- U.S. Route 29 in Maryland
-
This article is about the section of U.S. Route 29 in Maryland. For the entire length of the highway, see U.S. Route 29.
U.S. Route 29 Colesville Road
Columbia Pike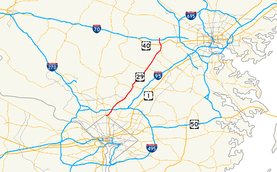
Route information Maintained by MDSHA Length: 25.859 mi[2][3] (41.62 km) Existed: 1934 – present Major junctions South end:  US 29 at D.C. line near Silver Spring
US 29 at D.C. line near Silver Spring MD 410 in Silver Spring
MD 410 in Silver Spring
 MD 97 in Silver Spring
MD 97 in Silver Spring
 I-495 near Four Corners
I-495 near Four Corners
 MD 193 in Four Corners
MD 193 in Four Corners
 MD 200 (Intercounty Connector) (under construction)
MD 200 (Intercounty Connector) (under construction)
 MD 198 in Burtonsville
MD 198 in Burtonsville
 MD 32 near Columbia
MD 32 near Columbia
 MD 100 in Ellicott City
MD 100 in Ellicott City
 US 40 in Ellicott City
US 40 in Ellicott City I-70 in Ellicott City
I-70 in Ellicott CityNorth end:  MD 99 in Ellicott City
MD 99 in Ellicott CityLocation Counties: Montgomery, Howard Highway system United States Numbered Highways
List • Bannered • Divided • ReplacedMaryland highway system
Interstate • US • State • Minor • Former • Turnpikes←  MD 28
MD 28MD 30  →
→U.S. Route 29 (US 29) is a north–south United States highway that runs for 1,036 miles (1,667 km) from the western suburbs of Baltimore, Maryland, to Pensacola, Florida. In the U.S. state of Maryland, US 29 is a major highway that emerges from Washington D.C. and runs north into eastern Montgomery County, stretching over 25.859 miles (41.62 km) through the state and terminating at Maryland Route 99 outside of Ellicott City. It serves the cities of Columbia and Ellicott City and provides the westernmost north–south route between Washington D.C. and Baltimore.
US 29 in Maryland was a late addition to the United States Numbered Highway System fabricated in 1926, beginning along a corridor once known as Maryland Route 27. Since its redesignation, it has been realigned and upgraded many times, now containing freeway and expressway sections.
Contents
Route description
Georgia Avenue and Colesville Road
US 29 emerges from Washington, D.C. along Georgia Avenue. Running alongside the Jessup Blair Park it intersects MD 410, the East–West Highway, just outside the D.C. border. It then meets the northern terminus of MD 384 and the southern terminus of MD 97 at a four-way intersection in Silver Spring; US 29 subsequently becomes Colesville Road, taking over from MD 384, while MD 97 continues as Georgia Avenue.
Crossing Sligo Creek Park the highway intersects the Sligo Creek Parkway just to the south of Interstate 495 (Capital Beltway); a partial cloverleaf interchange between the highways prevents direct access from US 29 south to I-495 east and I-495 west to US 29 north. Now a divided highway, US 29 continues north, intersecting MD 193 just beyond the Capital Beltway; this highway provides access to I-495 that is not available at the aforementioned interchange.
Columbia Pike
After crossing the Northwest Branch Park the route is now known as Columbia Pike and becomes a four-lane divided expressway. It interchanges with MD 650 to the northwest of the Naval Surface Weapons Center. The route passes through Paint Branch Park, over the Paint Branch, before meeting Randolph Road at a recently[when?] constructed diamond interchange. Continuing northeast the route intersects Fairland Road, then passes through the construction area for its interchange with MD 200, the InterCounty Connector (scheduled for completion in 2011) before meeting Briggs Chaney Road at another recently constructed diamond interchange.
Running northwest of Fairland Regional Park US 29 reaches its first major freeway segment at Burtonsville, bypassing a former, heavily curved at-grade expressway portion through the town. The bypass incorporates the southern end of the former alignment and a diamond interchange with MD 198 within its southern endpoint; US 29 continues straight ahead through the combined interchange, meeting the northern end of the former alignment at a partial diamond interchange.
