- Cyclin A2
-
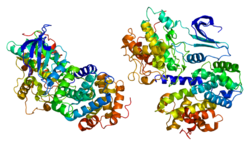
Cyclin-A2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNA2 gene.[1]
The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the highly conserved cyclin family, whose members are characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance through the cell cycle. Cyclins function as regulators of CDK kinases. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression and degradation patterns which contribute to the temporal coordination of each mitotic event. In contrast to cyclin A1, which is present only in germ cells, this cyclin is expressed in all tissues tested. This cyclin binds and activates CDC2 or CDK2 kinases, and thus promotes both cell cycle G1/S and G2/M transitions.[2]
See also
Interactions
Cyclin A2 has been shown to interact with ITGB3BP,[3] Retinoblastoma-like protein 1,[4][5] E2F1,[6] CDC6,[7][8] SKP2[9][10] and Flap structure-specific endonuclease 1.[11]
References
- ^ Paterlini P, De Mitri MS, Martin C, Munnich A, Brechot C (July 1991). "A Taql polymorphism in the human cyclin A gene". Nucleic Acids Res 19 (9): 2516. doi:10.1093/nar/19.9.2516. PMC 329485. PMID 1675006. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=329485.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: CCNA2 cyclin A2". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=890.
- ^ Ohtoshi, A; Maeda T, Higashi H, Ashizawa S, Yamada M, Hatakeyama M (January 2000). "beta3-endonexin as a novel inhibitor of cyclin A-associated kinase". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. (UNITED STATES) 267 (3): 947–52. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.2007. ISSN 0006-291X. PMID 10673397.
- ^ Dyson, N; Dembski M, Fattaey A, Ngwu C, Ewen M, Helin K (December 1993). "Analysis of p107-associated proteins: p107 associates with a form of E2F that differs from pRB-associated E2F-1". J. Virol. (UNITED STATES) 67 (12): 7641–7. ISSN 0022-538X. PMC 238233. PMID 8230483. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=238233.
- ^ Joaquin, Manel; Bessa Maria, Saville Mark K, Watson Roger J (November 2002). "B-Myb overcomes a p107-mediated cell proliferation block by interacting with an N-terminal domain of p107". Oncogene (England) 21 (52): 7923–32. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206001. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 12439743.
- ^ Xu, M; Sheppard K A, Peng C Y, Yee A S, Piwnica-Worms H (December 1994). "Cyclin A/CDK2 binds directly to E2F-1 and inhibits the DNA-binding activity of E2F-1/DP-1 by phosphorylation". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 14 (12): 8420–31. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 359381. PMID 7969176. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=359381.
- ^ Petersen, B O; Lukas J, Sørensen C S, Bartek J, Helin K (January 1999). "Phosphorylation of mammalian CDC6 by cyclin A/CDK2 regulates its subcellular localization". EMBO J. (ENGLAND) 18 (2): 396–410. doi:10.1093/emboj/18.2.396. ISSN 0261-4189. PMC 1171134. PMID 9889196. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1171134.
- ^ Saha, P; Chen J, Thome K C, Lawlis S J, Hou Z H, Hendricks M, Parvin J D, Dutta A (May 1998). "Human CDC6/Cdc18 Associates with Orc1 and Cyclin-cdk and Is Selectively Eliminated from the Nucleus at the Onset of S Phase". Mol. Cell. Biol. (UNITED STATES) 18 (5): 2758–67. ISSN 0270-7306. PMC 110655. PMID 9566895. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=110655.
- ^ Rosner, Margit; Hengstschläger Markus (November 2004). "Tuberin binds p27 and negatively regulates its interaction with the SCF component Skp2". J. Biol. Chem. (United States) 279 (47): 48707–15. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405528200. ISSN 0021-9258. PMID 15355997.
