- Rocky Mountains
map_size=275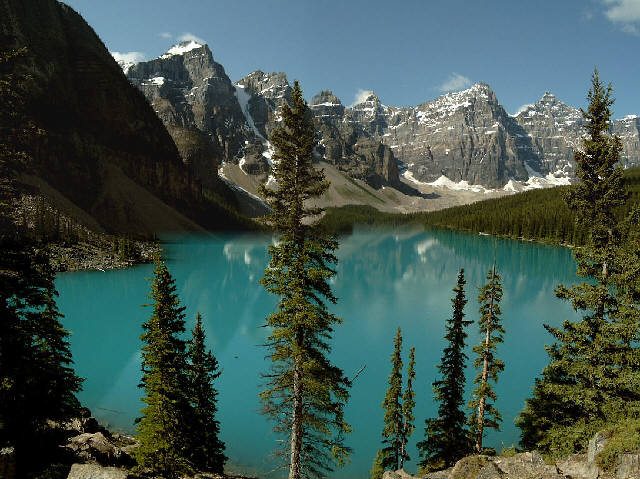
image_size=275
image_caption=Moraine Lake , and theValley of the Ten Peaks ,Banff National Park ,Alberta ,Canada
other_name=Rockies
country=Canada
country1=United States
region=British Columbia
region1=Alberta
region2=Idaho
region3=Montana
region4=Wyoming
region5=Utah
region6=Colorado
region7=New Mexico
parent=Pacific Cordillera
geology=Igneous|geology1=Sedimentary
geology2=Metamorphic
period=Precambrian|period1=Cretaceous |orogeny=
highest=Mount Elbert
highest_elevation_imperial=14440
highest_lat_d=39|highest_lat_m=07|highest_lat_s=03.90|highest_lat_NS=N
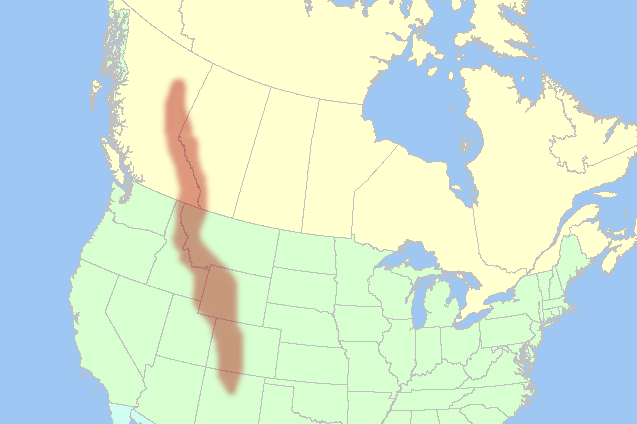
highest_long_d=106|highest_long_m=26|highest_long_s=43.29|highest_long_EW=WThe Rocky Mountains, often called the Rockies, are a
mountain range in westernNorth America . The Rocky Mountains stretch more than 4,800 kilometers (3,000mile s) from northernmostBritish Columbia , inCanada , toNew Mexico , in theUnited States . The range's highest peak isMount Elbert inColorado at 14,440 feet (4,401 meters) abovesea level . Though part of North America'sPacific Cordillera , the Rockies are distinct from thePacific Coast Ranges which are located immediately adjacent to the Pacific coast.The Eastern edge of the rockies rises impressively above the
Interior Plains of central North America, including theFront Range which runs from northernNew Mexico to northernColorado , theWind River Range andBig Horn Mountains ofWyoming , theCrazy Mountains and theRocky Mountain Front ofMontana , and the Clark Range ofAlberta . In Canada geographers define three main groups of ranges - theContinental Ranges ,Hart Ranges andMuskwa Ranges (the latter two flank thePeace River , the only river to pierce the Rockies, and are collectively referred to as the Northern Rockies).Mount Robson inBritish Columbia , at 3,954 meters (12,972 ft), is the highest peak in theCanadian Rockies .The western edge of the Rockies, such as the
Wasatch Range nearSalt Lake City, Utah , divides theGreat Basin from other mountains further to the west. The Rockies do not extend into theYukon orAlaska , or into central British Columbia, where the Rocky Mountain System (but not the Rocky Mountains) includes theColumbia Mountains , the southward extension of which is considered part of the Rockies in the U.S. The Rocky Mountain System within the United States is aUnited States physiographic region .Geography and geology
The Rocky Mountains are commonly defined as stretching from the
Liard River in British Columbia south to theRio Grande in New Mexico. Other mountain ranges continue beyond those two rivers, including the Selwyn Range inYukon , theBrooks Range inAlaska , and theSierra Madre inMexico , but those are not part of the Rockies, though they are part of theAmerican cordillera . The United States definition of the Rockies, however, includes the Cabinet andSalish Mountains of Idaho and Montana, whereas their counterparts north of theKootenai River , theColumbia Mountains , are considered a separate system in Canada, lying to the west of the hugeRocky Mountain Trench , which runs the length of British Columbia from its beginnings in the middleFlathead River valley in western Montana to the south bank of theLiard River . The Rockies vary in width from 70 to 300 miles (110 to 480 kilometers). Also west of the Rocky Mountain Trench, farther north and facing theMuskwa Ranges across the Trench, are theStikine Ranges andOmineca Mountains of theInterior Mountains system of British Columbia.The younger ranges of the Rocky Mountains uplifted during the late
