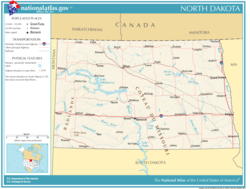
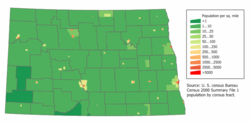
- North Dakota
-
This article is about the U.S. state of North Dakota. For other uses, see North Dakota (disambiguation).
State of North Dakota 

Flag Seal Nickname(s): Peace Garden State,
Roughrider State, Flickertail State, Norse Dakota, The 701, HeavenMotto(s): Liberty and Union, Now and Forever, One and Inseparable Official language(s) English[1] Demonym North Dakotan Capital Bismarck Largest city Fargo Area Ranked 19th in the U.S. - Total 70,700 sq mi
(183,272 km2)- Width 210 miles (340 km) - Length 340 miles (545 km) - % water 2.4 - Latitude 45° 56′ N to 49° 00′ N - Longitude 96° 33′ W to 104° 03′ W Population Ranked 48th in the U.S. - Total (2010) 672,591 - Density 9.3/sq mi (3.58/km2)
Ranked 47th in the U.S.Elevation - Highest point White Butte[2][3]
3,508 ft (1069 m)- Mean 1,900 ft (580 m) - Lowest point Red River of the North at Manitoba border[2][3]
751 ft (229 m)Admission to Union November 2, 1889[a] (39th) Governor Jack Dalrymple (R) Lieutenant Governor Drew Wrigley (R) Legislature Legislative Assembly - Upper house Senate - Lower house House of Representatives U.S. Senators Kent Conrad (D)
John Hoeven (R)U.S. House delegation Rick Berg (R) (list) Time zones - most of state Central: UTC-6/-5 - southwest Mountain: UTC-7/-6 Abbreviations ND US-ND Website nd.gov North Dakota
 i/ˌnɔrθ dəˈkoʊtə/ is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States of America, along the Canadian border. The state is bordered by Canada to the north, Minnesota to the east, South Dakota to the south and Montana to the west.[4] North Dakota is the 19th-largest state by area in the U.S. It is also the third least populous, with 672,591 residents according to the 2010 census.[5] North Dakota was carved out of the Dakota Territory and admitted to the Union on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with South Dakota.
i/ˌnɔrθ dəˈkoʊtə/ is a state located in the Midwestern region of the United States of America, along the Canadian border. The state is bordered by Canada to the north, Minnesota to the east, South Dakota to the south and Montana to the west.[4] North Dakota is the 19th-largest state by area in the U.S. It is also the third least populous, with 672,591 residents according to the 2010 census.[5] North Dakota was carved out of the Dakota Territory and admitted to the Union on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with South Dakota.The state capital is Bismarck and the largest city is Fargo. The primary public universities are located in Grand Forks and Fargo. The U.S. Air Force operates Air Force Bases at Minot AFB and Grand Forks AFB.
For more than a decade, the state has had a strong economy, with unemployment lower than the national average, job and population growth, and low housing vacancies. Much of the growth has been based on development of the Bakken oil shale fields in the western part of the state, but it has also had growth in the technology and service sectors. Flooding in June 2011 has caused extensive damage to Minot and threatened Bismarck, the capital city.
Contents
Geography
Main article: Geography of North DakotaSee also: List of North Dakota countiesNorth Dakota is considered to be in the U.S. region known as the Great Plains, and is sometimes referred to as being the "High Plains". The state shares the Red River of the North with Minnesota on the east; South Dakota is to the south, Montana is to the west, and the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Manitoba are north. North Dakota sits essentially in the middle of North America, and in fact a stone marker in Rugby, North Dakota, identifies itself as being the "Geographic Center of the North American Continent". With 70,762 square miles (183,273 km2),[6] North Dakota is the 19th largest state.[7]
The western half of the state consists of the hilly Great Plains, and the northern part of the Badlands to the west of the Missouri River. The state's high point, White Butte at 3,506 feet (1,069 m), and Theodore Roosevelt National Park[8] are located in the Badlands. The region is abundant in fossil fuels including crude oil and lignite coal. The Missouri River forms Lake Sakakawea, the third largest man-made lake in the United States, behind the Garrison Dam.[9]
The central region of the state is divided into the Drift Prairie and the Missouri Plateau. The eastern part of the state consists of the flat Red River Valley, the bottom of glacial Lake Agassiz. Its fertile soil, drained by the meandering Red River flowing northward into Lake Winnipeg, supports a large agriculture industry.[10] Devils Lake, the largest natural lake in the state, is also found in the east.[11]
Eastern North Dakota is overall flat, however, there are significant hills and buttes in western North Dakota. Most of the state is covered in grassland; crops cover most of eastern North Dakota but are sparse in the center and west. Natural trees in North Dakota are found usually where there is good drainage such as the ravines and valley near the Pembina Gorge and Killdeer Mountains, the Turtle Mountains, the hills around Devil's Lake, in the dunes area of McHenry County in central North Dakota, and along the Sheyenne Valley slopes and the Sheyenne delta.
Climate
Main article: Climate of North DakotaMeteorological events can include rain, snow, hail, blizzards, polar fronts, tornadoes, thunderstorms, and high-velocity straight-line winds. Depending on location, average annual precipitation ranges from 14 to 22 in (360 to 560 mm).[12]
Springtime flooding is a relatively common event in the Red River Valley, because of the river flowing north into Canada, creating ice jams. The spring melt and the eventual runoff typically begins earlier in the southern part of the valley than in the northern part.[13] The most destructive flooding in eastern North Dakota occurred in 1997.[14]
North Dakota is largely semi-arid; however, the low temperatures and snowpack prevents the state from having a xeric character.
The American Lung Association in its 2009 "State of the Air" report ranked Fargo, North Dakota as the cleanest city in the United States, and gave the balance of the state 11 "A" ratings on air quality.[15][16]
History
Main article: History of North DakotaPrior to European contact, Native Americans inhabited North Dakota for thousands of years. The first European to reach the area was the French-Canadian trader La Vérendrye, who led an exploration party to Mandan villages in 1738.[17] The trading arrangement between tribes was such that North Dakota tribes rarely dealt directly with Europeans. However, the native tribes were in sufficient contact that by the time that Lewis and Clark entered North Dakota in 1804, they were aware of the French and then Spanish claims to their territory.[18]
 Settlers in front of their sod house in Milton in 1898
Settlers in front of their sod house in Milton in 1898
Much of present-day North Dakota was included in the Louisiana Purchase of 1803; the remainder was acquired in the Treaty of 1818. Much of the acquired land was organized into Minnesota and Nebraska Territories. Dakota Territory, making up present-day North and South Dakota, along with parts of present-day Wyoming and Montana, was organized on March 2, 1861.[19] Dakota Territory was settled sparsely until the late 19th century, when the railroads entered the region and aggressively marketed the land. An omnibus bill for statehood for North Dakota, South Dakota, Montana, and Washington titled the Enabling Act of 1889 was passed on February 22, 1889 during the administration of Grover Cleveland. After Cleveland left office, it was left to his successor, Benjamin Harrison, to sign proclamations formally admitting North and South Dakota to the Union on November 2, 1889.[20] The rivalry between the two new states presented a dilemma of which was to be admitted first. Harrison directed Secretary of State James G. Blaine to shuffle the papers and obscure from him which he was signing first and the actual order went unrecorded, thus no one knows which of the Dakotas was admitted first.[21][22] However, since North Dakota alphabetically appears before South Dakota, its proclamation was published first in the Statutes At Large. Since that day, it has become common to list the Dakotas alphabetically and thus North Dakota is usually listed as the 39th state.