- ^ Marti, A; Wirbelauer C, Scheffner M, Krek W (May 1999). "Interaction between ubiquitin-protein ligase SCFSKP2 and E2F-1 underlies the regulation of E2F-1 degradation". Nat. Cell Biol. (ENGLAND) 1 (1): 14–9. doi:10.1038/8984. ISSN 1465-7392. PMID 10559858.
- ^ Henneke, Ghislaine; Koundrioukoff Stéphane, Hübscher Ulrich (July 2003). "Phosphorylation of human Fen1 by cyclin-dependent kinase modulates its role in replication fork regulation". Oncogene (England) 22 (28): 4301–13. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206606. ISSN 0950-9232. PMID 12853968.
- Pagano M, Pepperkok R, Verde F, et al. (1992). "Cyclin A is required at two points in the human cell cycle". EMBO J. 11 (3): 961–71. PMC 556537. PMID 1312467. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=556537.
- Bailly E, Pines J, Hunter T, Bornens M (1992). "Cytoplasmic accumulation of cyclin B1 in human cells: association with a detergent-resistant compartment and with the centrosome". J. Cell. Sci. 101 ( Pt 3): 529–45. PMID 1387877.
- Faha B, Ewen ME, Tsai LH, et al. (1992). "Interaction between human cyclin A and adenovirus E1A-associated p107 protein". Science 255 (5040): 87–90. doi:10.1126/science.1532458. PMID 1532458.
- Bandara LR, Adamczewski JP, Hunt T, La Thangue NB (1991). "Cyclin A and the retinoblastoma gene product complex with a common transcription factor". Nature 352 (6332): 249–51. doi:10.1038/352249a0. PMID 1830372.
- Blanquet V, Wang JA, Chenivesse X, et al. (1991). "Assignment of a human cyclin A gene to 4q26-q27". Genomics 8 (3): 595–7. doi:10.1016/0888-7543(90)90052-V. PMID 1962755.
- Wang J, Chenivesse X, Henglein B, Bréchot C (1990). "Hepatitis B virus integration in a cyclin A gene in a hepatocellular carcinoma". Nature 343 (6258): 555–7. doi:10.1038/343555a0. PMID 1967822.
- Jeffrey PD, Russo AA, Polyak K, et al. (1995). "Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex". Nature 376 (6538): 313–20. doi:10.1038/376313a0. PMID 7630397.
- Xu M, Sheppard KA, Peng CY, et al. (1994). "Cyclin A/CDK2 binds directly to E2F-1 and inhibits the DNA-binding activity of E2F-1/DP-1 by phosphorylation". Mol. Cell. Biol. 14 (12): 8420–31. PMC 359381. PMID 7969176. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=359381.
- Castro A, Jaumot M, Vergés M, et al. (1994). "Microsomal localization of cyclin A and cdk2 in proliferating rat liver cells". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 201 (3): 1072–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1994.1814. PMID 8024548.
- Henglein B, Chenivesse X, Wang J, et al. (1994). "Structure and cell cycle-regulated transcription of the human cyclin A gene". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91 (12): 5490–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.91.12.5490. PMC 44021. PMID 8202514. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=44021.
- Dyson N, Dembski M, Fattaey A, et al. (1993). "Analysis of p107-associated proteins: p107 associates with a form of E2F that differs from pRB-associated E2F-1". J. Virol. 67 (12): 7641–7. PMC 238233. PMID 8230483. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=238233.
- Li Y, Graham C, Lacy S, et al. (1994). "The adenovirus E1A-associated 130-kD protein is encoded by a member of the retinoblastoma gene family and physically interacts with cyclins A and E". Genes Dev. 7 (12A): 2366–77. doi:10.1101/gad.7.12a.2366. PMID 8253383.
- Lees EM, Harlow E (1993). "Sequences within the conserved cyclin box of human cyclin A are sufficient for binding to and activation of cdc2 kinase". Mol. Cell. Biol. 13 (2): 1194–201. PMC 359004. PMID 8423786. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=359004.
