
- ^ Xiong, Y, , Beach D, Beach, D (Aug. 1993). "Subunit rearrangement of the cyclin-dependent kinases is associated with cellular transformation". Genes Dev. (UNITED STATES) 7 (8): 1572–83. doi:10.1101/gad.7.8.1572. ISSN 0890-9369. PMID 8101826.
- ^ a b Rual, Jean-François, Hao Tong, Hirozane-Kishikawa Tomoko, Dricot Amélie, Li Ning, Berriz Gabriel F, Gibbons Francis D, Dreze Matija et al. (Oct. 2005). "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network". Nature (England) 437 (7062): 1173–8. doi:10.1038/nature04209. PMID 16189514.
- ^ Arsenijevic, Tatjana, Dumont Jacques E, Roger Pierre P, , Pirson Isabelle, Pirson, Isabelle (Mar. 2004). "A novel partner for D-type cyclins: protein kinase A-anchoring protein AKAP95". Biochem. J. (England) 378 (Pt 2): 673–9. doi:10.1042/BJ20031765. PMC 1223988. PMID 14641107. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1223988.
- ^ a b c Lin, J, , Okayama H, Okayama, Hiroto (Apr. 2001). "Cdk6-cyclin D3 complex evades inhibition by inhibitor proteins and uniquely controls cell's proliferation competence". Oncogene (England) 20 (16): 2000–9. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1204375. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 11360184.
- ^ Zhang, Q, , Wolgemuth D J, Wolgemuth, DJ (Jun. 1999). "Developmentally regulated expression of cyclin D3 and its potential in vivo interacting proteins during murine gametogenesis". Endocrinology (UNITED STATES) 140 (6): 2790–800. doi:10.1210/en.140.6.2790. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 10342870.
- ^ Taulés, M, Talaya D, López-Girona A, Bachs O, , Agell N, Agell, N (Dec. 1998). "Calmodulin is essential for cyclin-dependent kinase 4 (Cdk4) activity and nuclear accumulation of cyclin D1-Cdk4 during G1". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 273 (50): 33279–86. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.50.33279. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9837900.
- ^ a b Cariou, S, Flanagan W M, Milic A, Bhattacharya N, , Slingerland J M, Slingerland, JM (Aug. 2000). "Down-regulation of p21WAF1/CIP1 or p27Kip1 abrogates antiestrogen-mediated cell cycle arrest in human breast cancer cells". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (UNITED STATES) 97 (16): 9042–6. doi:10.1073/pnas.160016897. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 16818. PMID 10908655. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=16818.
- ^ a b Coleman, K G, Morrissey D, Mulheron J, Sedman S A, Brinkley P, Price S, , Webster K R, Webster, KR (Jul. 1997). "Identification of CDK4 sequences involved in cyclin D1 and p16 binding". J. Biol. Chem. (UNITED STATES) 272 (30): 18869–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.272.30.18869. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 9228064.
- ^ Guan, K L, Li Y, Nichols M A, Wu X, Keefe C L, Matera A G, , O' Xiong Y, Xiong, Y (Dec. 1994). "Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function". Genes Dev. (UNITED STATES) 8 (24): 2939–52. doi:10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. ISSN 0890-9369. PMID 8001816.
- ^ Zhang, J M, Wei Q, , Paterson B M, Paterson, BM (Dec. 1999). "Direct inhibition of G(1) cdk kinase activity by MyoD promotes myoblast cell cycle withdrawal and terminal differentiation". EMBO J. (ENGLAND) 18 (24): 6983–93. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.24.6983. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 1171761. PMID 10601020. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171761.
- ^ Zhang, J M, Zhao X, , Paterson B M, Paterson, Bruce M. (Feb. 1999). "Coupling of the cell cycle and myogenesis through the cyclin D1-dependent interaction of MyoD with cdk4". EMBO J. (ENGLAND) 18 (4): 926–33. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.4.926. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 1171185. PMID 10022835. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171185.
- ^ Fåhraeus, R, Ball K L, Laín S, , Lane D P, Lane, David P. (Jan. 1996). "Inhibition of pRb phosphorylation and cell-cycle progression by a 20-residue peptide derived from p16CDKN2/INK4A". Curr. Biol. (ENGLAND) 6 (1): 84–91. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00425-6. ISSN 0960-9822. PMID 8805225.
- ^ Stelzl, Ulrich, Lalowski Maciej, Haenig Christian, Brembeck Felix H, Goehler Heike, Stroedicke Martin, Zenkner Martina, Schoenherr Anke et al. (Sep. 2005). "A human protein-protein interaction network: a resource for annotating the proteome". Cell (United States) 122 (6): 957–68. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.029. ISSN 0092-8674. PMID 16169070.
Further reading
- Hanks SK (1987). "Homology probing: identification of cDNA clones encoding members of the protein-serine kinase family". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (2): 388–92. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.2.388. PMC 304212. PMID 2948189. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=304212.