Unrest among wheat farmers, especially among Norwegians, led to a radical political movement after World War I centered in the left-wing Non Partisan League ("NPL"). The NPL, which eventually merged into the Democratic Party, attempted to insulate North Dakota from the power of out-of-state banks and corporations. In addition to founding the state-owned Bank of North Dakota and North Dakota Mill and Elevator (both still in existence), the NPL established a state-owned railroad line (later sold to the Soo Line Railroad). Anti-corporate laws were passed that virtually prohibited a corporation or bank from owning title to land zoned as farmland. These laws, still in force today, after having been upheld by both State and Federal courts, make it almost impossible to foreclose on farmland, as even after foreclosure, the property title cannot be held by a bank or mortgage company.
A round of federal construction projects began in the 1950s, including the Garrison Dam and the Minot and Grand Forks Air Force bases.[23] There was a boom in oil exploration in western North Dakota in the 1980s, as rising petroleum prices made development profitable.[24] The original North Dakota State Capitol burned to the ground on December 28, 1930, and was replaced by a limestone faced art deco skyscraper that still stands today.[25]
Demographics
Population
From fewer than 2,000 people in 1870, North Dakota's population grew to near 680,000 by 1930. Growth then slowed, and the population has fluctuated slightly over the past seven decades, hitting a low of 617,761 in the 1970 census, with a total of 642,200 in the 2000 census.[26] The United States Census Bureau, as of July 1, 2008, estimated North Dakota's population at 641,481,[27] which represents a decrease of 714, or 0.1%, since the last census in 2000.[28] This includes a natural increase since the last census of 20,460 people (that is 67,788 births minus 47,328 deaths) and a decrease due to net migration of 17,787 people out of the state.[28] Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 3,323 people, and migration within the country produced a net loss of 21,110 people.[28] The age and gender distributions approximate the national average. Except for Native Americans, the North Dakota population has a lesser percentage of minorities than in the nation as a whole.[29] The center of population of North Dakota is located in Wells County, near Sykeston.[30]
Historical populations Census Pop. %± 1870 2,405 — 1880 36,909 1,434.7% 1890 190,983 417.4% 1900 319,146 67.1% 1910 577,056 80.8% 1920 646,872 12.1% 1930 680,845 5.3% 1940 641,935 −5.7% 1950 619,636 −3.5% 1960 632,446 2.1% 1970 617,761 −2.3% 1980 652,717 5.7% 1990 638,800 −2.1% 2000 642,200 0.5% 2010 672,591 4.7% Source: 1910–2010[31] Emigration
From 1923 through the beginning of the 21st century, North Dakota experienced a virtually constant decline in population, particularly among younger people with university degrees. Subsistence farming proved to be too risky for families, and many people moved to urban areas for jobs.[32] One of the major causes of emigration in North Dakota is the lack of skilled jobs for college graduates. Some propose the expansion of economic development programs to create skilled and high-tech jobs, but the effectiveness of such programs has been open to debate.[33] During the first decade of the 21st century, the population increased, in large part because of jobs in the oil industry, related to development of oil-shale fields.[citation needed]
Languages
In addition to English, 2.5% of the population speak German.[34]
Race and ancestry
Most North Dakotans are of Northern European descent. As of 2009, the five largest ancestry groups in North Dakota are:
- German: 47.2% (305,322)
- Norwegian: 30.8% (199,154)
- Irish: 7.7% (49,892)
- Swedish: 4.7% (30,194)
- Russian: 4.1% (26,642)
- French: 4.1% (26,320)
- English: 3.9% (25,331)
According to the 2010 Census, the racial and ethnic composition of North Dakota was as follows:[35]
- White: 90.0%
- Native American: 5.4%
- Hispanic or Latino (of any race): 2.0%
- Black or African American: 1.2%
- Asian: 1.0%
- Pacific Islander: 0.1%
- Some other race: 0.5%
- Two or more races:
Religion
North Dakota has the lowest percentage of non-religious people of any state, and it also has the most churches per capita of any state.[36]
A 2001 survey indicated that 35% of North Dakota's population was Lutheran, and 30% was Roman Catholic. Other religious groups represented were Methodists (7%), Baptists (6%), the Assemblies of God (3%), and Jehovah's Witness (1%). Christians with unstated or other denominational affiliations, including other Protestants and the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (Mormonism), totaled 3%, bringing the total Christian population to 86%. Other religions, such as Judaism, Islam, Buddhism, and Hinduism, together represented 4% of the population. There were an estimated 920 Muslims and 730 Jews in the state in 2000.[37] Three percent of respondents answered "no religion" on the survey, and 6% declined to answer.[36]
The largest denominations by number of adherents in 2000 were the Roman Catholic Church with 179,349; the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America with 174,554; and the Lutheran Church–Missouri Synod with 23,720.[38]
Culture
American Indian presence
North Dakota has a great number of Native Americans. Powwows (or pow-wows) are an important aspect of Native American culture. Throughout Native American history, powwows were held, usually in the spring, to rejoice on the beginning of new life. These events brought Native American tribes together for singing and dancing and allowed them to meet up with old friendships, as well as to make new ones. Many powwows also held religious significance for some tribes. Today, powwows are still a part of the Native American culture, and are attended by Native and non-Natives alike. In North Dakota, the United Tribes International Powwow, held each September in Bismarck, is one of the largest powwows in the United States.
A powwow is complete with parades and dancers in regalia, with many dancing styles presented. It is traditional for male dancers to wear regalia decorated with beads, quills and eagle feathers; male grass dancers wear colorful fringe regalia; and male fancy dancers wear brightly colored feathers. Female dancers dance much more subtly than the male dancers. Fancy female dancers wear cloth, beaded moccasins and jewelry, while the jingle dress dancer wears a dress made of metal cones. There are intertribal dances throughout the powwow, where everyone (even spectators) can take part in the dancing.
Norwegian and Icelandic influence
Around 1870 many European immigrants from Norway settled in North Dakota's northeastern corner, especially near the Red River. Icelanders also arrived from Canada.[39] Pembina housed many Norwegians when it was founded; they worked on family farms. They started Lutheran churches and schools and they greatly outnumbered other denominations in the area. This group has unique foods such as lefse and lutefisk. The continent's largest Scandinavian event, Norsk Høstfest, is celebrated each September in Minot. The Icelandic State Park in Pembina County and an annual Icelandic festival reflect immigrants from that country.
Old world folk customs have persisted for decades, with revival of techniques in weaving, silver crafting, and wood carving. Traditional turf-roof houses are displayed in parks; this style originated in Iceland. A stave church is a landmark in Minot. Ethnic Norwegians constitute nearly one-third or 32.3% of Minot's total population and 30.8% of North Dakota's total population.