The route crosses the Rocky Gorge Reservoir and enters Howard County just beyond the northern end of the bypass. It intersects Old Columbia Road just beyond the reservoir and then upgrades into a six-lane grade-separated almost-freeway within its interchange with MD 216 at Scaggsville. Continuing as an almost-freeway it interchanges with Johns Hopkins Road after two miles (3 km), then intersects Rivers Edge Road at a half-signalled intersection (Rivers Edge Road, which is the sole entryway into a subdivision containing over 300 homes, intersects the southbound carriageway, which has the signals; the northbound carriageway has an unsignalled turn lane and an unsignalled acceleration lane, both within the median).
Next, US 29 encounters MD 32 at a symmetrical cloverleaf; for an extended period this interchange marked the southern end of US 29's grade separation, with the entire route south of there being an at-grade expressway. North of the interchange, US 29 intersects several major routes that serve the town of Columbia: Shaker Drive/Seneca Drive, Broken Land Parkway, MD 175, and MD 108. Between Broken Land Parkway and MD 175, US 29 has a right-in/right-out interchange between the southbound carriageway and South Entrance Road; the northbound carriageway has two at-grade direct turnoffs to Gates Lane and Old Columbia Road, with median crossovers provided for southbound traffic. Near the MD 108 interchange the northbound carriageway has another direct turnoff to Diamondback Drive.
Beyond the MD 108 interchange, US 29 upgrades again into a fully limited-access six-lane grade-separated freeway as it encounters the western terminus of MD 100. The heavy flows to and from MD 100 result in US 29 widening again to eight lanes within the interchange, which also incorporates a three-quarter diamond interchange with the western terminus of MD 103. The eight-lane segment narrows to six lanes again as it encounters the historic northern end of the US 29 expressway at U.S. Route 40 within Ellicott City.
Beyond US 40, US 29 interchanges with Interstate 70 at a modified directional cloverleaf, and finally terminates at an at-grade intersection with MD 99 near Mount Hebron.
29th Infantry Division Memorial Highway
The entire route in Maryland is also known as the 29th Infantry Division Memorial Highway, and some trailblazer assemblies in the Ellicott City area are marked with the division's distinctive yin-yang symbol. At the US 40 interchange, a monument dedicating the highway to the division has been installed and can be seen from both carriageways.
Points of interest
- Jessup Blair Park
- Sligo Creek Park
- Northwest Branch Park
- Naval Surface Weapons Center
- Paint Branch Park
- Fairland Regional Park
- Rocky Gorge Reservoir
- Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory
- The Mall in Columbia
- Lake Kittamaqundi
- Centennial Park
- Historic Ellicott City
- Montgomery Blair High School
History
In 1933, the Maryland state government and the D.C. government approached AASHO and the Virginia state government about the possible northern extension of US 29 from its original northern terminus in Culpeper, Virginia on US 15. After much deliberation, AASHO and Virginia assented to the modifications, and US 29 was extended from Culpepper along US 15 and US 211 into D.C. and thence into Maryland.[4]
Turnpikes
On January 10, 1810, the Columbia Turnpike Road Company was chartered by the General Assembly of Maryland to "make a turnpike road from where the road leading from Montgomery courthouse to Baltimore intersects the Baltimore and Frederick turnpike road near Ellicott's lower mills, in a direction towards Georgetown, until it intersects the line of the district of Columbia, and so that it shall cross Rock creek at not less than three miles above Georgetown"[5] The road later came to be known as the Columbia Pike.[6]
The Washington, Colesville and Ashton Turnpike Company was established in 1870 in Maryland in the United States. Its path began at the Washington and Brookeville Turnpike (also known as the Union plank and turnpike road, today's Georgia Avenue), followed the modern path of Colesville Road (US 29) until the crossing of the Northwest Branch at Burnt Mills, where the turnpike took the route of modern Lockwood Drive to join the path of modern New Hampshire Avenue (MD 650) near White Oak north to Colesville and then to Ashton.[7]
“Toll Gate #1” was located just as travelers approached the end of the turnpike at Sligo. The small wooden toll gate, located at the intersection of today’s Georgia Avenue and Dale Drive, closed in 1910 with the death of its last toll keeper, Henry Charles Ulrich (born 1849). By the mid 1910s, privately run turnpikes had ceased operations with the establishment of Maryland’s State Roads Commission. On April 1, 1930, Harvey and Blanche (Mrs. K) Kreuzberg opened Mrs. K’s Toll House Restaurant in the toll house (with significant expansion) at 9201 Colesville Road.[8][9]
MD 27 and MD 29
US 29 as Colesville Road in Silver Spring US 29 as Colesville Road in Silver Spring
US 29 as Colesville Road in Silver Spring
US 29 arrived in Maryland in 1934, a year after the initial creation of the Maryland highway numbering scheme. US 29 followed a route initially designated as Maryland Route 27, while today's MD 27 was designated as Maryland Route 29. The first MD 27 emerged from Washington D.C. along Colesville Road, then followed US 29's existing route as far as White Oak, where it turned north along MD 650 and followed its alignment as far as Ashton. This route had previously been the Washington, Colesville and Ashton Turnpike. At Ashton, MD 27 then turned east along MD 108 and followed its alignment through Clarksville (overlapping MD 32 before 1996) until it reached an intersection with Columbia Road, just to the west of MD 108's current interchange with US 29's current route. Then, MD 27 turned north and followed Columbia Road (formerly designated MD 982), becoming Old Columbia Pike (formerly designated as MD 987) after crossing MD 103 and continuing north until reaching Main Street (old US 40) in old Ellicott City, where it ended.