Cretaceous period (100 million-65 million years ago), although some portions of the southern mountains date from uplifts during thePrecambrian (3,980 million-600 million years ago). The mountains' geology is a complex of igneous andmetamorphic rock ; youngersedimentary rock occurs along the margins of the southern Rocky Mountains, and volcanic rock from theTertiary (65 million-1.8 million years ago) occurs in theSan Juan Mountains and in other areas. Millennia of severe erosion in theWyoming Basin transformed intermountain basins into a relatively flat terrain. TheTetons and other north-central ranges contain folded and faulted rocks ofPaleozoic andMesozoic age draped above cores ofProterozoic andArchean igneous and metamorphic rocks ranging in age from 1.2 billion (e.g., Tetons) to more than 3.3 billion years (Beartooth Mountains ).cite book|url=http://web.archive.org/web/20060927145110/http://biology.usgs.gov/s+t/SNT/noframe/wm146.htm|chapter=Rocky Mountains|title=Status and Trends of the Nation's Biological Resources|author=Stohlgren, T.J.|editor=M.J. Mac, P.A. Opler, C.E. Puckett Haeker, and P.D. Doran|year=1998|publisher=U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey
location=Reston, Va. (public domain source)]Periods of glaciation occurred from the
Pleistocene Epoch (1.8 million-70,000 years ago) to theHolocene Epoch (fewer than 11,000 years ago). Recent episodes included theBull Lake Glaciation that began about 150,000 years ago and thePinedale Glaciation that probably remained at full glaciation until 15,000-20,000 years ago.cite book|last=Pierce|first=K. L.|year=1979|title=History and dynamics of glaciation in the northern Yellowstone National Park area|id=Professional Paper 729-F|publisher=U.S. Geological Survey|location=Washington, D.C|pages=1-90] Ninety percent of Yellowstone National Park was covered by ice during the Pinedale Glaciation.Thelittle ice age was a period of glacial advance that lasted a few centuries from about 1550 to 1860. For example, the Agassiz and Jackson glaciers in Glacier National Park reached their most forward positions about 1860 during the little ice age.Water in its many forms sculpted the present Rocky Mountain landscape. Runoff and snowmelt from the peaks feed Rocky Mountain rivers and lakes with the water supply for one-quarter of the United States. The rivers that flow from the Rocky Mountains eventually drain into three of the world's
Oceans : theAtlantic Ocean , thePacific Ocean , and theArctic Ocean . These rivers include:;Gulf of Mexico drainage
*Arkansas River
*Platte River
*Rio Grande
*Missouri River
* Wind River
*Yellowstone River ;Arctic Ocean drainage
*Athabasca River
* Peace River
**Parsnip River
***Misinchinka River
*Finlay River
*Liard River
**Muskwa River
**Kechika River
***Gataga River
**Toad River ;Northwest Pacific Ocean drainage
*Columbia River
**Kicking Horse River
**Blaeberry River
**Bush River
**Wood River
**Bitterroot River
**Kootenay River
*** Elk River
***Bull River ]
*** Vermilion River
**Clark Fork River
** Clearwater River
**Coeur d'Alene River
** Salmon River
**Snake River
**Payette River
**Selway River
**Lochsa River
*Fraser River
**McGregor River ;Gulf of California drainage
* Colorado River