Germans from Russia
See also: Germans from RussiaEthnic Germans who had settled in Russia for several generations grew dissatisfied in the nineteenth century. About 100,000 immigrated to the U.S. by 1900, settling primarily in North and South Dakota, Kansas and Nebraska. The south-central part of North Dakota became known as "the German-Russian triangle". By 1910, about 60,000 ethnic Germans from Russia lived in Central North Dakota. They were Lutherans and Roman Catholics who had kept many German customs of the time when their ancestors emigrated to Russia. They were committed to agriculture. A famous art form by such ethnic Germans are wrought iron crosses, which are used to mark grave sites.[40]
Fine and performing arts
North Dakota's major fine art museums and venues include the Chester Fritz Auditorium, Empire Arts Center, the Fargo Theatre, North Dakota Museum of Art, and the Plains Art Museum. The Bismarck-Mandan Symphony Orchestra, Fargo-Moorhead Symphony Orchestra, Greater Grand Forks Symphony Orchestra, Minot Symphony Orchestra and Great Plains Harmony Chorus are full-time professional and semi-professional musical ensembles that perform concerts and offer educational programs to the community.
Entertainment
See also: Music of North DakotaNorth Dakotan musicians of many genres include blues guitarist Jonny Lang, country music singer Lynn Anderson, jazz and traditional pop singer and songwriter Peggy Lee, big band leader Lawrence Welk, and pop singer Bobby Vee. The state is also home to two groups of the Indie rock genre that have become known on a national scale: GodheadSilo (originally from Fargo, but later relocated to Olympia, Washington and became signed to the Kill Rock Stars label) and June Panic (also of Fargo, signed to Secretly Canadian).
Ed Schultz is known around the country as the host of progressive talk radio show The Ed Schultz Show, and The Ed Show on MSNBC. Shadoe Stevens hosted American Top 40 from 1988 to 1995. Josh Duhamel is an Emmy Award-winning actor known for his roles in All My Children and Las Vegas.[41] Nicole Linkletter and CariDee English were winning contestants of Cycles 5 and 7, respectively, of America's Next Top Model. Kellan Lutz has appeared in movies such as Stick It, Accepted, Prom Night, and Twilight.
Popular culture
See also: Cuisine of North DakotaNorth Dakota cuisine includes Knoephla soup: a thick, stew-like chicken soup with dumplings, lutefisk: lye-treated fish, Kuchen: a pie-like pastry, lefse: a flat bread made from riced potatoes that is eaten with butter and sugar, Fleischkuekle, a deep fried entree of ground beef covered in dough, and served with chips and a pickle in most restaurants; strudel: a dough-and-filling item that can either be made as a pastry, or a savory dish with onions or meat; and other traditional German and Norwegian dishes. North Dakota also shares concepts such as hot dishes along with other Midwestern states.
Along with having the most churches per capita of any state, North Dakota has the highest percentage of church-going population of any state.[36]
Outdoor activities such as hunting and fishing are hobbies for many North Dakotans. Ice fishing, raccoon hunting, and snowmobiling are also popular during the winter months. Residents of North Dakota may own or visit a cabin along a lake. Popular sport fish include walleye, perch, and northern pike.[42]
The western terminus of the North Country National Scenic Trail is located on Lake Sakakawea where it abuts the Lewis and Clark Trail.
Economy
 North Dakota state quarter
North Dakota state quarter See also: List of North Dakota companies
See also: List of North Dakota companiesAgriculture is the largest industry in North Dakota, although petroleum and food processing are also major industries.[43] The economy of North Dakota had a gross domestic product of $24 billion in 2005.[44] The per capita income in 2006 was $33,034, ranked 29th in the nation.[45] The three-year median household income from 2002–2004 was $39,594, ranking 37th in the U.S.[46] North Dakota is also the only state with a state owned bank, the Bank of North Dakota in Bismarck, and a state owned flour mill, the North Dakota Mill and Elevator in Grand Forks.
As of September 2010, the state's unemployment rate is the lowest in the nation at 3.7%[47] and it never touched 5 percent since 1987, the state with the nation's lowest unemployment rate. At end of 2010, the state per capita income was rank in 17th of the nation, the biggest increase of any state in a decade from rank 38th.[48]
Agriculture
North Dakota's earliest industries were fur trading and agriculture. Although less than 10% of the population is employed in the agricultural sector,[49] it remains a major part of the state's economy, ranking 9th in the nation in the value of crops and 18th in total value of agricultural products sold. North Dakota has about 90% of its land area in farms with 27,500,000 acres (111,000 km2) of cropland, the third largest in the nation. Between 2002 and 2007 total cropland increased by about one million acres (4,000 km²), the only state showing an increase. Over the same period, 1,800,000 acres (7,300 km2) were shifted into soybean and corn production, the largest such shift in the United States.[50]
The state is the largest producer in the U.S. of many cereal grains including barley (36% of U.S. crop), durum wheat (58%), hard red spring wheat (48%), oats (17%), and combined wheat of all types (15%). It is the second leading producer of buckwheat (20%). As of 2007, corn became the state's largest crop produced, although only 2% of U.S. production.[50]
The state is the leading producer of many oilseeds including 92% of the U.S. canola crop, 94% of flax seed, 53% of sunflower seeds, 18% of safflower seeds, and 62% of mustard seed. Soybeans are also an increasingly important crop with 400,000 acres (1,600 km2) additional planted between 2002 and 2007.[50]
North Dakota is the second leading producer of sugarbeets, grown in the Red River Valley. The state is also the largest producer of honey, dry edible peas and beans, lentils, and the third largest producer of potatoes.[50]
North Dakota's economy is aided by nearly $1 billion in federal agricultural subsidies annually.
Energy
The energy industry is a major contributor to the economy. Lignite coal reserves in Western North Dakota are used to generate about 90% of the electricity consumed, and is also exported to nearby states.[51] North Dakota has the second largest lignite coal production in the U.S.[52]
Oil was discovered near Tioga in 1951, generating 53 million barrels (8,400,000 m3) of oil a year by 1984.[53] Recoverable oil reserves have jumped dramatically recently. The oil reserves of the Bakken Formation may hold up to 400 billion barrels (6.4×1010 m3) of oil, 25 times larger than the reserves in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge.[54][55] However, a report issued in April 2008 by the U.S. Geological Survey estimates that the oil recoverable by current technology in the Bakken formation is two orders of magnitude less, in the range of 3 billion barrels (480×106 m3) to 4.3 billion barrels (680×106 m3), with a mean of 3.65 billion barrels (580×106 m3).[56] Western North Dakota is currently in an oil boom: the Williston, Tioga, Stanley and Minot-Burlington communities are experiencing rapid growth. As of 2010, the state has the 4th largest oil production in the U.S. of 355,000 barrels per day, more than triple 2007 production.[57][58]
The Great Plains area, which North Dakota is a part of, is called the "Saudi Arabia" of wind energy,[59] Wind energy in North Dakota is also very cost effective because the state has large rural expanses and wind speeds seldom go below 10 mph (16 km/h).
State taxes
North Dakota has a slightly progressive income tax structure; the five brackets of state income tax rates are 2.1%, 3.92% 4.34%, 5.04%, and 5.54% as of 2004.[60] In 2005 North Dakota ranked 22nd highest by per capita state taxes.[61] The sales tax in North Dakota is 5% for most items.[62] The state allows municipalities to institute local sales taxes and special local taxes, such as the 1.75% supplemental sales tax in Grand Forks.[63] Excise taxes are levied on the purchase price or market value of aircraft registered in North Dakota. The state imposes a use tax on items purchased elsewhere but used within North Dakota. Owners of real property in North Dakota pay property tax to their county, municipality, school district, and special taxing districts.[64]
The Tax Foundation ranks North Dakota as the state with the 20th most "business friendly" tax climate in the nation.[65] Tax Freedom Day arrives on April 1, 10 days earlier than the national Tax Freedom Day.[65] In 2006, North Dakota was the state with the lowest number of returns filed by taxpayers with an Adjusted Gross Income of over $1M – only 333.[66]
Tourism
North Dakota is considered the least visited state, owing, in part, to its not having a major tourist attraction.[67] Areas popular with visitors include Theodore Roosevelt National Park in the western part of the state. The park often exceeds 475,000 visitors each year.[68] Regular events in the state that attract tourists include Norsk Høstfest in Minot, billed as North America's largest Scandinavian festival;[69] the Medora Musical; and the North Dakota State Fair.
