- Upstate California
-
Upstate California Northstate Region Motto: "Above it all" Country United States State California Region Northern California Highest point Mount Shasta - location Siskiyou County - elevation 14,179 ft (4,322 m) - coordinates 41°24′33.11″N 122°11′41.60″W / 41.4091972°N 122.194889°W Lowest point Pacific Ocean - location North Coast - elevation 0 ft (0 m) Length 200 mi (322 km) Width 200 mi (322 km) Area 46,900 sq mi (121,470 km2) Population 1,611,717 (2000) Density 34 / sq mi (13 / km2) Timezone Pacific Standard Time - summer (DST) Pacific Daylight Time Area code 530, 707, 916 Website: upstatecalifornia.com Upstate California Economic Development Council[1] For other uses, see Upstate.Upstate California is a region of California consisting of its northernmost 20 counties, most of which are rural.[1] Generally, this 46,900-square-mile (121,000 km2) area consists of all territory within California north of the San Francisco Bay and Sacramento areas.
Upstate California is visually recognizable on a map as the north-south trending portion of the state's boundaries, northward of Point Arena and Lake Tahoe. It coincides with the northern half of Northern California's span of latitude. It includes the northern portions of the North Coast, Sacramento Valley, and Sierra Nevada as well as all of the Shasta Cascade region, which is California's portion of the Cascade Range.
The largest cities in Upstate California are Roseville, Redding, Chico, Yuba City, and Eureka.
Contents
History
Upstate California is a name for the more-rural region north of Northern California's major urban areas. The term Northern California includes the San Francisco Bay Area and Sacramento. The region to the north of Sacramento has traditionally used the name Northstate to differentiate itself from the major metropolitan areas which are actually more centrally located in the state. However, "Northstate" has had little or no name recognition even in other parts of California. The coastal counties of Marin, Sonoma, Mendocino, Humboldt, and Del Norte are known as California's North Coast or Redwood Coast, which has a similar issue by including the northern San Francisco Bay Area counties. In 2001, the 20 northernmost counties and their local economic development organizations decided on a new name without "north" in it. The name "Upstate California" was also intended to borrow from the recognizability of Upstate New York.[2]
The region has a history of trying to assert its identity, including attempts to secede from the state. A movement to combine the northernmost counties of California and southernmost counties of Oregon into the State of Jefferson in 1941 fell apart after the December 7 attack on Pearl Harbor and the US entry into World War II. In the early 1990s, Assemblyman Stan Statham led an unsuccessful effort to split the northern counties into a new state.[3] In a historical echo of the timing of the 1941 secession movement, the Upstate California promotional campaign began on September 10, 2001,[4] becoming overshadowed in the news the next day by the September 11 attacks on New York and Washington.
In spite of the slow start, the name has increased in usage. For example, in state government agencies, the California Labor & Workforce Development Agency[5] and the 10-campus University of California system[6] include Upstate California among their regional divisions of the state. Some regional divisions group El Dorado, Nevada, Placer, Sutter and/or Yuba counties with Sacramento rather than Upstate California, including the United States Census Bureau which includes all 5 counties in the Sacramento CSA area.[7]
A study released in June 2009 by the Center for Economic Development at California State University, Chico titled "Renewable Electricity Production in Upstate California" found that the region produces 43% of its electricity usage from renewable sources. That already puts the area ahead of a statewide mandate to reach 33% by the year 2020. The study suggests that the region is in a good position to use further development of renewable energy production also as a direction for regional economic development. The study identifies current sources as hydroelectric (dams), biomass and geothermal and future potential for solar. The area does not have significant potential for wind power production.[8][9][10]
Geography
Upstate California is the area visually discernible on a map from Point Arena in Mendocino County on the North Coast to Lake Tahoe in the Sierra Nevada and all points in California north to the Oregon border. The southern boundary consists of each of the counties' southern boundaries from Mendocino to El Dorado. The area also roughly equals the northern half of Northern California or the northern third of the state, by span of latitude.