- Sebastian B, Kakizuka A, Hunter T (1993). "Cdc25M2 activation of cyclin-dependent kinases by dephosphorylation of threonine-14 and tyrosine-15". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90 (8): 3521–4. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.8.3521. PMC 46332. PMID 8475101. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=46332.
- Carbonaro-Hall D, Williams R, Wu L, et al. (1993). "G1 expression and multistage dynamics of cyclin A in human osteosarcoma cells". Oncogene 8 (6): 1649–59. PMID 8502485.
- Meikrantz W, Schlegel R (1996). "Suppression of apoptosis by dominant negative mutants of cyclin-dependent protein kinases". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (17): 10205–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.17.10205. PMID 8626584.
- Poon RY, Jiang W, Toyoshima H, Hunter T (1996). "Cyclin-dependent kinases are inactivated by a combination of p21 and Thr-14/Tyr-15 phosphorylation after UV-induced DNA damage". J. Biol. Chem. 271 (22): 13283–91. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.22.13283. PMID 8662825.
- Russo AA, Jeffrey PD, Patten AK, et al. (1996). "Crystal structure of the p27Kip1 cyclin-dependent-kinase inhibitor bound to the cyclin A-Cdk2 complex". Nature 382 (6589): 325–31. doi:10.1038/382325a0. PMID 8684460.
- Russo AA, Jeffrey PD, Pavletich NP (1996). "Structural basis of cyclin-dependent kinase activation by phosphorylation". Nat. Struct. Biol. 3 (8): 696–700. doi:10.1038/nsb0896-696. PMID 8756328.
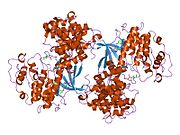
PDB gallery 1e9h: THR 160 PHOSPHORYLATED CDK2 - HUMAN CYCLIN A3 COMPLEX WITH THE INHIBITOR INDIRUBIN-5-SULPHONATE BOUND1fin: CYCLIN A-CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE 2 COMPLEX1fvv: THE STRUCTURE OF CDK2/CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH AN OXINDOLE INHIBITOR1gy3: PCDK2/CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH MGADP, NITRATE AND PEPTIDE SUBSTRATE1h1p: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR NU20581h1q: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR NU60941h1r: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR NU60861h1s: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH THE INHIBITOR NU61021h24: CDK2/CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH A 9 RESIDUE RECRUITMENT PEPTIDE FROM E2F1h25: CDK2/CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH AN 11-RESIDUE RECRUITMENT PEPTIDE FROM RETINOBLASTOMA-ASSOCIATED PROTEIN1h26: CDK2/CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH AN 11-RESIDUE RECRUITMENT PEPTIDE FROM P531h27: CDK2/CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH AN 11-RESIDUE RECRUITMENT PEPTIDE FROM P271h28: CDK2/CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH AN 11-RESIDUE RECRUITMENT PEPTIDE FROM P1071jst: PHOSPHORYLATED CYCLIN-DEPENDENT KINASE-2 BOUND TO CYCLIN A1jsu: P27(KIP1)/CYCLIN A/CDK2 COMPLEX1ogu: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH A 2-ARYLAMINO-4-CYCLOHEXYLMETHYL-5-NITROSO-6-AMINOPYRIMIDINE INHIBITOR1oi9: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH A 6-CYCLOHEXYLMETHYLOXY-2-ANILINO-PURINE