Medicine
North Dakota is the only US state that legally demands its pharmacies to have 51% shares owned by pharmacists.[70]
Transportation
See also: List of North Dakota numbered highways, List of North Dakota railroads, and Aviation in North DakotaTransportation in North Dakota is overseen by the North Dakota Department of Transportation. The major Interstate highways are Interstate 29 and Interstate 94, with I-29 and I-94 meeting at Fargo, with I-29 oriented north to south along the eastern edge of the state, and I-94 bisecting the state from east to west between Minnesota and Montana. A unique feature of the North Dakota Interstate Highway system, is that virtually all of it is paved in concrete, rather than blacktop, because of the extreme weather conditions it must endure. The largest rail systems in the state are operated by BNSF and the Canadian Pacific Railway. Many branch lines formerly used by BNSF and Canadian Pacific Railway are now operated by the Dakota, Missouri Valley and Western Railroad and the Red River Valley and Western Railroad.[71][72]
North Dakota's principal airports are the Hector International Airport (FAR) in Fargo, Grand Forks International Airport (GFK), Bismarck Municipal Airport (BIS), and the Minot International Airport (MOT).
Amtrak's Empire Builder runs through North Dakota, making stops at Fargo (2:13 am westbound, 3:35 am eastbound), Grand Forks (4:52 am westbound, 12:57 am eastbound), Minot (around 9 am westbound and around 9:30 pm eastbound), and four other stations.[73] It is the descendant of the famous line of the same name run by the Great Northern Railway, which was built by the tycoon James J. Hill and ran from St. Paul to Seattle. Intercity bus service is provided by Greyhound and Jefferson Lines. Public transit in North Dakota is currently limited to bus systems in the larger cities.
In March 2011, North Dakota ranked as a bottom-ten "worst" state (tied with Montana and Texas) in the American State Litter Scorecard. North Dakota suffers from poor effectiveness and quality of its statewide public space cleanliness—mostly roadside and adjacent property litter/debris—due to overall state and related eradication standards and performance indicators.[74]
Law and government
As with the federal government of the United States, power in North Dakota is divided into three branches: executive, legislative, and judicial.[75] Additionally, North Dakota was the first US state to introduce the initiative in 1898.
Executive
See also: List of Governors of North Dakota, List of Lieutenant Governors of North Dakota, List of Secretaries of State of North Dakota, and List of Attorneys General of North Dakota John Burke, 10th Governor of North Dakota
John Burke, 10th Governor of North Dakota
The executive branch is headed by the governor. The current governor is Jack Dalrymple, a Republican who took office December 7, 2010 after his predecessor, John Hoeven won his race for U.S. Senate, and resigned to prepare for that office. The current Lieutenant Governor of North Dakota is Drew Wrigley, who is also the President of the Senate. The offices of governor and lieutenant governor have four-year terms, which are next up for election in 2012. The governor has a cabinet consisting of the leaders of various state government agencies, called commissioners. The other elected constitutional offices are secretary of state, attorney general, and state auditor.
Legislative
The North Dakota Legislative Assembly is a bicameral body consisting of the Senate and the House of Representatives. The state has 47 districts. Each district has one senator and two representatives. Both senators and representatives are elected to four year terms. The state's legal code is named the North Dakota Century Code.
Judicial
North Dakota's court system has four levels. Municipal courts serve the cities, and most cases start in the district courts, which are courts of general jurisdiction. There are 42 district court judges in seven judicial districts.[76][77] Appeals from the trial courts and challenges to certain governmental decisions are heard by the North Dakota Court of Appeals, consisting of three-judge panels. The five-justice North Dakota Supreme Court hears all appeals from the district courts and the Court of Appeals.[78]
Regional
There are three Sioux, one Three Affiliated Tribes, and one Ojibwa reservations in North Dakota. These communities are self-governing.
Federal
See also: List of United States Senators from North Dakota, North Dakota United States Senate election, 2006, and United States House elections, 2006#North DakotaNorth Dakota's United States Senators are Democrat Kent Conrad and Republican John Hoeven. The state has one at-large congressional district represented by Republican representative Rick Berg.
Federal court cases are heard in the United States District Court for the District of North Dakota, which holds court in Bismarck, Fargo, Grand Forks, and Minot. Appeals are heard by the Eighth Circuit Court of Appeals based in St. Louis, Missouri.
Politics
Main article: Politics of North DakotaThe major political parties in North Dakota are the Democratic-NPL and the Republican Party. As of 2007[update], the Constitution Party and the Libertarian Party are also organized parties in the state.
At the state level, the governorship has been held by the Republican Party since 1992, along with a majority of the state legislature and statewide officers. Dem-NPL showings were strong in the 2000 governor's race, and in the 2006 legislative elections, but the League has not had a major breakthrough since the administration of former state governor George Sinner.
The Republican Party presidential candidate usually carries the state; in 2004, George W. Bush won with 62.9% of the vote. Of all the Democratic presidential candidates since 1892, only Grover Cleveland, Woodrow Wilson, Franklin Roosevelt, and Lyndon Johnson received Electoral College votes from North Dakota.
On the other hand, Dem-NPL candidates for North Dakota's federal Senate and Congressional seats have won every election between 1982 and 2008, and the state's federal delegation was entirely Democratic from 1987 to 2011.
Indian tribes and reservations
Federally recognized tribes within the boundaries of North Dakota have independent, sovereign relationships with the federal government and territorial reservations:
- Standing Rock Sioux of Standing Rock Indian Reservation;
- Turtle Mountain Band of Chippewa Indians at Turtle Mountain Reservation;
- Mandan, Hidatsa, and Arikara Nation, Fort Berthold Reservation; and
- Spirit Lake Tribe, whose reservation is near Devil's Lake
Bismarck
Bismarck, located in south-central North Dakota along the banks of the Missouri River, has been North Dakota's capital city since 1883, first as capital of the Dakota Territory, and then as state capital since 1889. While Bismarck had served adequately as the territorial capital, many thought the state's capital city should be located to the east since then, as now, the majority of North Dakotans lived in the eastern half of the state. To that end, the legislature chose Jamestown as the new capital, and the state's official records were moved there. They were stored in the new Stutsman County Court House, in preparation for the first session of the North Dakota Legislature.
Before the legislators gathered, a small group of Bismarck residents raided Jamestown in a January blizzard, broke into the court house and took the state records, transporting them back to Bismarck ahead of a pursuing posse. Bismarck leaders held the records hostage until the legislature agreed to meet in Bismarck. Once the legislators began meeting in Bismarck, they decided it was too much work to move the capital. They refused to formally vote to establish Bismarck as the state capital city.