After US 29's arrival in 1934, MD 27 and MD 29 swapped numbers; today's MD 27 received its current designation and did not physically change, while the original MD 27 was re-designated MD 29, and then immediately promoted to US 29, thus removing a conflict between the US highway number and the state highway number system, as AASHO prohibits number duplication between state and US route systems. US 29 followed MD 29's route all the way into Ellicott City, where it then turned east and overlapped US 40 through Catonsville all the way into Baltimore, where it ended at US 1 (Monroe Street) in southwestern Baltimore. Today, the Baltimore County portion of this route is part of MD 144.
US 29 Alternate
On November 11, 1954, the state of Maryland gained AASHO's consent to divert US 29 to a more direct alignment, paralleling the now-defunct MD 196 between MD 650 and MD 198, and then continuing onward to Ellicott City via Scaggsville.[4]
The diversion of the route necessitated the construction of a divided highway between the site of US 29's current interchange with MD 650 in White Oak and an intersection with MD 198 in Burtonsville, and a two-lane highway between Burtonsville, across the Patuxent River at the site of the future Rocky Gorge Reservoir, through Scaggsville and Columbia (then a small village east of today's US 29/MD 108 interchange) to a point south of Ellicott City, where the new route merged with the original route near the site of the US 29/MD 103 interchange and continued as normal. It is unclear if the new route was immediately signed as US 29 or as an extension of MD 196, but an undated GULF map of the state of Maryland shows no highway designation for the route between White Oak and Columbia.[4] The first new segment of the current route of US 29 opened on November 30, 1959,[10] and by 1964 MD 196 had been retracted to Burtonsville and US 29 had been rerouted to its current route.
Initially, the AASHO Executive Committee, meeting in Seattle, Washington, designated US 29's original route via Ashton as U.S. Route 29 Alternate, which would be signed upon the originally scheduled completion of the direct route in late 1955.[4] US 29 Alternate has since vanished, being replaced with a northward extension of MD 650 through Ashton (replacing MD 116 north of Ashton) and an eastward extension of MD 108 as far as MD 175 Waterloo Road (now itself part of MD 108).
The new Columbia Pike
US 29 north of Burtonsville US 29 in Burtonsville
US 29 in Burtonsville
The 1966 expansion of the tiny village of Columbia into a massive planned community under the auspices of the Rouse Company led to the construction of the modern Columbia Pike. By the early 1970s, with the completion of the new Columbia Pike, a four-lane divided at-grade highway, between Burtonsville and US 40, US 29 had assumed its current shape. In 1968, the terminus of US 29 was diverted away from Baltimore; it was retracted to US 40 in Ellicott City and then moved north two miles (3 km) to MD 99, and an interchange similar to the one in place between US 29 and US 40 was built to connect the route with Interstate 70 (then designated I-70N).[4]
US 29 Freeway
US 29A in Burtonsville
Initially, the northernmost 2 miles (3.2 km) of US 29 were the only grade-separated limited-access segment of that route in Maryland. However, gradual construction of interchanges south of US 40, starting with Howard County's segment in the late 1980s and continuing to the 2000s in Montgomery County, has resulted in a full freeway between I-70 and MD 108, an almost-freeway between MD 108 and MD 216, and a partially grade-separated expressway between MD 216 and MD 650, with interchanges at Johns Hopkins Road and MD 216 completed in the early 2000s. Interchanges were completed in 2004 at MD 198, in 2005 at E. Randolph Road/Cherry Hill Road, and in 2007 at Briggs Chaney Road. With the completion of the interchange at MD 198, US 29 was realigned slightly to the east. The former alignment is now designated as US 29A. Immediately south of Briggs Chaney Road, construction commenced on a new interchange with Maryland Route 200 (the Intercounty Connector) in 2008.