The most populated area is the Sacramento Valley region. The valley is surrounded by the North Coast Ranges on the west, the Shasta Cascade region to the north, and the Sierra Nevada to the east. The area east of the Sierra Nevada in Modoc, Lassen and Sierra Counties is in the high desert region of the Great Basin, where stream drainage does not flow out to the ocean. Lake Tahoe also drains to the Great Basin.
Significant landmarks in Upstate California include the coastal redwood forests, Lake Tahoe and the Cascade volcanoes Mount Shasta and Mount Lassen. Mount Lassen last erupted in 1918.
Sub-regions
The following regions are entirely contained within Upstate California:
- Honey Lake
- Lassen Peak
- Lost Coast
- Mount Shasta
- Shasta Cascade
- Surprise Valley
- Trinity Alps
- Yuba-Sutter Area
The following regions are partly contained within Upstate California:
- Gold Country – partly in other portions of Northern California in the Sierra Nevada
- Greater Sacramento – includes portions north of but not including Sacramento County
- Klamath Basin – partly in Oregon
- Lake Tahoe – partly in Nevada
- North Coast – partly in North Bay area
- Sacramento Valley – partly in Sacramento area
- Wine Country – partly in North Bay area
Upstate California contains the following telephone area codes, each of which also extend into counties bordering on the south:
- 530 – also includes Alpine and Yolo Counties
- 707 – also includes Marin, Napa, Solano and Sonoma Counties
The following larger geographic regions intersect with Upstate California:
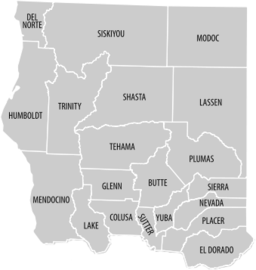
Counties
The following counties comprise Upstate California.[1]
Cities and towns
Area cities and towns listed below are major regional centers or county seats.
- Alturas (2,892)
- Auburn (12,462)
- Colusa (5,402)
- Crescent City (7,789)
- Chico (86,187)
- Downieville (325)
- Eureka (27,191)
- Lakeport (4,820)
- Marysville (12,268)
- Nevada City (3,001)
- Oroville (13,004)
- Placerville (9,610)
- Quincy (1,879)
- Red Bluff (13,147)
- Redding (89,861)
- Roseville (118,788)
- South Lake Tahoe (23,609)
- Susanville (13,541)
- Ukiah (15,497)
- Weaverville (3,554)
- Willows (6,220)
- Yuba City (36,758)
- Yreka (7,204)
Education
The California State University system has CSU Chico and Humboldt State University located within Upstate California.
There are no University of California campuses in the region. The nearest is UC Davis.
The following community college campus sites are in the region:[11]
- Butte College in Oroville, Butte County
- also serves Glenn County
- Feather River College in Quincy, Plumas County
- Lake Tahoe Community College in South Lake Tahoe, El Dorado County
- Lassen College in Susanville, Lassen County
- Mendocino College in Ukiah, Mendocino County
- also serves Lake County
- College of the Redwoods in Eureka, Humboldt County
- satellite campuses in Crescent City, Del Norte County and Fort Bragg, Mendocino County
- Shasta College in Redding, Shasta County
- Sierra College in Rocklin, Placer County
- College of the Siskiyous in Weed, Siskiyou County
- Yuba College in Marysville, Yuba County
There are no community colleges in Colusa, Modoc, Nevada, Sierra, Sutter or Tehama Counties.
Transportation
Upstate California has road, rail, air and water transportation infrastructure.
Major highways
 Interstate 5 near Mount Shasta
Interstate 5 near Mount Shasta
Most of the major highways in the region run north-south around the mountains. Interstate 5 is the primary highway in the center of the region. US 101 is the major coastal highway. US 395 provides access east of the Sierras. Interstate 80 crosses Placer, Nevada and Sierra Counties in the Sierra Nevada. A network of state and county highways connects the area, though sparsely in the mountains.