Bismarck's popularity and beauty attracts many people from other parts of the state. The state capitol building is the tallest building in the state, and the city has the largest museum in the state, a civic center, the largest opera/ballet house in the state, and the largest zoo in the state. Community life is reflected in night clubs, churches, schools, stadiums, and several universities in Bismarck: University of Mary, Bismarck State College, United Tribes Technical College, and Rasmussen College. Bismarck is the center in North Dakota of government, health care, banking, finance, nature protection and preservation, recreational activities, cultural opportunity, job availability, literature, and education. The city has many parks and recreational areas, three malls, and many plazas. Its downtown is located on top of rolling hills along the Missouri River.
Trees grow well in Bismarck because water is plentiful. Bismarck provides almost all radio signals and transfers data (weather predictions, news, newspaper, sporting events) to almost all of North Dakota. Eastern Montana and northern South Dakota are also covered by the city of Bismarck. Bismarck ranks second in tourism after Minot, and attracts tourism year round. Bismarck is the second-largest metro area after Fargo. Bismarck has been ranked the "Official Safest (Large Population) City in America to Live".
Major cities
See also: List of cities in North Dakota Downtown Fargo in 2007
Downtown Fargo in 2007
Fargo is the largest city in North Dakota. Bismarck grew with the discovery of gold in the Black Hills in 1874. Many miners and settlers came to the region from western gold fields in California and Colorado. A second economic impetus was the construction of Garrison Dam on Lake Sakakawea. Retail stores have flocked to the area to benefit from the city's growing population. Minot is a city in northern North Dakota is home of the North Dakota State Fair. Located a few miles west of Bismarck on the west side of the Missouri River, Mandan was named for the Mandan Indians who inhabited the area at the time of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. New Salem is the site of the world's largest statue of a holstein cow; the world's largest statue of a bison is in Jamestown.
Grand Forks and Devils Lake are located in scenic areas of North Dakota. Williston is located near the confluence of the Missouri River and the Yellowstone River near Montana. Medora in the North Dakota Badlands hosts the Medora Musical every summer and is the gateway to Theodore Roosevelt National Park. Fort Yates, located along the Missouri River on the Standing Rock Indian Reservation claims to host the final resting place of Hunkpapa Lakota leader Sitting Bull (Mobridge, South Dakota also claims his gravesite).
Education
Higher education
The state has 11 public colleges and universities, five tribal community colleges, and four private schools. The largest institutions are North Dakota State University and the University of North Dakota.
The higher education system consists of the following institutions:
North Dakota University System (public institutions):
-
- Bismarck State College in Bismarck
- Dickinson State University in Dickinson
- Lake Region State College in Devils Lake
- Mayville State University in Mayville
- Minot State University in Minot
- Dakota College at Bottineau in Bottineau
- North Dakota State University in Fargo
- North Dakota State College of Science in Wahpeton
- University of North Dakota in Grand Forks
- Valley City State University in Valley City
- Williston State College in Williston
Tribal institutions:
Private institutions:
State symbols
- State bird: Western Meadowlark, Sturnella neglecta
- State fish: Northern pike, Esox lucius
- State horse: Nokota horse
- State flower: Wild Prairie Rose, Rosa arkansana
- State tree: American Elm, Ulmus americana
- State fossil: Teredo Petrified wood
- State grass: Western Wheatgrass, Pascopyrum smithii (Rydb.) A. Löve
- State nicknames: Roughrider State, Flickertail State, Peace Garden State, Sioux state.
- State mottos:
- (Great Seal of North Dakota) Liberty and Union, Now and Forever, One and Inseparable
- (Coat of Arms of North Dakota) Strength from the Soil
- (Latin Motto of North Dakota, Affective August 1, 2011 "Serit ut alteri saeclo prosit" (One sows for the benefit of another age.)
- State slogan: Legendary
- State song: North Dakota Hymn
- State dance: Square Dance
- State fruit: Chokecherry
- State march: Flickertail March
- State beverage: Milk[79]
- State art museum: North Dakota Museum of Art
- State license plate: see the different types over time[80]
"The Flickertail State" is one of North Dakota's nicknames and is derived from Richardson's Ground Squirrel (Spermophilus richardsonii), a very common animal in the region. The ground squirrel constantly flicks its tail in a distinctive manner. In 1953, legislation to make the ground squirrel the state emblem was voted down in the state legislature.[81]
Media
North Dakota's media markets are Fargo-Grand Forks, (121st largest nationally), making up the eastern half of the state, and Minot-Bismarck (158th), making up the western half of the state.[82] Prairie Public Television (PPTV) is a statewide public television network affiliated with PBS.
Broadcast television in North Dakota started on April 3, 1953, when KCJB-TV (now KXMC-TV) in Minot began broadcasting.[83] There are currently 28 analog broadcast stations and 18 digital channels broadcast over North Dakota.
The state's largest newspaper is The Forum of Fargo-Moorhead. Other weekly and monthly publications (most of which are fully supported by advertising) are also available. The most prominent of these is the alternative weekly High Plains Reader, which covers Fargo and Grand Forks.
Prairie Public is a statewide radio network affiliated with National Public Radio. The state's oldest radio station, WDAY-AM, was launched on May 23, 1922.[84] The Forum Communications owned station is still on the air, and currently broadcasts a news/talk format.
North Dakotans
For a more comprehensive list, see List of people from North Dakota.- Sam Anderson, actor.
- Brian Bohrer, minister and author.
- James F. Buchli, former NASA astronaut.
- Quentin N. Burdick, former U.S. Senator, third longest-serving Senator among current members of this body.
- Warren Christopher, former U.S. Secretary of State, diplomat and lawyer.
- Shannon Curfman, American blues-rock guitarist and singer.
- Angie Dickinson, Golden Globe-winning television and film actress.
- Josh Duhamel, Emmy Award-winning actor and former male fashion model.
- Carl Ben Eielson, aviator, bush pilot and explorer.
- CariDee English, winner of Cycle 7 on America's Next Top Model. Host of Pretty Wicked.
- Louise Erdrich, Native American author of novels, poetry, and children's books.
- Darin Erstad, MLB all-star and World Series Champion.
- Travis Hafner, MLB Designated Hitter for the Cleveland Indians.
- Richard Hieb, former NASA astronaut.
- Virgil Hill, former WBA World Cruiserweight champion and Olympic boxer.
- Gordon Kahl, tax protestor best known for the Medina shootout in 1983.
- Chuck Klosterman, writer, journalist, critic, humorist, and essayist whose work often focuses on pop culture.
- Louis L'Amour, author of primarily Western fiction.
- Jonny Lang, Grammy-winning blues guitarist and singer.
- Peggy Lee, jazz and traditional pop singer and songwriter.
- Nicole Linkletter, winner of Cycle 5 on "America's Next Top Model".
- Kellan Lutz, actor who portrays Emmett Cullen in Twilight and New Moon. Former male fashion model.
- Roger Maris, right fielder in Major League Baseball and former single season home run record holder
- Phil Jackson, coach for the LA Lakers.
- Helen Marshall, poet and medievalist.
- Thomas McGrath, poet and political activist.
- Mancur Olson, economist.
- Alan Ritchson, participant in 3rd season of American Idol, singer, model and actor.
- Sakakawea, Shoshone woman of Lewis and Clark fame.
- Ed Schultz, host of The Ed Schultz Show.
- Eric Sevareid, CBS news journalist.
- Ann Sothern, Oscar nominated film and television actress.
- Richard St. Clair, Harvard-educated composer of modern classical music.
- Shadoe Stevens, host of American Top 40.
- Bobby Vee, pop music singer.
- Lawrence Welk, musician, accordion player, bandleader, and television impresario.
- Wiz Khalifa hip hop artist.
