- Demographic history of the United States
-
This article is about the demographic history of the United States.
Contents
Historical population
Census
yearPopulation 1610 3,800 1620 4,100 1630 4,600 1640 ? 1650 50,400 1660 ? 1670 111,900 1680 ? 1690 210,400 1700 250,900 1710 ? 1720 466,200 1730 ? 1740 905,600 1750 1,170,800 1760 ? 1770 2,148,100 1780 2,780,400 1790 3,929,214 1800 5,308,483 1810 7,239,881 1820 9,638,453 1830 12,866,020 1840 17,069,453 1850 23,191,876 1860 31,443,321 1870 38,558,371 1880 50,189,209 1890 62,979,766 1900 76,212,168 1910 92,228,496 1920 106,021,537 1930 123,202,624 1940 132,164,569 1950 151,325,798 1960 179,323,175 1970 203,211,926 1980 226,545,805 1990 248,709,873 2000 281,421,906 2010 308,745,538 Age at marriage
1890: Men 26.1, Women 22.0
1900: Men 25.9, Women 21.9
1910: Men 25.1, Women 21.6
1920: Men 24.6, Women 21.2
1930: Men 24.3, Women 21.3
1940: Men 24.5, Women 21.5
1950: Men 22.8, Women 20.3
1960: Men 22.8, Women 20.3
1970: Men 23.2, Women 20.6
1980: Men 24.7, Women 22.0
1990: Men 26.1, Women 23.9
2000: Men 26.8, Women 25.1
2007: Men 27.5, Women 25.6
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, in 1959, 47% of weddings were to women under the age of 19, and 51.5% of 20-year-old females had ever married.[clarification needed]
Immigration
Earlier Colonial era
Nearly all commercial activity was run in small privately owned businesses with good credit both at home and in England being essential since they were often cash poor. Most settlements were nearly independent of trade with Britain as most grew or made nearly everything they needed—the average cost of imports per most households was only about 5-15 English pounds per year. Most settlements were created by complete family groups with several generations often present in each settlement. Probably close to 80% of the families owned the land they lived and farmed on. They nearly all used English Common Law as their basic code of law and, except for the Dutch and Germans, spoke some dialect of English. They established their own popularly elected governments and courts and were, within a few years, mostly self governing, self supporting and self replicating.
Nearly all colonies and, later, states in the United States were settled by migration from another colony or state, as foreign immigration usually only played a minor role after the initial settlements were started. Many new immigrants did end up on the frontiers as that was where the land was usually the cheapest.
New England
The New England colonists included more educated men as well as many skilled farmers, tradesmen and craftsmen. They were mostly farmers and settled in small villages for common religious activity. Shipbuilding, commerce, and fisheries were important in coastal towns. New England's healthy climate (the cold winters killed the mosquitoes and other disease-bearing insects), and abundant food supply resulted in the lowest death rate and highest birth rate of any place in the world (marriage was expected and birth control was not, and a much higher than average number of children and mothers survived).
The eastern and northern frontier around the initial New England settlements was mainly settled by the Yankee descendants of the original New Englanders. Emigration to the New England colonies after 1640 and the start of the English Civil War decreased to less than 1% (about equal to the death rate) in nearly all years prior to 1845. The rapid growth of the New England colonies (total population ~700,000 by 1790) was almost entirely due to the high birth rate (>3%) and low death rate (<1%) per year.
Middle Colonies
The middle colonies' settlements were scattered west of New York City, New York (est. 1626 by Dutch, taken over by the English in 1664) and Philadelphia, Pennsylvania (est. 1682). The Dutch-started colony of New York had the most eclectic collection of residents from many different nations and prospered as a major trading and commercial center after about 1700. The Pennsylvania colonial center was dominated by the Quakers for decades after they emigrated there, mainly from the North Midlands of England, from about 1680 to 1725. The main commercial center of Philadelphia was run mostly by prosperous Quakers, supplemented by many small farming and trading communities with strong German contingents located in the Delaware River valley.
Many more settlers arrived in the middle colonies starting in about 1680, when Pennsylvania was founded and many Protestant sects were encouraged to settle there for freedom of religion and good, cheap land. These settlers were of about 60% British and 33% German extraction. By 1780 in New York about 17% of the population were descendants of Dutch settlers. The rest were mostly English with a wide mixture of other Europeans and about 6% Blacks. New Jersey and Delaware had a majority of British with 7-11% German-descended colonists, about a 6% black population, and a small contingent of Swedish descendants of New Sweden. Nearly all were at least third-generation natives.