INHIBITOR1oiu: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH A 6-CYCLOHEXYLMETHYLOXY-2-ANILINO-PURINE INHIBITOR1oiy: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2/CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH A 6-CYCLOHEXYLMETHYLOXY-2-ANILINO-PURINE INHIBITOR1okv: CYCLIN A BINDING GROOVE INHIBITOR H-ARG-ARG-LEU-ILE-PHE-NH21okw: CYCLIN A BINDING GROOVE INHIBITOR AC-ARG-ARG-LEU-ASN-(M-CL-PHE)-NH21ol1: CYCLIN A BINDING GROOVE INHIBITOR H-CIT-CIT-LEU-ILE-(P-F-PHE)-NH21ol2: CYCLIN A BINDING GROOVE INHIBITOR H-ARG-ARG-LEU-ASN-(P-F-PHE)-NH21p5e: The strucure of phospho-CDK2/cyclin A in complex with the inhibitor 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole (TBS)1pkd: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF UCN-01 IN COMPLEX WITH PHOSPHO-CDK2/CYCLIN A1qmz: PHOSPHORYLATED CDK2-CYCLYIN A-SUBSTRATE PEPTIDE COMPLEX1urc: CYCLIN A BINDING GROOVE INHIBITOR ACE-ARG-LYS-LEU-PHE-GLY1vin: BOVINE CYCLIN A31vyw: STRUCTURE OF CDK2/CYCLIN A WITH PNU-2921372bkz: STRUCTURE OF CDK2-CYCLIN A WITH PHA-4046112bpm: STRUCTURE OF CDK2-CYCLIN A WITH PHA-6305292c4g: STRUCTURE OF CDK2-CYCLIN A WITH PHA-5335142c5n: DIFFERENTIAL BINDING OF INHIBITORS TO ACTIVE AND INACTIVE CDK2 PROVIDES INSIGHTS FOR DRUG DESIGN2c5o: DIFFERENTIAL BINDING OF INHIBITORS TO ACTIVE AND INACTIVE CDK2 PROVIDES INSIGHTS FOR DRUG DESIGN2c5p:2c5v: DIFFERENTIAL BINDING OF INHIBITORS TO ACTIVE AND INACTIVE CDK2 PROVIDES INSIGHTS FOR DRUG DESIGN2c5x: DIFFERENTIAL BINDING OF INHIBITORS TO ACTIVE AND INACTIVE CDK2 PROVIDES INSIGHTS FOR DRUG DESIGN2c6t: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF THE HUMAN CDK2 COMPLEXED WITH THE TRIAZOLOPYRIMIDINE INHIBITOR2cch: THE CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF CDK2 CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH A SUBSTRATE PEPTIDE DERIVED FROM CDC MODIFIED WITH A GAMMA-LINKED ATP ANALOGUE2cci: CRYSTAL STRUCTURE OF PHOSPHO-CDK2 CYCLIN A IN COMPLEX WITH A PEPTIDE CONTAINING BOTH THE SUBSTRATE AND RECRUITMENT SITES OF CDC62cjm: MECHANISM OF CDK INHIBITION BY ACTIVE SITE PHOSPHORYLATION: CDK2 Y15P T160P IN COMPLEX WITH CYCLIN A STRUCTURE2g9x: Structure of Thr 160 phosphorylated CDK2/cyclin A in complex with the inhibitor NU62712i40: Cdk2/Cyclin A complexed with a thiophene carboxamide inhibitor2iw6: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2-CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH A BISANILINOPYRIMIDINE INHIBITOR2iw8: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2-CYCLIN A F82H-L83V-H84D MUTANT WITH AN O6-CYCLOHEXYLMETHYLGUANINE INHIBITOR2iw9: STRUCTURE OF HUMAN THR160-PHOSPHO CDK2-CYCLIN A COMPLEXED WITH A BISANILINOPYRIMIDINE INHIBITOR2uue: REPLACE: A STRATEGY FOR ITERATIVE DESIGN OF CYCLIN BINDING GROOVE INHIBITORSCell cycle proteins Cyclin CDK CDK inhibitor P53 p63 p73 family Phases and
checkpointsOther cellular phasesB bsyn: dna (repl, cycl, reco, repr) · tscr (fact, tcrg, nucl, rnat, rept, ptts) · tltn (risu, pttl, nexn) · dnab, rnab/runp · stru (domn, 1°, 2°, 3°, 4°) Categories:- Human proteins
- Cell cycle
- Chromosome 4 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.