See also
- Outline of North Dakota
- Index of North Dakota-related articles
- Great Plains
- List of National Register of Historic Places in North Dakota
- List of people from North Dakota
- Missouri River
- Red River of the North
- US state
References
- ^ North Dakota Century Code, CHAPTER 54-02-13
- ^ a b "Elevations and Distances in the United States". United States Geological Survey. 2001. http://egsc.usgs.gov/isb/pubs/booklets/elvadist/elvadist.html. Retrieved October 24, 2011.
- ^ a b Elevation adjusted to North American Vertical Datum of 1988.
- ^ Geography of North Dakota – netstate.com. Retrieved July 21, 2011.
- ^ North Dakota QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau – census.gov. Retrieved July 21, 2011.
- ^ "Facts and figures". infoplease.com. http://www.infoplease.com/ce6/us/A0860033.html. Retrieved 2006-06-22.
- ^ "Land and Water Area of States, 2000". Information Please. 2006. http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0108355.html. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ^ "Theodore Roosevelt National Park Virtual Tour". The Real North Dakota Project. 2007. http://www.realnd.com/badlandsindex.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ^ "History of Lake Sakakawea State Park". North Dakota Parks & Recreation Department. 2003. Archived from the original on 2007-09-28. http://web.archive.org/web/20070928061913/http://www.ndparks.com/Parks/Sakakawea/history.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ^ "A Glacier, A Lake, A Valley and Soil for the Future". University of Minnesota. 1979. http://mbbnet.umn.edu/hoff/hoff_agassiz.html. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ^ "North Dakota Facts and Trivia". 50States.com. 2007. http://www.50states.com/facts/ndakota.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-17.
- ^ "Climate of North Dakota" (PDF). National Weather Service Forecast Office. http://www5.ncdc.noaa.gov/climatenormals/clim60/states/Clim_ND_01.pdf. Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ^ "Anatomy of a Red River Flood". National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office. http://www.crh.noaa.gov/fgf/hydro/red_river_flood.php. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "The Grand Forks Flood". Alan Draves. 2002. http://www.grandforksflood.com/. Retrieved 2007-08-20.
- ^ American Lung Association of North Dakota (April 29, 2009). "Fargo Named 'America's Cleanest City' in American Lung Association's State of the Air Report". http://www.redorbit.com/news/health/1679099/fargo_named_americas_cleanest_city_in_american_lung_associations_state/. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ^ American Lung Association (2009). "State of the Air 2009" (PDF). http://www.lungusa.org/assets/documents/publications/state-of-the-air/state-of-the-air-report-2009.pdf. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ^ "Audio Transcript of Pierre Gaultier de La Vérendrye 1738". The Atlas of Canada. 2003. http://atlas.nrcan.gc.ca/site/english/maps/historical/exploration/1738_verendrye.mov/view. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "North Dakota, US". ByRegion Network. 2005. http://www.byregion.net/landpages/ND. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "North Dakota Historical Overview: Dakota Territory and Statehood (Northern Great Plains)". The Library of Congress. http://memory.loc.gov/ammem/award97/ndfahtml/ngp_nd_terr.html. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "Enabling Act". Washington State Legislature. Archived from the original on 2007-09-19. http://web.archive.org/web/20070919230052/http://www.leg.wa.gov/History/State/enabling.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "Coin of the Month". The United States Mint. http://www.usmint.gov/kids/coinNews/coinOfTheMonth/2006/09.cfm. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "North Dakota's Boundaries". North Dakota Geological Survey. 2002. https://www.dmr.nd.gov/ndgs//ndnotes/Boundaries/Boundaries.asp. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "North Dakota Timeline". WorldAtlas.com. http://worldatlas.com/webimage/countrys/namerica/usstates/ndtimeln.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "North Dakota History: Overview and Summary". State Historical Society of North Dakota. 1999. Archived from the original on 2007-04-03. http://web.archive.org/web/20070403060553/http://www.nd.gov/hist/ndhist.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "North Dakota State Capitol Building & Grounds Virtual Tour Map". The Real North Dakota Project. http://www.realnd.com/capitolmap.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "North Dakota Historical Population". North Dakota State University. http://www.ndsu.nodak.edu/instruct/sainieid/north-dakota-historical-population.html. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "Annual Estimates of the Resident Population for the United States, Regions, States, and Puerto Rico: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2008". United States Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/popest/states/tables/NST-EST2008-01.csv. Retrieved 2009-01-31.
- ^ a b c "Cumulative Estimates of the Components of Population Change for the United States, Regions and States: April 1, 2000 to July 1, 2008 (NST-EST2008-04)" (CSV). U.S. Census Bureau. 2008-12-15. http://www.census.gov/popest/states/tables/NST-EST2008-04.csv. Retrieved 2009-01-16.
- ^ "North Dakota QuickFacts from the US Census Bureau". http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/states/38000.html. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "statecenters". U.S. Census Bureau. 2000. http://www.census.gov/geo/www/cenpop/statecenters.txt. Retrieved 2006-11-21.
- ^ http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/apportionment-pop-text.php
- ^ "Leading Population Trends in North Dakota". North Dakota State University. 2007. http://www.ndsu.edu/sdc/data/populationtrends.htm. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "Agenda 2003 – Saving North Dakota". The Forum of Fargo-Moorhead. 2002. http://www.in-forum.com/specials/savingnd/index2.cfm?page=articles_inside&id=27390. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ US Census 2000
- ^ http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/
- ^ a b c "American Religious Identification Survey". Exhibit 15. The Graduate Center, City University of New York. http://www.gc.cuny.edu/faculty/research_briefs/aris/key_findings.htm. Retrieved 2006-11-24.
- ^ North Dakota – Religions
- ^ http://www.thearda.com/mapsReports/reports/state/38_2000.asp
- ^ William Charles Sherman, Playford V. Thorson, Warren A. Henke, Plains Folk: North Dakota's ethnic history (North Dakota Institute for Regional Studies, 1986) pp 189, 242, 256
- ^ Elwyn B. Robinson, History of North Dakota (1966) pp. 285–87, 557
- ^ "Josh Duhamel". IMDb. 2007. http://www.imdb.com/name/nm0241049/. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "Fish Species". North Dakota Game and Fish Department. 2007. http://gf.nd.gov/fishing/species.html. Retrieved 2007-08-19.
- ^ "Economy of North Dakota". NetState. 2007-06-04. http://www.netstate.com/economy/nd_economy.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ "Gross Domestic Product (GDP) by State". U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis. 2006-10-26. http://www.bea.gov/bea/newsrel/GSPNewsRelease.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ "Regional Economic Accounts". U.S. Bureau of Economic Analysis. http://www.bea.gov/bea/regional/bearfacts/stateaction.cfm?fips=27000&yearin=2006. Retrieved 2007-10-04.[dead link]
- ^ "United States and States — R2001. Median Household Income". U.S. Census Bureau. Archived from the original on 2007-09-14. http://web.archive.org/web/20070914142044/http://www.census.gov/hhes/www/income/income04/statemhi.html. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ Bls.gov; Local Area Unemployment Statistics
- ^ Cauchon, Dennis (2011-03-17). "North Dakota economy booms, population soars". USA Today. http://www.usatoday.com/news/nation/census/2011-03-16-north-dakota-census_N.htm?csp=34news&utm_source=feedburner&utm_medium=feed&utm_campaign=Feed%3A+usatoday-NewsTopStories+%28News+-+Top+Stories%29.