Baltimore Outer Beltway
The four miles (6 km) of the US 29 freeway between MD 100 and I-70 is part of the Baltimore Outer Beltway. The Outer Beltway was perceived as a 3/4 circular beltway designed to provide a route parallel to the Baltimore Beltway. MD 100 represents the major portion that was built; the aforementioned four miles (6 km) of US 29 is another portion. The Outer Beltway was projected beyond MD 99 to run through Howard and Baltimore Counties and intersect MD 140, Interstate 83, US 1, and Interstate 95 before terminating at US 40 northeast of Baltimore.
Junction list
County Location Mile # Destinations Notes US 29 continues from Washington D.C. Montgomery Silver Spring 0.18  MD 410 west (East-West Highway), Chevy Chase, Takoma Park
MD 410 west (East-West Highway), Chevy Chase, Takoma Park0.7 
 MD 97 north (Georgia Avenue) / MD 384 west (Colesville Road), Olney, Washington D.C.
MD 97 north (Georgia Avenue) / MD 384 west (Colesville Road), Olney, Washington D.C.US 29 turns onto Colesville Road; Georgia Avenue continues as MD 97 1.51 Dale Drive – Nolte Recreation Center former route of MD 391 Sligo Creek Park 1.74 Sligo Creek Parkway Four Corners 1.85 Franklin Avenue former route of MD 516 2.38  I-495 (Capital Beltway) – Rockville, College Park
I-495 (Capital Beltway) – Rockville, College Parkgrade-separated interchange between routes 2.72  MD 193 (University Boulevard) – Chevy Chase View, University of Maryland
MD 193 (University Boulevard) – Chevy Chase View, University of Maryland3.81
3.88Lockwood Drive former route of MD 895; part of original US 29 alignment prior to November 30, 1959 White Oak 4.76  MD 650 (New Hampshire Avenue) – Ashton, Takoma Park
MD 650 (New Hampshire Avenue) – Ashton, Takoma Parkgrade-separated interchange between routes 6.85 
 MD 929 (East Randolph Road/Cherry Hill Road) to US 1 – Paint Branch Park
MD 929 (East Randolph Road/Cherry Hill Road) to US 1 – Paint Branch Parknew grade-separated interchange between routes
Randolph Road connects to former route of MD 1967.68 Fairland Road – Paint Branch Park ~8.10 

 MD 200 (Intercounty Connector) to I-270 to I-95 / Briggs Chaney Road – Gaithersburg, Laurel
MD 200 (Intercounty Connector) to I-270 to I-95 / Briggs Chaney Road – Gaithersburg, Laurelgrade-separated interchange between routes; Opened November 22, 2011 8.46 Briggs Chaney Road – Fairland Regional Park (via Robey Road) new grade-separated interchange (completed in 2007) between routes. Northbound access via MD-200 Interchange 9.51 Greencastle Road - Fairland Regional Park Burtonsville 10.72  MD 198 east (Sandy Spring Road) – Laurel
MD 198 east (Sandy Spring Road) – LaurelMD 198 west via Norbeck Road connects to MD 28
Old Columbia Pike is former alignment of US 2911.48  MD 929 south (Dustin Road/Old Columbia Pike)
MD 929 south (Dustin Road/Old Columbia Pike)former alignment of US 29 Patuxent River Bridge Howard Scaggsville 13.629 13  MD 216 (Scaggsville Road) – Fulton, Laurel
MD 216 (Scaggsville Road) – Fulton, LaurelDumbbell interchange
US 29 upgrades into grade-separated semi-freeway14.309 Hammond Drive At-grade intersection
Access only from northbound carriageway
Noted in HLR as an "emergency access"14.769 15 Johns Hopkins Road - Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory 15.899 Rivers Edge Road signalled intersection with southbound carriageway; direct turnoff from northbound carriageway 16.559 16  MD 32 (Patuxent Freeway) – Clarksville, Fort Meade