Frontier
The colonial western frontier was mainly settled from about 1717 to 1775 by mostly Presbyterian settlers from northern England border lands, Scotland, and Northern Ireland, fleeing bad times and persecution in those areas. Most initially landed in family groups in Philadelphia or Baltimore but soon migrated to the western frontier where land was cheaper and restrictions less onerous.
Natural growth
All the colonies, after they were started, grew mostly by natural growth, with foreign born populations rarely exceeding 10% in isolated instances. The last significant colonies to be settled mainly by immigrants were Pennsylvania in the early 18th century and Georgia and the Borderlands in the late 18th century, as migration (not immigration) continued to provide nearly all the settlers for each new colony or state. This pattern would continue throughout U.S. history. The extent of colonial settlements by 1800 is shown by this map from the University of Texas map collection.[2]
Estimated Population of American Colonies 1620 to 1780 Series Z-19 U.S. Census
Year 1780 1760 1740 1720 1700 1680 1660 1640 1620 Tot Pop. 2,780,400 1,593,600 905,600 466,200 250,900 151,500 75,100 26,600 500 Maine -1 49,100 20,000 - - - - - 900 - New Hampshire-2 87,800 39,100 23,300 9,400 5,000 2,000 1,600 1,100 - Vermont -3 47,600 - - - - - - - - Plymouth -4 - - - - - 6,400 2,000 1,000 100 Massachusetts 268,600 202,600 151,600 91,000 55,900 39,800 20,100 8,900 Rhode Island 52,900 45,500 25,300 11,700 5,900 3,000 1,500 300 - Connecticut 206,700 142,500 89,600 58,800 26,000 17,200 8,000 1,500 - New York 210,500 117,100 63,700 36,900 19,100 9,800 4,900 1,900 - New Jersey 139,600 93,800 51,400 29,800 14,000 3,400 - - - Pennsylvania 327,300 183,700 85,600 31,000 18,000 700 - - - Delaware 45,400 33,300 19,900 5,400 2,500 1,000 500 - - Maryland 245,500 162,300 116,100 66,100 29,600 17,900 8,400 500 - Virginia 538,000 339,700 180,400 87,800 58,600 43,600 27,000 10,400 400 North Carolina 270,100 110,400 51,800 21,300 10,700 5,400 1,000 - - South Carolina 180,000 94,100 45,000 17,000 5,700 1,200 - - - Georgia 56,100 9,600 2,000 - - - - - - Kentucky 45,000 - - - - - - - - Tennessee 10,000 - - - - - - - Year 1780 1760 1740 1720 1700 1680 1660 1640 1620 New Eng. (ME to CT) 712,800 449,600 289,700 170,900 92,800 68,500 33,200 13,700 100 % Black -5 2.0% 2.8% 2.9% 2.3% 1.8% 0.7% 1.8% 1.5% 0.0% Middle (NY to DE) 722,900 427,900 220,600 103,100 53,600 14,900 5,400 1,900 - % Black -6 5.9% 6.8% 7.5% 10.5% 6.9% 10.1% 11.1% 10.5% 0.0% South (MD to TN) 1,344,700 716,000 395,300 192,300 104,600 68,100 36,400 11,000 400 % Black -7 38.6% 39.7% 31.6% 28.1% 21.5% 7.3% 4.7% 1.8% 0.0% - Maine was part of Massachusetts from about 1652 to 1820, when it was granted statehood.
- New Hampshire was part of Massachusetts until about 1685, when it was split off and established under a British appointed governor. It was one of the original 13 colonies.
- Vermont was contested between the French and British settlers until the French and Indian war (1758–1765) drove out the French authorities. The territory was then disputed between Massachusetts, New York and New Hampshire until the settlers declared their independence from all of them and were accepted as the 14th state in 1791 and participated in the 1790 census a year late.
- Plymouth, Massachusetts despite being the first permanent New England settlement, lost its charter in 1690 and became part of the Massachusetts colony.
- By 1784 all slavery in the New England states was either completely prohibited or transitioning to its total prohibition.
- By 1804 all slavery in the Middle colonies (except Delaware [6.6% Black]) was either completely prohibited or was transitioning to its total prohibition.
- All slavery was prohibited in the entire U.S. in 1865 by the 13th amendment to the constitution.