* Green River;Hudson Bay drainage
*North Saskatchewan River
*South Saskatchewan River
*Bow River
*Oldman River
*Red Deer River TheContinental Divide is located in the Rocky Mountains and designates the line at which waters flow either to theAtlantic orPacific Oceans.Triple Divide Peak (8,020 feet / 2,444 m) inGlacier National Park (U.S.) is so named due to the fact that water which falls on the mountain reaches not only the Atlantic and Pacific, butHudson Bay as well. Farther north in Alberta, the Athabasca and other rivers feed the basin of theMackenzie River , which has its outlet on theBeaufort Sea of theArctic Ocean .Human history
Since the last great Ice Age, the Rocky Mountains were home first to
Paleo-Indians and then to the indigenous peoples of theApache ,Arapaho , Bannock,Blackfoot ,Cheyenne ,Crow , Flathead, Shoshoni, Sioux, Ute,Kutenai (Ktunaxa in Canada),Sekani ,Dunne-za , and others.cite book|url=http://web.archive.org/web/20060927145110/http://biology.usgs.gov/s+t/SNT/noframe/wm146.htm|chapter=Rocky Mountains|title=Status and Trends of the Nation's Biological Resources|author=Stohlgren, T.J.|editor=M.J. Mac, P.A. Opler, C.E. Puckett Haeker, and P.D. Doran|year=1998|publisher=U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey
location=Reston, Va. (public domain source)] Paleo-Indians hunted the now-extinctmammoth andancient bison (an animal 20% larger than modern bison) in the foothills and valleys of the mountains. Like the modern tribes that followed them, Paleo-Indians probably migrated to the plains in fall and winter for bison and to the mountains in spring and summer forfish ,deer ,elk ,root s, and berries. In Colorado, along the crest of the Continental Divide, rock walls that Native Americans built for driving game date back 5,400-5,800 years. A growing body of scientific evidence indicates that indigenous peoples had significant effects on mammal populations by hunting and on vegetation patterns through deliberate burning.Recent human history of the Rocky Mountains is one of more rapid change. The Spanish explorer
Francisco Vásquez de Coronado — with a group of soldiers, missionaries, and African slaves — marched into the Rocky Mountain region from the south in 1540. The introduction of the horse, metal tools, rifles, new diseases, and different cultures profoundly changed the Native American cultures. Native American populations were extirpated from most of their historical ranges by disease, warfare, habitat loss (eradication of the bison), and continued assaults on their culture.In 1739, French
fur trade rs Pierre and Paul Mallet, while journeying through theGreat Plains , discovered a range of mountains at the headwaters of thePlatte River , which local American Indian tribes called the "Rockies", becoming the first Europeans to report on this uncharted mountain range. [ [http://www.pbs.org/weta/thewest/events/1650_1800.htm PBS - THE WEST - Events from 1650 to 1800 ] ]Sir Alexander MacKenzie (1764 - March 11, 1820) became the first European to cross the Rocky Mountains in 1793. He found the upper reaches of the Fraser River and reached what is now the Pacific coast of Canada on July 20 of that year, completing the first recorded transcontinental crossing of North America north of Mexico. He arrived at Bella Coola, British Columbia, where he first reached saltwater at South Bentinck Arm, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean.