 State Route 1: North Coast
State Route 1: North Coast State Route 3: Shasta-Cascade
State Route 3: Shasta-Cascade Interstate 5: Central Valley, Redding, Shasta-Cascade and Mount Shasta
Interstate 5: Central Valley, Redding, Shasta-Cascade and Mount Shasta State Route 20: North Coast, Clear Lake, Central Valley, Yuba City and Sierra Nevada
State Route 20: North Coast, Clear Lake, Central Valley, Yuba City and Sierra Nevada State Route 28: Lake Tahoe
State Route 28: Lake Tahoe State Route 29: North Coast, Clear Lake
State Route 29: North Coast, Clear Lake State Route 32: Central Valley, Chico and Sierra Nevada
State Route 32: Central Valley, Chico and Sierra Nevada State Route 36: North Coast, Central Valley, Sierra Nevada, Lake Almanor and Lassen Park
State Route 36: North Coast, Central Valley, Sierra Nevada, Lake Almanor and Lassen Park State Route 44: Central Valley, Redding, Shasta-Cascade and Lassen Park
State Route 44: Central Valley, Redding, Shasta-Cascade and Lassen Park State Route 45: Central Valley
State Route 45: Central Valley State Route 49: Sierra Nevada
State Route 49: Sierra Nevada U.S. Route 50: Sierra Nevada and Lake Tahoe
U.S. Route 50: Sierra Nevada and Lake Tahoe State Route 53: Clear Lake
State Route 53: Clear Lake State Route 65: Roseville, Central Valley
State Route 65: Roseville, Central Valley State Route 70: Central Valley and Sierra Nevada
State Route 70: Central Valley and Sierra Nevada Interstate 80: Roseville, Sierra Nevada
Interstate 80: Roseville, Sierra Nevada State Route 89: Sierra Nevada, Lake Tahoe, Lake Almanor, Lassen Park, Shasta-Cascade and Mount Shasta
State Route 89: Sierra Nevada, Lake Tahoe, Lake Almanor, Lassen Park, Shasta-Cascade and Mount Shasta State Route 96: Shasta-Cascade
State Route 96: Shasta-Cascade U.S. Route 97: Shasta-Cascade and Mount Shasta
U.S. Route 97: Shasta-Cascade and Mount Shasta State Route 99: Central Valley, Yuba City and Chico
State Route 99: Central Valley, Yuba City and Chico U.S. Route 101: North Coast, Redwood Parks and Eureka
U.S. Route 101: North Coast, Redwood Parks and Eureka State Route 128: North Coast
State Route 128: North Coast State Route 139: Great Basin
State Route 139: Great Basin
 State Route 147: Lake Almanor
State Route 147: Lake Almanor State Route 153: California gold discovery site
State Route 153: California gold discovery site State Route 161: Shasta-Cascade
State Route 161: Shasta-Cascade State Route 162: Central Valley
State Route 162: Central Valley State Route 169: North Coast
State Route 169: North Coast State Route 172: Sierra Nevada
State Route 172: Sierra Nevada State Route 174: Sierra Nevada
State Route 174: Sierra Nevada State Route 175: North Coast, Clear Lake
State Route 175: North Coast, Clear Lake State Route 193: Sierra Nevada
State Route 193: Sierra Nevada State Route 197: North Coast and Redwood Parks
State Route 197: North Coast and Redwood Parks U.S. Route 199: North Coast and Redwood Parks
U.S. Route 199: North Coast and Redwood Parks State Route 211: North Coast
State Route 211: North Coast State Route 253: North Coast
State Route 253: North Coast State Route 255: Eureka
State Route 255: Eureka State Route 263: Shasta-Cascade
State Route 263: Shasta-Cascade State Route 267: Sierra Nevada and Lake Tahoe
State Route 267: Sierra Nevada and Lake Tahoe State Route 271: Redwood Parks
State Route 271: Redwood Parks State Route 273: Redding
State Route 273: Redding State Route 281: Clear Lake
State Route 281: Clear Lake State Route 284: Sierra Nevada
State Route 284: Sierra Nevada State Route 299: North Coast, Eureka, Central Valley, Redding, Shasta-Cascade and Great Basin
State Route 299: North Coast, Eureka, Central Valley, Redding, Shasta-Cascade and Great Basin U.S. Route 395: Great Basin
U.S. Route 395: Great Basin
There are two signed historic US highway system routes in Upstate California. Historic US 40 was replaced by I-80 but follows parallel to it along many city and rural roads. The former US Route 40 Alternate through the Feather River Canyon became California State Route 70.