Population in 1790
According to the source, The Source: A Guidebook of American Genealogy by Kory L. Meyerink and Loretto Dennis Szucs, the following were the countries of origin for new arrivals coming to the United States before 1790. The regions marked * were part of Great Britain. The ancestry of the 3.9 million population in 1790 has been estimated by various sources by sampling last names in the 1790 census and assigning them a country of origin. The Irish in the 1790 census were mostly Scots Irish. The French were mostly Huguenots. The total U.S. Catholic population in 1790 was probably less than 5%. The Indian population inside territorial U.S. 1790 boundaries was less than 100,000.
U.S. Historical Populations Country Immigrants Before 1790 Population 1790 -1 Africa -2 360,000 757,000 England* 230,000 2,100,000 Ulster Scot-Irish* 135,000 300,000 Germany -3 103,000 270,000 Scotland* 48,500 150,000 Ireland* 8,000 (Incl. in Scot-Irish) Netherlands 6,000 100,000 Wales* 4,000 10,000 France 3,000 15,000 Jews -4 1,000 2,000 Sweden 500 2,000 Other -5 50,000 200,000 Total -6 950,000 3,900,000 - Data From Ann Arbor, MI: Inter-university Consortium for Political and Social Research (ICPS)
- Several West African regions were the home to most African immigrants. Population from US 1790 Census
- Germany in this time period consists of a large number of separate countries, the largest of which was Prussia.
- Jewish settlers were from several European countries.
- The Other category probably contains mostly English ancestry settlers; but the loss of several states detailed census records in the burning of Washington D.C. in the War of 1812 makes estimating closer difficult. Nearly all states that lost their 1790 (and 1800) census records have tried to reconstitute their original census from tax records etc. with various degrees of success. The summaries of the 1790 and 1800 census from all states survived.
- The Total is the total immigration over the approximately 130 year span of colonial existence of the U.S. colonies as found in the 1790 census. Many of the colonists, especially from the New England colonies, are already into their fifth generation of being in America. At the time of the American Revolution the foreign born population is estimated to be from 300,000 to 400,000.
The 1790 population already reflects the approximate 50,000 “Loyalists or Tories”, who emigrated to Canada at the end of the American Revolution and the less than 10,000 more who emigrated to other British possessions including England.
Already by 1790 the ancestry question is starting to become meaningless as many people from many different countries intermarry in each generation and nearly all these ancestries are starting to merge to become American. The total white population in 1790 was about 80% British ancestry and roughly doubles by natural increase every 25 years. The native born population of the U.S. has never fallen below 85% of the population after about 1675–100 years before the American Revolution.
Relentless population expansion pushed the U.S. frontier to the Pacific by 1848. Given the U.S. geography, most immigrants came long distances to settle in the U.S.. However the Irish leaving Canada for the US in the 1840s, the French Canadians who came down from Quebec after 1860, and the Mexicans who came north after 1911, found it easy to move back and forth.
Immigration 1790 to 1849
In the early years of the U.S., immigration was only about 6000 people a year on average, including French refugees from the slave revolt in Haiti. The French Revolution, starting in 1789, and the Napoleonic Wars from 1792 to 1814 severely limited immigration from Europe. The War of 1812 (1812–1814) with Britain again prevented any significant immigration. By 1808 Congress had banned the importation of slaves, slowing that human traffic to a trickle.
After 1820 immigration gradually increased. For the first time federal records, including ship passenger lists, were kept for immigration. Total immigration for one year in 1820 was 8,385, gradually building to 23,322 by 1830, with 143,000 total immigrating during the intervening decade. From 1831 to 1840 immigration increased greatly, to 599,000 total, as 207,000 Irish, even before the famine of 1845-49, started to emigrate in large numbers as Britain eased travel restrictions. 152,000 Germans, 76,000 British, and 46,000 French formed the next largest immigrant groups in that decade.
From 1841 to 1850 immigration exploded to 1,713,000 total immigrants and at least 781,000 Irish, with the famine of 1845-1919 driving them, fled their homeland to escape poverty and death. In attempting to divert some of this traffic to help settle Canada, the British offered bargain fares of 15 shillings for transit to Canada, instead of the normal 5 pounds (100 shillings). Thousands of poor Irish took advantage of this offer and headed to Canada on what came to be called the "coffin ships" because of their high death rates. Once in Canada, many Irish walked across the border or caught an intercoastal freighter to the nearest major city in the United States - usually Boston or New York.