MD 32 (Patuxent Freeway) – Clarksville, Fort MeadeInterchange 17.209 17 Seneca Drive/Shaker Drive - Atholton Park Interchange Columbia 18.199 18 Broken Land Parkway - The Mall in Columbia (to Snowden River Parkway) Modified cloverleaf interchange 18.547 South Entrance Road - Lake Kittamaqundi right-in/right-out interchange with southbound carriageway 18.839 Gales Lane direct turnoff from northbound carriageway
median crossover provided for southbound traffic19.439 Old Columbia Road 19.649 20  MD 175 east (Little Patuxent Parkway/Rouse Parkway) – Waterloo, The Mall in Columbia
MD 175 east (Little Patuxent Parkway/Rouse Parkway) – Waterloo, The Mall in Columbia20.569 Diamondback Drive right-in/right-out interchange with northbound carriageway only 21.099 21  MD 108 (Clarksville Pike/Old Annapolis Road) – Clarksville
MD 108 (Clarksville Pike/Old Annapolis Road) – Clarksvilleformer route of US 29 west from interchange
Begin US 29 freewayEllicott City 22.299 22  MD 100 east – Dorsey, Glen Burnie
MD 100 east – Dorsey, Glen Burnie22.539 23  MD 103 east (St. Johns Lane/Montgomery Road) – Elkridge
MD 103 east (St. Johns Lane/Montgomery Road) – ElkridgeMD 103 connects to former route of US 29 into Ellicott City (former MD 987) 24.069 24  US 40 (Baltimore National Pike) – West Friendship, Catonsville
US 40 (Baltimore National Pike) – West Friendship, Catonsvilleformer end of US 29 freeway
US 29 once turned east along US 4025.419 25  I-70 – Frederick, Baltimore
I-70 – Frederick, BaltimoreInterchange Mount Hebron 25.859  MD 99 west (Old Frederick Road/Rogers Avenue) – Ellicott City, Alpha Ridge Park
MD 99 west (Old Frederick Road/Rogers Avenue) – Ellicott City, Alpha Ridge Parknational northern terminus of US 29
route ends in temporary configurationSee also
References
- ^ "Maryland Unveils 3 Area Road Projects". Washington Post and Times Herald. December 1, 1959, page B1.
- ^ Maryland State Highway Administration (2007). "Highway Location Reference: Howard County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/KeepingCurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2007_hlr_all/co13.pdf. Retrieved 2010-02-05.
- ^ Maryland State Highway Administration (2007). "Highway Location Reference: Montgomery County" (PDF). http://apps.roads.maryland.gov/KeepingCurrent/performTrafficStudies/dataAndStats/hwyLocationRef/2007_hlr_all/co15.pdf. Retrieved 2010-02-05.
- ^ a b c d e Federal Highway Administration. U.S. 29 Maryland to Florida URL accessed 15:05, 21 January 2007.
- ^ Facsimile of act creating the Columbia Turnpike Road Company
- ^ Davis, Joseph Stancliffe (2006). Essays In The Earlier History Of American Corporations. The Lawbook Exchange, Ltd.. ISBN 1584774274.
- ^ Archives of Maryland, Volume 0188, Page 3236 - Proceedings and Acts of the General Assembly, 1870
- ^ Takoma Voice: Features - Silver Spring Then & Again
- ^ http://books.google.com/books?id=vFX-vGYz7FgC&pg=PA59&dq=washington+colesville+ashton+turnpike&sig=6DpK_Lb_BvApchk-mNY42Zg28Ag#PPA122,M1
- ^ Washington Post, 11/11/1959 & 12/1/1959, page B1
Roads in Montgomery County, Maryland Maryland State Highways 
U.S. Routes 29Interstate Highways Roads by name Cabin John Parkway · Clara Barton Parkway · Cherry Hill Road · Connecticut Avenue · Georgia Avenue · Montrose Road · New Hampshire Avenue · Randolph Road · Sligo Creek Parkway · Wisconsin Avenue · 16th Street U.S. Route 29
U.S. Route 29Previous state:
District of ColumbiaMaryland Next state:
TerminusCategories:- U.S. Route 29
- U.S. Highways in Maryland
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.