- ^ "North Dakota — DP-3. Profile of Selected Economic Characteristics: 2000". U.S. Census Bureau. http://factfinder.census.gov/servlet/QTTable?_bm=y&-geo_id=04000US38&-qr_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U_DP3&-ds_name=DEC_2000_SF3_U&-redoLog=false. Retrieved 2007-08-30.
- ^ a b c d United States Department of Agriculture (December 2009). 2007 Census of Agriculture. 1. Part 51. pp. 276–293, pp. 345–355, p. 434, pp. 474–489. [1]
- ^ State Renewable Fuels Profile. U.S. Energy Information Administration.[2]. Retrieved 2011-02-05.
- ^ Coal General Statistics, National Mining Association.[3] Retrieved 2011-02-05.
- ^ "Things To Do In North Dakota". ThingsToDo.com. http://www.thingstodo.com/states/ND/history.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ Gunderson, Dan (2006-08-28). "North Dakota oil patch is booming". Minnesota Public Radio. http://minnesota.publicradio.org/display/web/2006/08/18/ndoil/. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ Donovan, Lauren (2006-06-20). "North Dakota may be bigger oil player than Alaska". Bismarck Tribune.
- ^ "3 to 4.3 Billion Barrels of Technically Recoverable Oil Assessed in North Dakota and Montana’s Bakken Formation—25 Times More Than 1995 Estimate". U.S. Geological Survey. April 10, 2008. http://www.usgs.gov/newsroom/article.asp?ID=1911. Retrieved 2008-04-11.
- ^ North Dakota Drilling & Production Statistics. [4] Retrieved 2011-02-05.
- ^ Crude Oil Production. U.S. Energy Information Administration.[5] Retrieved 2011-02-05.
- ^ "Earth Policy Reader". http://www.earth-policy.org/Books/Epr/Epr1_ss16.htm. Retrieved 2009-02-25.
- ^ "FAQ: Individual Income Tax". Office of State Tax Commissioner, Tax Department, North Dakota. http://www.nd.gov/tax/misc/faq/indincome/index.html#gi2. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ "States Ranked by Total State Taxes and Per Capita Amount: 2005". U.S. Census Bureau. http://www.census.gov/govs/statetax/05staxrank.html. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ "Sales and Use". Office of State Tax Commissioner, Tax Department, North Dakota. http://www.nd.gov/tax/salesanduse/. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ "Grand Forks: Economy — Major Industries and Commercial Activity". City-Data.com. http://www.city-data.com/us-cities/The-Midwest/Grand-Forks-Economy.html. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ "Property". Office of State Tax Commissioner, Tax Department, North Dakota. http://www.nd.gov/tax/property/. Retrieved 2007-10-04.
- ^ a b http://www.taxfoundation.org/research/topic/48.html
- ^ IRS – Tax Stats at a Glance
- ^ Lukas, Paul (November 1, 1999). "State Secret North Dakota, our least visited state, is also among the most underappreciated". CNNMoney.com. http://money.cnn.com/magazines/moneymag/moneymag_archive/1999/11/01/268029/index.htm. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ^ "First Annual Centennial Strategy for Theodore Roosevelt National Park"] (PDF). August 2007. http://www.nps.gov/thro/parkmgmt/upload/THRO-Centennial-Strategy.pdf. Retrieved 2010-07-13.
- ^ "Norsk Høstfest". October 7, 2006. http://www.kxnet.com/hostfest. Retrieved 2010-07-013.
- ^ Why Walgreens In Fargo, N.D., Can't Fill Your Prescriptions December 6, 2010
- ^ "Dakota, Missouri Valleya and Western Railroad". Dakota, Missouri Valleya and Western Railroad. http://www.dmvwrr.com/. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- ^ "About Us". Red River Valley and Western Railroad. http://www.rrvw.net/about/about.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- ^ "Amtrak — Routes — Northwest". Amtrak. http://www.amtrak.com/servlet/ContentServer?pagename=Amtrak/am2Route/Horizontal_Route_Page&c=am2Route&cid=1081256321887&ssid=135. Retrieved 2007-10-05.
- ^ 2011 American State Litter Scorecard: New Rankings for an Increasingly Environmentally Concerned Populous
- ^ "State Government". State of North Dakota. http://www.nd.gov/category.htm?id=82. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ "District Courts". North Dakota Supreme Court. http://www.ndcourts.com/court/districts/districts.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ "All District Judges". North Dakota Supreme Court. http://www.ndcourts.com/court/districts/judges.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ "North Dakota Judicial System". North Dakota Supreme Court. http://www.ndcourts.com/court/brochure.htm. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ http://www.nd.gov/category.htm?id=75
- ^ http://www.worldlicenceplates.com/usa/US_NDXX.html
- ^ S. D. Senate Bill No. 134.
- ^ "210 Designated Market Areas – 07-08". Nielsen Media. http://www.nielsenmedia.com/nc/nmr_static/docs/2007-2008_DMA_Ranks.xls. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ "North Dakota’s First Television Station". Prairie Public. Archived from the original on 2007-10-23. http://web.archive.org/web/20071023065044/http://www.prairiepublic.org/programs/datebook/bydate/06/0406/040306.jsp. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
- ^ "First Stations in Each State". National Radio Club. http://www.nrcdxas.org/articles/1-states.txt. Retrieved 2007-10-06.
Further reading
- Arends, Shirley Fischer. The Central Dakota Germans: Their History, Language, and Culture. (1989). 289 pp.
- Berg, Francie M., ed. Ethnic Heritage in North Dakota. (1983). 174 pp.
- Blackorby, Edward C. Prairie Rebel: The Public Life of William Lemke (1963), radical leader in 1930s online edition
- Collins, Michael L. That Damned Cowboy: Theodore Roosevelt and the American West, 1883–1898 (1989). Teddy was a rancher here in the 1880s
- Cooper, Jerry and Smith, Glen. Citizens as Soldiers: A History of the North Dakota National Guard. (1986). 447 pp.
- Crawford, Lewis F. History of North Dakota (3 vol 1931), excellent history in vol 1; biographies in vol. 2–3
- Danbom, David B. "Our Purpose Is to Serve": The First Century of the North Dakota Agricultural Experiment Station. (1990). 237 pp.
- Eisenberg, C. G. History of the First Dakota-District of the Evangelical-Lutheran Synod of Iowa and Other States. (1982). 268 pp.
- Ginsburg, Faye D. Contested Lives: The Abortion Debate in an American Community. (1989). 315 pp. the issue in Fargo
- Hargreaves, Mary W. M. Dry Farming in the Northern Great Plains: Years of Readjustment, 1920–1990. (1993). 386 pp.
- Howard, Thomas W., ed. The North Dakota Political Tradition. (1981). 220 pp.
- Hudson, John C. Plains Country Towns. (1985). 189 pp. geographer studies small towns
- Junker, Rozanne Enerson. The Bank of North Dakota: An Experiment in State Ownership. (1989). 185 pp.
- Lamar, Howard R. Dakota Territory, 1861–1889: A Study of Frontier Politics (1956).