Bad potato crops and failed revolutions struck the heart of Europe in 1848, contributing to the decade's total of 435,000 Germans, 267,000 British and 77,000 French immigrants to America. Bad times in Europe drove people out; land, relatives, freedom, opportunity, and jobs in America lured them in.
Population and Foreign Born 1790 to 1849
Census Population, Immigrants per DecadeCensus Population Immigrants-1 Foreign Born % 1790 3,918,000 60,000 1800 5,236,000 60,000 1810 7,036,000 60,000 1820 10,086,000 60,000 1830 12,785,000 143,000 200,000 -2 1.6% 1840 17,018,000 599,000 800,000 -2 4.7% 1850 23,054,000 1,713,000 2,244,000 9.7% The number of immigrants from 1830 on are from immigration records. The census of 1850 was the first census in which place of birth was asked. It is probably a reasonable estimate that the foreign born population in the U.S. reached its minimum in about 1815 at something like 100,000, or 1.4% of the population. By 1815 most of the immigrants that arrived before the American Revolution had passed on, and there had been almost no new immigration.
- The total number immigrating in each decade from 1790 to 1820 are estimates.
- The number foreign born in 1830 and 1840 decades are extrapolations.
Nearly all population growth up to 1830 was by internal increase; about 98.5% of the population was native-born. By 1850, this had shifted to about 90% native-born. The first significant Catholic immigration started in the mid 1840s.
Migration within the United States
The American West
In 1848, the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo, concluding the Mexican War, extended U.S. citizenship to approximately 60,000 Mexican residents of the New Mexico Territory and 10,000 living in California. However, much like Texas, the Mexican government had encouraged immigration and settlement of these regions from groups in the United States and Europe. Approximately half of this population is estimated to have been of American origin. In 1849, the California Gold Rush spurred significant immigration from Mexico, South America, China, Australia, Europe and caused a mass migration within the US, resulting in California gaining statehood in 1850, with a population of about 90,000.
Rural flight
Rural flight is the departure of excess populations (usually young men and women) from farm areas. In some cases whole families left, as in the Dust Bowl in the 1930s. Much of rural America has seen steady population decline since 1920.
Black migration out of the South
see Great Migration (African American)
The Great Migration was the movement of millions African Americans out of the rural Southern United States from 1914 to 1960. Most moved to large industrial cities, as well as to many smaller industrial cities. African-Americans moved as individuals or small groups. There was no government assistance. They migrated because of a variety of push and pull factors:
Pull factors
- Income levels were much higher in the North, with far higher wages in the service sector.
- The enormous growth of war industries in WW1 and WW2 created new job openings for blacks—not in the factories but in the service jobs that new factory workers vacated;
- World War I effectively put a halt to the flow of European immigrants to the industrial centers , causing shortages of workers in the factories.
- After 1940, as the U.S. rearmed for World War II (see Homefront-United States-World War II), industrial production increased rapidly.
- The FEPC equal opportunity laws were more enforced in the North and West.[3]
Recent demographic trends
Post-war baby boom
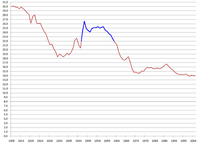 United States birth rate (births per 1000 population).[4] The United States Census Bureau defines the demographic birth boom as between 1946 and 1964[5] (blue).
United States birth rate (births per 1000 population).[4] The United States Census Bureau defines the demographic birth boom as between 1946 and 1964[5] (blue).
In the years after WWII, the United States, as well as a number of other industrialized countries, experienced an unexpected sudden birth rate jump. The cause of the baby boom was millions of men from the US who had to fight in WWII which prevented women from starting families and women also had to take the place of men in the workplace. The millions of men coming back and couples eager to start families led to the sharp rise in the US birth rate. Since the men came back got jobs in the workplace again, women became strongly pressured to once again stay home to take care of the house and children and let their husbands be the breadwinner of the household. Women felt great pressure to be married by her early 20s or else she would be considered lonely later on in life.
During the baby boom years, between 1946 and 1964, the birth rate doubled for third children and tripled for fourth children.[6]
The total fertility rate of the United States jumped from 2.49 in 1945 to 2.94 in 1946, a rise of 0.45 children therefore beginning the baby boom. It continued to rise throughout the 1940s to reach 3.10 in 1950 with a peak of 3.77 in 1957. Declining slowly thereafter to 3.65 in 1960 and finally a steep from decline after 1964, therefore ending the baby boom.