Similarly, historic US 99 has been replaced by I-5, and is signed as the historic route along some of the business routes and frontage roads which used to be the highway. In the Central Valley, US 99 was split into two routes, US 99W which became I-5 and US 99E which became California State Route 99.
Rail
Passenger rail in the region is limited to Amtrak long-haul lines. The Coast Starlight stops late at night in Chico, Redding and Dunsmuir (near Mount Shasta). The California Zephyr stops during daytime hours in Truckee, Colfax and Roseville. Amtrak California also operates bus connections to the Capitol Corridor and San Joaquins trains. Greyhound buses cover the major highways.
Freight rail is served by commercial railroads. Union Pacific Railroad and BNSF Railway operate mainline freight through the region. Union Pacific's J.R. Davis Yard in Roseville, located in Placer County, is the largest rail facility in the western states.[12] Smaller railroads in the region include the Almanor Railroad (now defunct), California Northern Railroad, Central Oregon and Pacific Railroad, Lake County Railroad, Modoc Northern Railroad, Quincy Railroad and Yreka Western Railroad.
Air
Regional airline service within the area is available at Arcata-Eureka, Chico, Crescent City and Redding. Regional airline service is also across the state line in Klamath Falls, Oregon.
The nearest major airline service is at Sacramento, Reno (Nevada) and Medford (Oregon).
Military airfields exist at Beale Air Force Base near Marysville in Yuba County and the Sierra Army Depot near Herlong in Lassen County. The Coast Guard Air Station Humboldt Bay is co-located with the Arcata-Eureka Airport near McKinleyville in Humboldt County.
General aviation airports exist in all 20 counties.
Water
The only deep-water port in coastal Upstate California is located at Humboldt Bay, California's second largest natural deep-water bay, which has Eureka, the region's largest coastal city, located on its eastern shore. This underutilized port is managed by the Humboldt Bay Harbor Recreation & Conservation District, which also manages facilities at Shelter Cove located on the Lost Coast. Other harbors and marinas include Crescent City Harbor in Crescent City, Noyo Harbor in Fort Bragg, and Trinidad Harbor in Trinidad. Water recreation marinas are also on inland lakes and rivers, such as Lake Tahoe, Lake Shasta, Lake Oroville, Trinity Lake, Clear Lake, Lake Almanor, Whiskeytown Lake, and many others.
Parks and other protected areas
Notes
The following links indicate participation in the Upstate California Economic Development Council (EDC) or other promotion of the Upstate California region by federal, state and local governments or economic development organizations.
- El Dorado County
- El Dorado County, California – economic summary report
- Humboldt County
- Nevada County
- Placer County
- City of Roseville Community Assessment
- Plumas County
- Plumas Corporation – Plumas County economic development organization
- Shasta County
- Shasta EDC Annual Investor Report 2007-2008
- City of Anderson – refers to Upstate California on city home page
- City of Shasta Lake: contract between city Redevelopment Agency and Shasta County EDC
- Whole Earth and Watershed Festival – City of Redding describes planned Earth Day 2010 event as "the premier environmental event of Upstate California"
- Siskiyou County
- Tehema County
- City of Corning – refers to Upstate California on city home page
- Yuba County
- Yuba-Sutter Chamber of Commerce: Location describes region as "centrally located in upstate California"
- Yuba County Strategic Plan 2008: Cities and Partnership Resources
- Yuba County Strategic Plan 2008: 2007 Year in Review
- US Congress
- "Resolution of the Board of Yuba County in support of locating the new cyberspace command center to Beale Air Force Base" (Aug 2007) attachment to letter from Senators Boxer & Feinstein and Congressman Herger to USAF, makes multiple references to the economy of Upstate California
These are news and columns which document local governments' or economic development organizations' activity related to Upstate California.