The
Lewis and Clark Expedition (1804-1806) was the first scientific reconnaissance of the Rocky Mountains. Specimens were collected for contemporary botanists, zoologists, and geologists. The expedition was said to have paved the way to (and through) the Rocky Mountains for European-Americans from the East, although Lewis and Clark met at least 11 European-American mountain men during their travels.Mountain men, primarily French, Spanish, and British, roamed the Rocky Mountains from 1720 to 1800 seeking mineral deposits and furs. The fur-trading
North West Company establishedRocky Mountain House as a trading post in what is now the Rocky Mountain foothills of Alberta in 1799, and their business rivals theHudson's Bay Company established Acton House nearby. These posts served as bases for most European activity in the Canadian Rockies in the early 1800s, most notably the expeditions ofDavid Thompson (explorer) , the fourth European to follow the Columbia River to the Pacific Ocean. After 1802, Americanfur trader s and explorers ushered in the first widespread caucasian presence in the Rockies south of the 49th parallel. The more famous of these include Americans includedWilliam Henry Ashley ,Jim Bridger ,Kit Carson ,John Colter ,Thomas Fitzpatrick , Andrew Henry, andJedediah Smith . On July 24, 1832,Benjamin Bonneville led the firstwagon train across the Rocky Mountains by usingWyoming 's South Pass. Thousands passed through the Rocky Mountains on theOregon Trail beginning in 1842. TheMormon s began to settle near theGreat Salt Lake in 1847. From 1859 to 1864,Gold was discovered inColorado ,Idaho ,Montana , andBritish Columbia sparking severalgold rush es bringing thousands of prospectors and miners to explore every mountain and canyon and to create the Rocky Mountain's first major industry. The Idaho gold rush alone produced more gold than the California and Alaska gold rushes combined and was important in the financing of theUnion Army during theAmerican Civil War . Thetranscontinental railroad was completed in 1869, andYellowstone National Park was established as the world's first national park in 1872. While settlers filled the valleys and mining towns, conservation and preservation ethics began to take hold. President Harrison established several forest reserves in the Rocky Mountains in 1891-1892. In 1905, President Theodore Roosevelt extended theMedicine Bow Forest Reserve to include the area now managed asRocky Mountain National Park . Economic development began to center onmining ,forestry ,agriculture , andrecreation , as well as on the service industries that support them. Tents and camps became ranches and farms, forts and train stations became towns, and some towns became cities.Industry and development
Economic resources of the Rocky Mountains are varied and abundant.
Mineral s found in the Rocky Mountains include significant deposits ofcopper ,gold ,lead ,molybdenum ,silver ,tungsten , andzinc . The Wyoming Basin and several smaller areas contain significant reserves ofcoal ,natural gas ,oil shale , andpetroleum . For example, the Climax mine, located nearLeadville, Colorado , was the largest producer ofMolybdenum in the world. Molybdenum is used in heat-resistant steel in such things as cars and planes. The Climax mine employed over 3,000 workers. The Coeur d’Alene mine of northern Idaho produces silver, lead, and zinc. Canada's largestcoal mines are nearFernie, British Columbia andSparwood, British Columbia ; additional coal mines exist nearHinton, Alberta and in the Northern Rockies surroundingTumbler Ridge, British Columbia .Abandoned mines with their wakes of mine tailings and toxic wastes dot the Rocky Mountain landscape. In one major example, eighty years of zinc mining profoundly polluted the river and bank near Eagle River in north-central Colorado. High concentrations of the metal carried by spring runoff harmedalgae ,moss , andtrout populations. An economic analysis of mining effects at this site revealed declining property values, degraded water quality, and the loss of recreational opportunities. The analysis also revealed that cleanup of the river could yield $2.3 million in additional revenue from recreation. In 1983, the former owner of the zinc mine was sued by the Colorado Attorney General for the $4.8 million cleanup costs; 5 years later, ecological recovery was considerable.cite journal|last=Brandt|first=E.|year=1993|title=How much is a gray wolf worth?|journal=National Wildlife|volume=31|pages=412]Agriculture and forestry are major industries. Agriculture includes dryland and irrigated farming and
livestock grazing. Livestock are frequently moved between high-elevation summerpasture s and low-elevation winter pastures, a practice known astranshumance .Human population is not very dense in the Rocky Mountains, with an average of four people per square kilometer (10 per square mile) and few cities with over 50,000 people. However, the human population grew rapidly in the Rocky Mountain states between 1950 and 1990. The 40-year statewide increases in population range from 35% in Montana to about 150% in Utah and Colorado. The populations of several mountain towns and communities have doubled in the last 40 years.