The number of children aged 0–4 sprouted to 16,410,000 in 1950 from 11,000,000 in 1940, it continued into the 1960s where it peaked at 20,000,000 children under the age of 5.
The number of children under 19 rose to 69 million in 1960 from 51 million in 1950, a 35.3% increase, while the proportion of the population rose to 38.8% up from 33.8% in 1950.
Marriages
According to statistics, the United States currently has the highest marriage rate in the developed world, as of 2008, with a marriage rate of 7.1 per 1,000 people or 2,162,000 marriages. The average age for first marriage for men is 27.4 and 25.6 years for women. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nvsr/nvsr57/nvsr57_19.htm The United States also has one of the highest proportions of people who do marry by age 40, which approximately 85% Americans are married at 40, compared to only 60% in Sweden.
During the 1930s, the number of marriages and the marriage rate dropped steeply due to the Great Depression, but rebounded almost immediately after the Depression ended. Marriage rates increased and remained at high levels in the late 1930 to the mid 1940s. The number of marriages shot up to reach over 2 million in 1946, with a marriage rate of 16.4 per 1,000 people as WWII had ended. The average age at first marriage for both men and women began to fall after WWII, dropping 22.8 for men and 20.3 for women in 1950 and dropping even more to 22.5 and 20.1 years in 1956. In 1959, the United States Census Bureau estimated that 47% of all brides marrying for their first time were teenagers aged 19 and under. In 1955, 51.2% of women were married by their 20th birthday and 88% by their 25th birthday; 40.3% of men and 28.5% of women aged 20–24 in 1955 had never married, down from 77.8% for men and 57.4% for women in 1940.
As of 2002, 4.3% of men and 18.1% of women aged 20 are married, increasing to 37% of men and 52% of women by age 25, and then 61% of men and 76% of women by age 30.
Population growth projections
The U.S. population in 1900 was 76 million. In 1950, it rose to 152 million; by 2000 it had reached 282 million. By 2050, it is expected to reach 420 million.
Demographic models in Historiography
Easterlin models
Richard Easterlin, an economist who has researched economic growth in the United States, explains the growth pattern of American population in the 20th century through fertility rate fluctuations and the decreasing mortality rate. Easterlin has attempted to explain the cause of the Baby Boom and Baby Bust through the “relative income” theory. The “relative income” theory suggests that couples choose to have children based on a couple’s ratio of potential earning power and the desire to obtain material objects. This ratio depends on the economic stability of the country in which they live and how people are raised to value material objects. The “relative income” theory explains the Baby Boom by suggesting that the late 1940s and 1950s brought low desires to have material objects, as a result of the Great Depression and WWII, as well as huge job opportunities, because of it being a post war period. These two factors gave rise to a high relative income, which encouraged high fertility. Following this period, the next generation had a greater desire for material objects; however, an economic slowdown in the United States made jobs harder to acquire. This resulted in lower fertility rates, causing the Baby Bust.
State trends
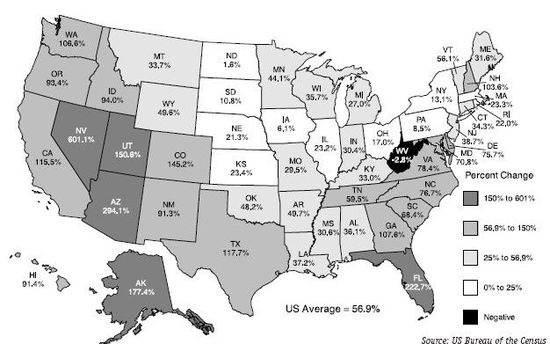
Between 1880 and 1900, the urban population of the United States rose from 28% to 40% (1), and reached 50% by 1920, in part due to 9,000,000 European immigrants. After 1890 the US rural population began to plummet, as farmers were displaced by mechanization and forced to migrate to urban factory jobs. After World War II, the US experienced a shift away from the cities, mostly due to the gaining popularity of the automobile and heavy government funding of suburban housing and highways. Many of the original manufacturing cities lost as much as half their populations between 1950 and 1980. There was a shift in the population from the dense manufacturing centers of the Northeast (Rust Belt) to the outer suburbs of these cities, and to newer, less dense cities in the Southwest (Sun Belt).
Arizona
In the 1990s, Arizona's rural population grew by 29% while the rural retiree population grew by 43%.