- Lounsberry, Clement A. Early history of North Dakota (1919) excellent history by editor of Bismark Tribune; 645pp online edition
- Lysengen, Janet Daley and Rathke, Ann M., eds. The Centennial Anthology of "North Dakota History: Journal of the Northern Plains." (1996). 526 pp. articles from state history journal covering all major topics in the state's history
- Morlan, Robert L. Political Prairie Fire: The Nonpartisan League, 1915–1922. (1955). 414 pp. NPL comes to power briefly
- Peirce, Neal R. The Great Plains States of America: People, Politics, and Power in the Nine Great Plains States (1973) excerpt and text ssearch, chapter on North Dakota
- Robinson, Elwyn B., D. Jerome Tweton, and David B. Danbom. History of North Dakota (2nd ed. 1995) standard history, by leading scholars; extensive bibliography
- Robinson, Elwyn B. History of North Dakota (1966) First edition online
- Schneider, Mary Jane. North Dakota Indians: An Introduction. (1986). 276 pp.
- Sherman, William C. and Thorson, Playford V., eds. Plains Folk: North Dakota's Ethnic History. (1988). 419 pp.
- Sherman, William C. Prairie Mosaic: An Ethnic Atlas of Rural North Dakota. (1983). 152 pp.
- Smith, Glen H. Langer of North Dakota: A Study in Isolationism, 1940–1959. (1979). 238 pp. biography of influential conservative Senator
- Snortland, J. Signe, ed. A Traveler's Companion to North Dakota State Historic Sites. (1996). 155 pp.
- Stock, Catherine McNicol. Main Street in Crisis: The Great Depression and the Old Middle Class on the Northern Plains. (1992). 305pp. online edition
- Tauxe, Caroline S. Farms, Mines and Main Streets: Uneven Development in a Dakota County. (1993). 276 pp. coal and grain in Mercer county
- Tweton, D. Jerome and Jelliff, Theodore B. North Dakota: The Heritage of a People. (1976). 242 pp. textbook history
- Wilkins, Robert P. and Wilkins, Wynona Hutchette. North Dakota: A Bicentennial History. (1977) 218 pp. popular history
- Wishart, David J. ed. Encyclopedia of the Great Plains, University of Nebraska Press, 2004, ISBN 0-8032-4787-7. complete text online; 900 pages of scholarly articles
- Young, Carrie. Prairie Cooks: Glorified Rice, Three-Day Buns, and Other Reminiscences. (1993). 136 pp.
Primary sources
- Benson, Bjorn; Hampsten, Elizabeth; and Sweney, Kathryn, eds. Day In, Day Out: Women's Lives in North Dakota. (1988). 326 pp.
- Maximilian, Prince of Wied. Travels in the Interior of North America in the rears 1832 to 1834 (Vols. XXII-XXIV of "Early Western Travels, 1748–1846," ed. by Reuben Gold Thwaites; 1905–1906). Maximilian spent the winter of 1833–1834 at Fort Clark.
- University of North Dakota, Bureau of Governmental Affairs, ed., A Compilation of North Dakota Political Party Platforms, 1884–1978. (1979). 388 pp.
- WPA. North Dakota: A Guide to the Northern Prairie State (2nd ed. 1950), the classic guide online edition
External links
- State of North Dakota official website
- North Dakota tourism website
- Energy Profile for North Dakota
- USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of North Dakota
- U.S. Census Bureau facts of North Dakota
- North Dakota State Facts – USDA
- Pictures of the Dakotas: Badlands and Theodore Roosevelt National Parks
- GhostsOfNorthDakota.com – a pictorial documentary of North Dakota "ghost towns"
- North Dakota at the Open Directory Project
 OpenStreetMap has geographic data related to North Dakota
OpenStreetMap has geographic data related to North Dakota

 Canada
Canada
 Saskatchewan •
Saskatchewan •  Manitoba
Manitoba
 Montana
Montana
 Minnesota
Minnesota North Dakota: Outline • Index
North Dakota: Outline • Index 

 Wyoming
Wyoming South Dakota
South DakotaPolitical divisions of the United States States - Alabama
- Alaska
- Arizona
- Arkansas
- California
- Colorado
- Connecticut
- Delaware
- Florida
- Georgia
- Hawaii
- Idaho
- Illinois
- Indiana
- Iowa
- Kansas
- Kentucky
- Louisiana
- Maine
- Maryland
- Massachusetts
- Michigan
- Minnesota
- Mississippi
- Missouri
- Montana
- Nebraska
- Nevada
- New Hampshire
- New Jersey
- New Mexico
- New York
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- Ohio
- Oklahoma
- Oregon
- Pennsylvania
- Rhode Island
- South Carolina
- South Dakota
- Tennessee
- Texas
- Utah
- Vermont
- Virginia
- Washington
- West Virginia
- Wisconsin
- Wyoming
Federal district Insular areas Outlying islands Preceded by
ColoradoList of U.S. states by date of statehood
Admitted on November 2, 1889 (39th)Succeeded by
South DakotaCoordinates: 47°30′N 100°30′W / 47.5°N 100.5°W
United States (Outline) History Pre-Columbian era · Colonial era (Thirteen Colonies · Colonial American military history) · American Revolution (War) · Federalist Era · War of 1812 · Territorial acquisitions · Territorial evolution · Mexican–American War · Civil War · Reconstruction era · Indian Wars · Gilded Age · African-American Civil Rights Movement (1896–1954) · Spanish–American War · Imperialism · World War I · Roaring Twenties · Great Depression · World War II (Home front) · Cold War · Korean War · Space Race · African-American Civil Rights Movement (1955–1968) · Feminist Movement · Vietnam War · Post-Cold War (1991–present) · War on Terror (War in Afghanistan · Iraq War) · Timeline of modern American conservatismTopicsDemographic · Discoveries · Economic (Debt Ceiling) · Inventions (before 1890 · 1890–1945 · 1946–1991 · after 1991) · Military · Postal · Technological and industrialFederal
governmentLegislature - Congress
Senate
· Vice President
· President pro tem
House of Representatives
· Speaker
Judiciary - Supreme Court
Federal courts
Courts of appeal
District courtsExecutive - President
Executive Office
Cabinet / Executive departments
Civil service
Independent agencies
Law enforcement
Public policy
Intelligence
Central Intelligence Agency
Defense Intelligence Agency
National Security Agency
Federal Bureau of InvestigationPolitics Divisions · Elections (Electoral College) · Foreign policy · Foreign relations · Ideologies · Local governments · Parties (Democratic Party · Republican Party · Third parties) · Political status of Puerto Rico · Red states and blue states · Scandals · State governments · Uncle SamGeography Cities, towns, and villages · Counties · Extreme points · Islands · Mountains (Peaks · Appalachian · Rocky) · National Park System · Regions (Great Plains · Mid-Atlantic · Midwestern · New England · Northwestern · Southern · Southwestern · Pacific · Western) · Rivers (Colorado · Columbia · Mississippi · Missouri · Ohio · Rio Grande) · States · Territory · Water supply and sanitationEconomy Agriculture · Banking · Communications · Companies · Dollar · Energy · Federal Budget · Federal Reserve System · Financial position · Insurance · Mining · Public debt · Taxation · Tourism · Trade · Transportation · Wall StreetSociety TopicsCrime · Demographics · Education · Family structure · Health care · Health insurance · Incarceration · Languages (American English · Spanish · French) · Media · People · Public holidays · Religion · SportsArchitecture · Art · Cinema · Cuisine · Dance · Fashion · Flag · Folklore · Literature · Music · Philosophy · Radio · Television · TheaterIssues Book ·
Book ·  Category ·
Category ·  Portal ·
Portal ·  WikiProjectCategories:
WikiProjectCategories:- North Dakota
- States of the United States
- States and territories established in 1889
- American Indian reservations in North Dakota
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.