Jackson Hole, Wyoming , increased 260%, from 1,244 to 4,472 residents, in 40 years.Tourism
"See also:" List of U.S. Rocky Mountain ski resorts, List of Alberta ski resorts, List of B.C. ski resorts
Every year the scenic areas and recreational opportunities of the Rocky Mountains draw millions of tourists. The main language of the Rocky Mountains is English. But there are also linguistic pockets of Spanish and Native American languages.
People from all over the world visit the sites to hike, camp, or engage in mountain sports. In the summer, mainFact|date=September 2008 tourist attractions are:
In the United States:
*Pikes Peak
*Royal Gorge
*Rocky Mountain National Park
*Yellowstone National Park
*Grand Teton National Park
*Glacier National Park (U.S.)
*Sawtooth National Recreation Area In Canada, the mountain range contains these national parks:
*Banff National Park
*Jasper National Park
*Kootenay National Park
*Waterton Lakes National Park
*Yoho National Park Glacier National Park in Montana and Waterton Lakes National Park in Alberta border each other and collectively are known as
Waterton-Glacier International Peace Park . (See alsoInternational Peace Park .)In the winter,
skiing is the main attraction. A list of the major ski resorts can be found at List of U.S. Rocky Mountain ski resorts.The adjacent
Columbia Mountains in British Columbia contain major resorts such, Fernie, Panorama and Kicking Horse, as well asMount Revelstoke National Park .Climate
The Rocky Mountains have a highland climate. The average annual temperature in the valley bottoms of the Colorado Rockies near the latitude of Boulder is 43 °F (6 °C). July is the hottest month there with an average temperature of 82 °F (28 °C). In January, the average monthly temperature is 7 °F (−14 °C), making it the region's coldest month. The average precipitation per year there is approximately 14 inches (360 mm).
The summers in this area of the Rockies are warm and dry, because the western fronts impede the advancing of water-carrying storm systems. The average temperature in summer is 59 °F (15 °C) and the average precipitation is 5.9 inches (150 mm). Winter is usually wet and very cold, with an average temperature of 28 °F (−2 °C) and average snowfall of 11.4 inches (29.0 cm). In spring, the average temperature is 40 °F (4 °C) and the average precipitation is 4.2 inches (107 mm). And in the fall, the average precipitation is 2.6 inches (66 mm) and the average temperature is 44 °F (7 °C).
ee also
*
Geography of the United States Rocky Mountain System
**Canadian Rockies
**Southern Rocky Mountains
***Colorado mountain passes
***Mountain peaks of Colorado
***Mountain ranges of Colorado
*Geology of the Rocky Mountains
*Mountain peaks of the Rocky Mountains
*Rocky Mountains subalpine zone
*Geography of North America
*Geology of North America
*Lists of mountains References
External links
* [http://wrgis.wr.usgs.gov/docs/parks/province/rockymtn.html U.S. Geological Survey website on the Rocky Mountains]
* [http://www.headwatersnews.org Headwaters News] - Headwaters News - Reporting on the Rockies
* [http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu/bioimages/ecoregions/50511frame.htm Colorado Rockies Forests ecoregion images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu] ( [http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu/bioimages/ecoregions/50511.htm slow modem version] )
* [http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu/bioimages/ecoregions/50518frame.htm North Central Rockies Forests ecoregion images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu] ( [http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu/bioimages/ecoregions/50518.htm slow modem version] )
* [http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu/bioimages/ecoregions/50528frame.htm South Central Rockies Forests ecoregion images at bioimages.vanderbilt.edu] ( [http://www.cas.vanderbilt.edu/bioimages/ecoregions/50528.htm slow modem version] )
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.