Colorado
During the 1990s, Colorado's rural working-age population grew by 40% and the rural retiree population grew by 23%. The statewide population grew 31%, the statewide retiree population grew by 27%, and the statewide working-age population grew by 31%.
Florida
In the 1990s, the population of Florida's rural counties grew 25%. The state's rural retiree population grew 28%. The overall population increased by 24%, while the retiree population increased 19%. It's projected to surpass New York as the 3rd most populous state between 2009-2014.
Illinois
During the 1990s the rural population of Illinois increased by 1%, while the population of Chicago, Illinois increased 12%.
Kansas
During the 1990s the rural population of Kansas increased by 2%, while the statewide increase was 9%.
Minnesota
During the 1990s, the population of Minnesota increased 12%. The working-age population increased 14% and the retiree population increased 9%.
North Dakota
In the 1990s, the rural population of North Dakota decreased 6% while the overall population remained constant.
Washington
During the 1990s, Washington's rural population grew by 20%. Meanwhile, the rural working-age population grew 22% and the rural retiree population grew 16%. Overall there was 21% growth, with 23% for statewide working-age populations and 15% for retirees.
See also
- Great Migration (African American)
- Mean center of U.S. population
- White flight in the United States
General:
Bibliography
- Richard E. Barrett, Donald J. Bogue, and Douglas L. Anderton. The Population of the United States 3rd Edition (1997) compendium of data
- Susan B. Carter, Scott Sigmund Gartner, Michael R. Haines, and Alan L. Olmstead, eds. The Historical Statistics of the United States (Cambridge UP: 6 vol; 2006) vol 1 on population; available online; massive data compendium; online bersion in Excel
- Chadwick Bruce A. and Tim B. Heaton, eds. Statistical Handbook on the American Family. (1992)
- Gerhan David R. and Robert V. Wells. A Retrospective Bibliography of American Demographic History from Colonial Times to 1983. ( Greenwood Press, 1989)
- Michael R. Haines and Richard H. Steckel (eds.), A Population History of North America. Cambridge University Press, 2000, 752 pp. advanced scholarship
- Hawes Joseph M. and Elizabeth I. Nybakken, eds. American Families: a Research Guide and Historical Handbook. (Greenwood Press, 1991)
- Klein, Herbert S. A Population History of the United States. Cambridge University Press, 2004. 316 pp
- Mintz Steven and Susan Kellogg. Domestic Revolutions: a Social History of American Family Life. (1988)
- Riley Moffat. Population History of Western U.S. Cities and Towns, 1850-1990 (1996); Population History of Eastern U.S. Cities and Towns, 1790-1870 (1992)
- U.S. Bureau of the Census, Historical Statistics of the United States: Colonial Times to 1970 (1976)
- Robert V. Wells. Revolutions in Americans' Lives: A Demographic Perspective on the History of Americans, Their Families, and Their Society (1982)
- Robert V. Wells. Uncle Sam's Family (1985), general demographic history
Primary sources
- Kennedy, Joseph C. G. Population of the United States in 1860 (1864) official returns of 8th census complete text online
References
- ^ http://www.infoplease.com/ipa/A0005061.html
- ^ http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/united_states/exploration_1675.jpg
- ^ Grossman, James R. Land of Hope: Chicago, Black Southerners, and the Great Migration (1991); Lemann, Nicholas. The Great Black Migration and How It Changed America (1992); and Scott, Emmett J., Negro Migration during the War (1920).
- ^ CDC Bottom of this page http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/products/vsus.htm "Vital Statistics of the United States, 2003, Volume I, Natality", Table 1-1 "Live births, birth rates, and fertility rates, by race: United States, 1909-2003."