- "PG&E Continues Its Strong Support of Economic Vitality for Local Communities: $400,000 in Grants Awarded to 75 Economic and Community Development Projects in Northern and Central California" – press release by Team California, Oct 11, 2007, shows $10,000 grant to Upstate California EDC
- Upstate California Economic Development Council Conference – Nov 30, 2007 column by Siskiyou County District 5 Supervisor Marcia Armstrong
- Shasta Home – visitor guide to Mount Shasta and Siskiyou County promotes the area as "the top of Upstate California"
- Lake California between Redding and Red Bluff promotes the area as "Upstate California's prestige address"
See also
References
- ^ a b c "Upstate California". Upstate California Economic Development Council. http://www.upstatecalifornia.com/. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ^ "It's the New Upstate, Way Out There". New York Times. 2001-10-20. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9C03E5DE113EF933A15753C1A9679C8B63. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ^ "Upstate, downstate: The “Upstate California” campaign is déjà vu all over again for Stan Statham"". Sacramento News & Review. 2002-01-03. http://www.newsreview.com/sacramento/Content?oid=10287. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ^ Levy, Dan (2001-09-07). "Region reinvented: The state's northernmost counties take on a new image to boost business". San Francisco Chronicle. http://www.sfgate.com/cgi-bin/article.cgi?file=/chronicle/archive/2001/09/07/BU228754.DTL&type=business. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ^ "California Business Investment Services". California Labor & Workforce Development Agency, State of California. Archived from the original on 2008-06-08. http://web.archive.org/web/20080608030948/http://www.labor.ca.gov/calBIS/cbcalregions2.htm. Retrieved 2008-09-08.
- ^ "Regional Teams Established to Support A-G Course Development". University of California. February 2002. http://www.ucop.edu/pathways/ucnotes/feb02/a-g.html. Retrieved 2008-09-18.
- ^ "Location Assistance". Team California. http://teamca.org/location_assistance.php. Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- ^ Gallo, David; Warren Jensen, Danny Dimeo, and James O’Grady (2009-06-25). "Renewable Electricity Production in Upstate California" (PDF). Center for Economic Development, California State University, Chico. http://www.cedcal.com/assets/renewable-electricity-production-study.pdf. Retrieved 2009-06-26.
- ^ Green, Michael S. (2009-06-26). "Study: Renewable energy could be boon to north state". Colusa Sun-Herald (Freedom Communications). http://www.colusa-sun-herald.com/news/north-3121-state-benefit.html. Retrieved 2009-06-26.
- ^ "Is any power green enough for California?". Redding.com (Redding Record-Searchlight). 2009-07-09. http://www.redding.com/news/2009/jul/12/is-any-power-green-enough-for-california/. Retrieved 2009-09-06.
- ^ "College Listings". California Community Colleges Chancellor's Office. http://www.cccco.edu/CommunityColleges/CommunityCollegeListings/CollegeListingsAlphabetical/tabid/643/Default.aspx. Retrieved 2010-01-23.
- ^ "J. R. Davis Yard". Union Pacific Railroad. http://www.uprr.com/aboutup/facilities/davis.shtml. Retrieved 2008-12-11.
External links
- Upstate California Economic Development Council
- Focus on Upstate California, Yuba County web archive of news article from Yuba Appeal Democrat, 2001-09-11
- "Helping Upstate Entrepreneurs Succeed", article reprint from Upstate Business Journal by its author at The Chico Project
- Upstate Business Journal covering the Upper Sacramento Valley including Chico and Redding
- Upstate California Adventures
- Upstate California Connect at Center for Economic Development, CSU Chico
Categories:- Northern California
- Regions of California
- Pacific Northwest
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.