- Hall M, Bates S, Peters G (1995). "Evidence for different modes of action of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors: p15 and p16 bind to kinases, p21 and p27 bind to cyclins". Oncogene 11 (8): 1581–8. PMID 7478582.
- Tassan JP, Jaquenoud M, Léopold P et al. (1995). "Identification of human cyclin-dependent kinase 8, a putative protein kinase partner for cyclin C". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92 (19): 8871–5. doi:10.1073/pnas.92.19.8871. PMC 41069. PMID 7568034. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=41069.
- Mitchell EL, White GR, Santibanez-Koref MF et al. (1995). "Mapping of gene loci in the Q13-Q15 region of chromosome 12". Chromosome Res. 3 (4): 261–2. doi:10.1007/BF00713052. PMID 7606365.
- Wölfel T, Hauer M, Schneider J et al. (1995). "A p16INK4a-insensitive CDK4 mutant targeted by cytolytic T lymphocytes in a human melanoma". Science 269 (5228): 1281–4. doi:10.1126/science.7652577. PMID 7652577.
- Hirai H, Roussel MF, Kato JY et al. (1995). "Novel INK4 proteins, p19 and p18, are specific inhibitors of the cyclin D-dependent kinases CDK4 and CDK6". Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 (5): 2672–81. PMC 230497. PMID 7739547. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=230497.
- Chan FK, Zhang J, Cheng L et al. (1995). "Identification of human and mouse p19, a novel CDK4 and CDK6 inhibitor with homology to p16ink4". Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 (5): 2682–8. PMC 230498. PMID 7739548. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=230498.
- Guan KL, Jenkins CW, Li Y et al. (1995). "Growth suppression by p18, a p16INK4/MTS1- and p14INK4B/MTS2-related CDK6 inhibitor, correlates with wild-type pRb function". Genes Dev. 8 (24): 2939–52. doi:10.1101/gad.8.24.2939. PMID 8001816.
- Kato JY, Matsuoka M, Strom DK, Sherr CJ (1994). "Regulation of cyclin D-dependent kinase 4 (cdk4) by cdk4-activating kinase". Mol. Cell. Biol. 14 (4): 2713–21. PMC 358637. PMID 8139570. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=358637.
- Khatib ZA, Matsushime H, Valentine M et al. (1993). "Coamplification of the CDK4 gene with MDM2 and GLI in human sarcomas". Cancer Res. 53 (22): 5535–41. PMID 8221695.
- Serrano M, Hannon GJ, Beach D (1994). "A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4". Nature 366 (6456): 704–7. doi:10.1038/366704a0. PMID 8259215.
- Demetrick DJ, Zhang H, Beach DH (1994). "Chromosomal mapping of human CDK2, CDK4, and CDK5 cell cycle kinase genes". Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 66 (1): 72–4. doi:10.1159/000133669. PMID 8275715.
- Kato J, Matsushime H, Hiebert SW et al. (1993). "Direct binding of cyclin D to the retinoblastoma gene product (pRb) and pRb phosphorylation by the cyclin D-dependent kinase CDK4". Genes Dev. 7 (3): 331–42. doi:10.1101/gad.7.3.331. PMID 8449399.
- Zuo L, Weger J, Yang Q et al. (1996). "Germline mutations in the p16INK4a binding domain of CDK4 in familial melanoma". Nat. Genet. 12 (1): 97–9. doi:10.1038/ng0196-97. PMID 8528263.
- Andersson B, Wentland MA, Ricafrente JY et al. (1996). "A "double adaptor" method for improved shotgun library construction". Anal. Biochem. 236 (1): 107–13. doi:10.1006/abio.1996.0138. PMID 8619474.
- Knudsen ES, Wang JY (1996). "Differential regulation of retinoblastoma protein function by specific Cdk phosphorylation sites". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (14): 8313–20. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.14.8313. PMID 8626527.
- Poon RY, Jiang W, Toyoshima H, Hunter T (1996). "Cyclin-dependent kinases are inactivated by a combination of p21 and Thr-14/Tyr-15 phosphorylation after UV-induced DNA damage". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (22): 13283–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.22.13283. PMID 8662825.
- Stepanova L, Leng X, Parker SB, Harper JW (1996). "Mammalian p50Cdc37 is a protein kinase-targeting subunit of Hsp90 that binds and stabilizes Cdk4". Genes Dev. 10 (12): 1491–502. doi:10.1101/gad.10.12.1491. PMID 8666233.
- Dai K, Kobayashi R, Beach D (1996). "Physical interaction of mammalian CDC37 with CDK4". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (36): 22030–4. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.36.22030. PMID 8703009.
- Fåhraeus R, Paramio JM, Ball KL et al. (1996). "Inhibition of pRb phosphorylation and cell-cycle progression by a 20-residue peptide derived from p16CDKN2/INK4A". Curr. Biol. 6 (1): 84–91. doi:10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00425-6. PMID 8805225.
External links
Cell cycle proteins Cyclin CDK CDK inhibitor P53 p63 p73 family Phases and
checkpointsOther cellular phasesCategories:- Human proteins
- Cell cycle
- Proteins
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.