- ^ U.S. Census Bureau — Oldest Boomers Turn 60 (2006)[dead link]
- ^ William Henry Chafe (2003). The Unfinished Journey: America Since World War I. New York: Oxford University press. ISBN 0-19-515048-1. pp. 118
- City Ranks is an interactive map showing population densities of US cities
- World Population: A Guide to the Web
Demographics of the United States Demographic historyEconomic and social Affluence · Educational attainment · Emigration · Homeownership · Household income · Immigration · Income inequality · Language · LGBT · Middle classes · Personal income · Poverty · Social class · Unemployment by state · Wealth

Religion Prominent examples: Buddhists · Christians (Catholics, Protestants, etc.) · Hindus · Jews · Muslims · Neopagans · Non-religious · Sikhs
Race and ethnicity People of the United States/Americans · Ethnic groups in the United States · American people by ethnic or national origin · History of the United States by ethnic group · American culture by ethnicity · Race and ethnicity in the Census · Maps of American ancestries · 2010 Census · in the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission · Racism
White Americans (European Americans, Non-Hispanic Whites, White Hispanic and Latino Americans, Albanian Americans, Arab Americans, English Americans, German Americans, Irish Americans, Italian Americans, Polish Americans, etc.) · Black Americans (African Americans, Black Hispanic and Latino Americans, African immigrants and descendants, Afro-Caribbean/West Indian Americans, etc.) · Asian Americans (Chinese Americans, Filipino Americans, Asian Hispanic and Latino Americans, Indian Americans, Vietnamese Americans, Japanese Americans, Pakistani Americans, etc.) · Hispanic and Latino Americans (Mexican Americans, Puerto Ricans (Stateside), Cuban Americans, Colombian Americans, etc.) · Jewish Americans · Multiracial Americans · Native Americans and Alaska Natives · Pacific Islander Americans (Chamorro Americans, Native Hawaiians, Samoan Americans, etc.)
United States (Outline) History Pre-Columbian era · Colonial era (Thirteen Colonies · Colonial American military history) · American Revolution (War) · Federalist Era · War of 1812 · Territorial acquisitions · Territorial evolution · Mexican–American War · Civil War · Reconstruction era · Indian Wars · Gilded Age · African-American Civil Rights Movement (1896–1954) · Spanish–American War · Imperialism · World War I · Roaring Twenties · Great Depression · World War II (Home front) · Cold War · Korean War · Space Race · African-American Civil Rights Movement (1955–1968) · Feminist Movement · Vietnam War · Post-Cold War (1991–present) · War on Terror (War in Afghanistan · Iraq War) · Timeline of modern American conservatismTopicsDemographic · Discoveries · Economic (Debt Ceiling) · Inventions (before 1890 · 1890–1945 · 1946–1991 · after 1991) · Military · Postal · Technological and industrialFederal
governmentLegislature - Congress
Senate
· Vice President
· President pro tem
House of Representatives
· Speaker
Judiciary - Supreme Court
Federal courts
Courts of appeal
District courtsExecutive - President
Executive Office
Cabinet / Executive departments
Civil service
Independent agencies
Law enforcement
Public policy
Intelligence
Central Intelligence Agency
Defense Intelligence Agency
National Security Agency
Federal Bureau of InvestigationPolitics Divisions · Elections (Electoral College) · Foreign policy · Foreign relations · Ideologies · Local governments · Parties (Democratic Party · Republican Party · Third parties) · Political status of Puerto Rico · Red states and blue states · Scandals · State governments · Uncle SamGeography Cities, towns, and villages · Counties · Extreme points · Islands · Mountains (Peaks · Appalachian · Rocky) · National Park System · Regions (Great Plains · Mid-Atlantic · Midwestern · New England · Northwestern · Southern · Southwestern · Pacific · Western) · Rivers (Colorado · Columbia · Mississippi · Missouri · Ohio · Rio Grande) · States · Territory · Water supply and sanitationEconomy Agriculture · Banking · Communications · Companies · Dollar · Energy · Federal Budget · Federal Reserve System · Financial position · Insurance · Mining · Public debt · Taxation · Tourism · Trade · Transportation · Wall StreetSociety TopicsCrime · Demographics · Education · Family structure · Health care · Health insurance · Incarceration · Languages (American English · Spanish · French) · Media · People · Public holidays · Religion · SportsArchitecture · Art · Cinema · Cuisine · Dance · Fashion · Flag · Folklore · Literature · Music · Philosophy · Radio · Television · TheaterIssuesDemographic history of North America Sovereign states - Antigua and Barbuda
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Belize
- Canada
- Costa Rica
- Cuba
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- El Salvador
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Haiti
- Honduras
- Jamaica
- Mexico
- Nicaragua
- Panama
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Trinidad and Tobago
- United States
Dependencies and
other territories- Anguilla
- Aruba
- Bermuda
- Bonaire
- British Virgin Islands
- Cayman Islands
- Curaçao
- Greenland
- Guadeloupe
- Martinique
- Montserrat
- Puerto Rico
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saba
- Sint Eustatius
- Sint Maarten
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.